Autonomous Expenditure Meaning Examples Factors Slope
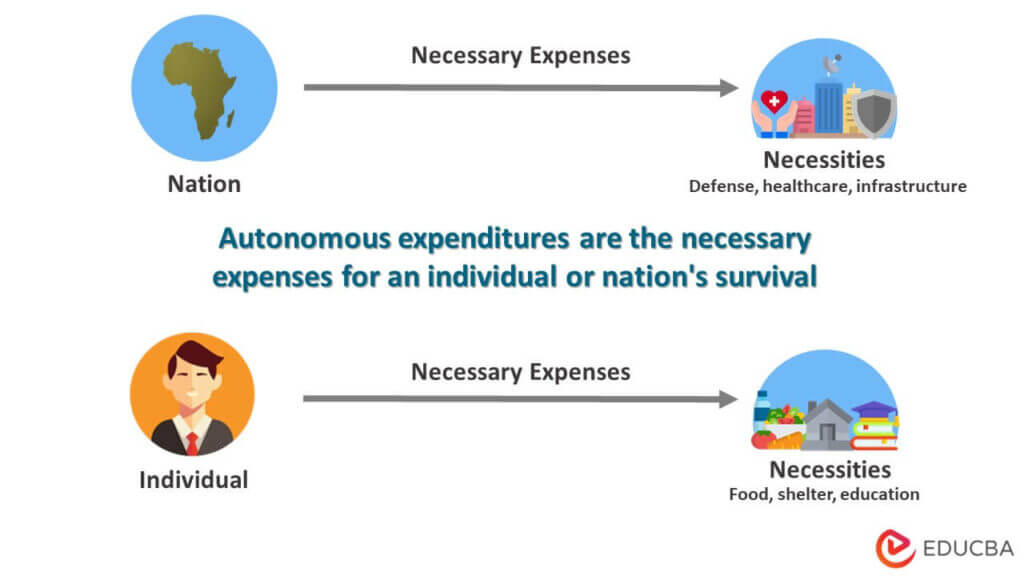
Autonomous Expenditure Meaning Examples Factors Slope The slope of autonomous expenditure is the rate of change in autonomous spending per year. it shows how spending is increasing or decreasing relative to income. your slope is zero if you have a constant revenue and spending rate. the slope is positive if your spending increases faster than your income and negative if it decreases faster. An autonomous expenditure describes the components of an economy's aggregate expenditure that are not impacted by that same economy's real level of income. this type of spending is considered.
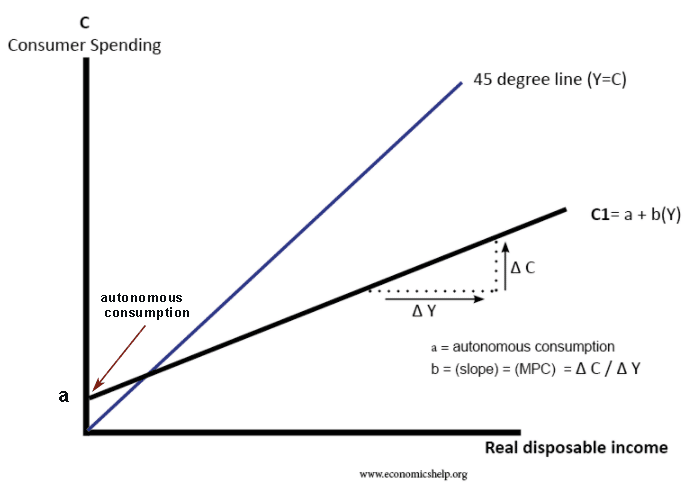
Autonomous Consumption Economics Help The expression or equation that helps calculate autonomous expenditure is mentioned below: ae = c by. where, ae is the aggregate expenditure. c is the autonomous spending. y is the real gdp or income. b is the marginal propensity to consume (mps), which is the slope that represents the change in ae when y changes. Autonomous consumption can go up or down depending on foreseen or unforeseen events that may limit or take away income, or even shifts in a person's ability to borrow, like a plummeting credit score. As defined above, autonomous spending is independent of income levels. the value is constant, even if income is zero. then, economists write it into a linear mathematical formula like the equation below: ae = c by. ae represents aggregate expenditure. c represents autonomous spending. y represents income (real gdp). Expenditures that do not vary with the economy’s real level of income are called autonomous expenditures. autonomous expenditures are mostly influenced by external factors such as trade policies, political uncertainties, interest rates, etc. the ssm model emphasizes the role of autonomous demand growth in shaping the dynamics of the total.

Autonomous Expenditure Definition Example How To Calculate As defined above, autonomous spending is independent of income levels. the value is constant, even if income is zero. then, economists write it into a linear mathematical formula like the equation below: ae = c by. ae represents aggregate expenditure. c represents autonomous spending. y represents income (real gdp). Expenditures that do not vary with the economy’s real level of income are called autonomous expenditures. autonomous expenditures are mostly influenced by external factors such as trade policies, political uncertainties, interest rates, etc. the ssm model emphasizes the role of autonomous demand growth in shaping the dynamics of the total. Conclusion. autonomous expenditure stands as a fundamental concept in economics, depicting essential spending that remains constant regardless of income fluctuations. its comprehension aids in understanding an economy’s dynamics, policy making, and the impact of external factors on spending patterns. Autonomous consumption is defined as the expenditures that consumers must make even when they have no disposable income. certain goods need to be purchased, regardless of how much income or money.

Autonomous Expenditure Conclusion. autonomous expenditure stands as a fundamental concept in economics, depicting essential spending that remains constant regardless of income fluctuations. its comprehension aids in understanding an economy’s dynamics, policy making, and the impact of external factors on spending patterns. Autonomous consumption is defined as the expenditures that consumers must make even when they have no disposable income. certain goods need to be purchased, regardless of how much income or money.

Comments are closed.