Herzberg S Two Factor Theory Of Motivation Hygiene An Overview
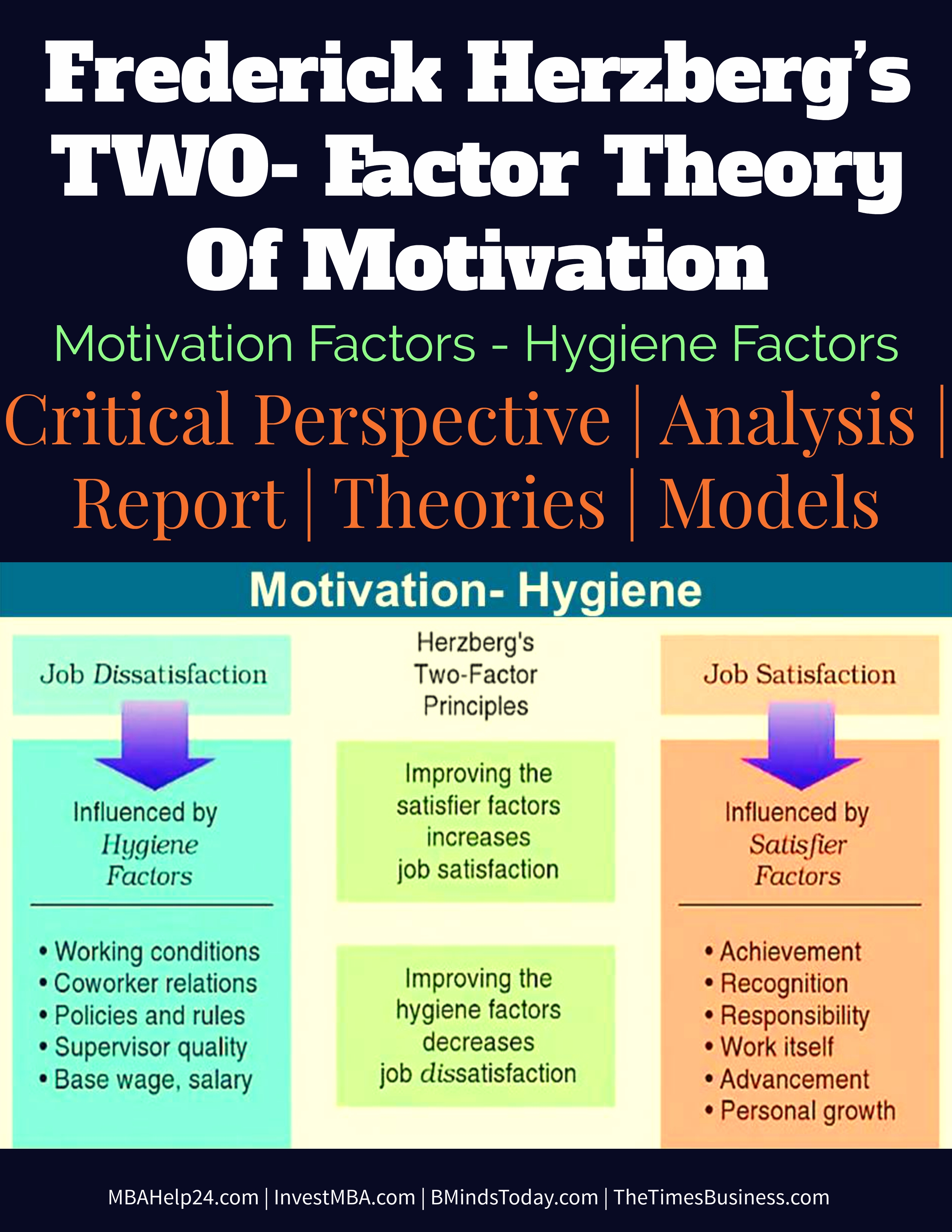
юааherzberg тащsюаб юааtwoюаб юааfactorюаб юааtheoryюаб юааof Motivationюаб юааhygieneюаб юааfactors Herzberg (1959) considers two factors that can add to or detract from job satisfaction: hygiene and motivation. while hygiene factors are related to “the need to avoid unpleasantness,” motivation factors more directly lead to job satisfaction because of “the need of the individual for self growth and self actualization.”. The two factor theory, also known as herzberg’s motivation hygiene theory, supposes that when it comes to our work lives, there are different, mutually exclusive factors that contribute to our ultimate feelings of job satisfaction or dissatisfaction: hygiene factors — the context in which the role is performed.

Herzberg S Motivation Hygiene Theory Two Factor Education Librar What is herzberg theory? frederick herzberg, a renowned psychologist, proposed a theory that everything influencing how you work can be categorized into two main groups: hygiene factors and motivators. hygiene factors include aspects such as working conditions, salary, work life balance, company policies, job security, and status. 1.2. herzberg's two factor theory of motivation. most theories discuss job satisfaction within the context of motivation (kian et al., 2014).the herzberg theory has been used as a method to explore job satisfaction among employees (lundberg et al., 2009) according to herzberg's theory of motivation applied to the workplace, there are two types of motivating factors: 1) satisfiers (motivators. Herzberg’s two factor theory outlines that humans are motivated by two things: motivators and hygiene factors (see figure 1). these two factors are both critical to motivation: motivators encourage job satisfaction and hygiene factors prevent job dissatisfaction. frederick irving herzberg (april 18, 1923 – january 19, 2000 [1]) was an. Herzberg identified two types of needs in a workplace. the first type are those required to prevent dissatisfaction. these are known as hygiene factors and include job security. he also identified.
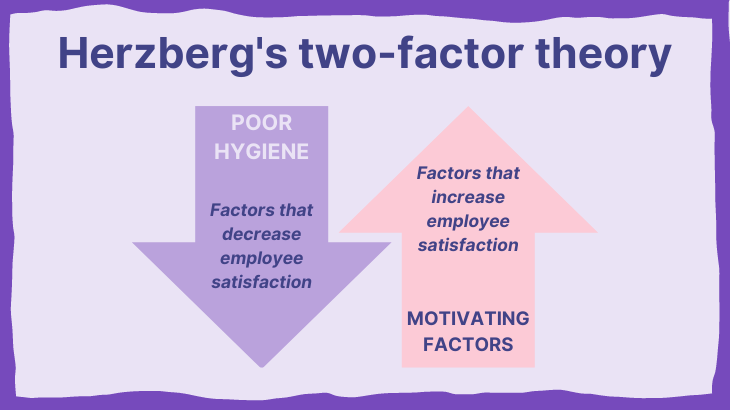
Herzberg S Two Factor Theory Of Motivation Hygiene An Overview Herzberg’s two factor theory outlines that humans are motivated by two things: motivators and hygiene factors (see figure 1). these two factors are both critical to motivation: motivators encourage job satisfaction and hygiene factors prevent job dissatisfaction. frederick irving herzberg (april 18, 1923 – january 19, 2000 [1]) was an. Herzberg identified two types of needs in a workplace. the first type are those required to prevent dissatisfaction. these are known as hygiene factors and include job security. he also identified. The two factor theory (also known as herzberg's motivation hygiene theory and dual factor theory) states that there are certain factors in the workplace that cause job satisfaction while a separate set of factors cause dissatisfaction, all of which act independently of each other. it was developed by psychologist frederick herzberg. Herzberg called the causes of dissatisfaction "hygiene factors." to get rid of them, you need to: provide effective, supportive and non intrusive supervision. create and support a culture of respect and dignity for all team members. build job status by providing meaningful work for all positions.

Herzberg S Two Factor Theory Of Motivation Motivator Hygiene The two factor theory (also known as herzberg's motivation hygiene theory and dual factor theory) states that there are certain factors in the workplace that cause job satisfaction while a separate set of factors cause dissatisfaction, all of which act independently of each other. it was developed by psychologist frederick herzberg. Herzberg called the causes of dissatisfaction "hygiene factors." to get rid of them, you need to: provide effective, supportive and non intrusive supervision. create and support a culture of respect and dignity for all team members. build job status by providing meaningful work for all positions.

юааherzbergтащsюаб юааtwoюаб юааfactorюаб юааtheoryюаб юааof Motivationюаб юааhygieneюаб

Comments are closed.