How To Calculate Autonomous Consumption Induced Consumption Total
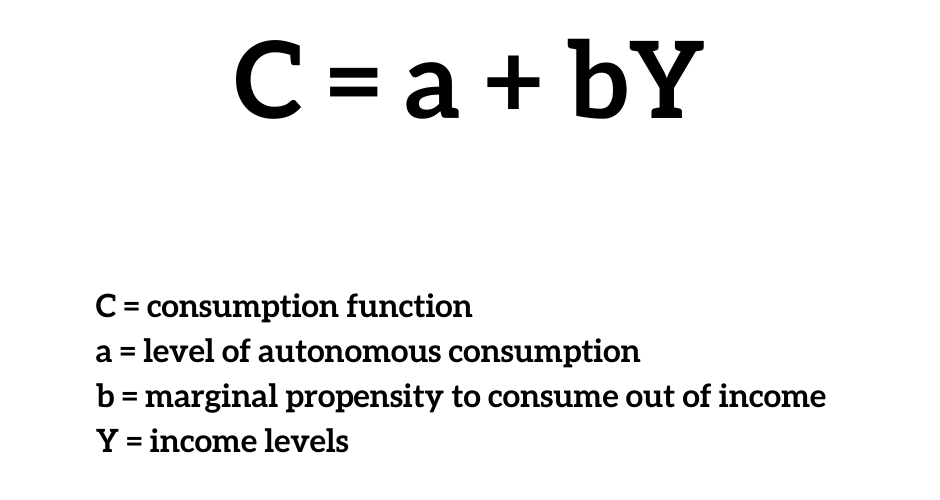
What Is Autonomous Consumption Supermoney The consumption function is used to calculate the relationship between consumption and disposable income. formula – how to calculate the consumption function. consumption = autonomous consumption (marginal propensity to consume x real disposable income) example. autonomous consumption is 400,000, mpc is 0.8, and real disposable income is. The consumption function is an economic formula that represents the relationship between total consumption and gross national income (gni). it was first introduced by british economist john.

Autonomous Consumption Definition Formula Example But we can calculate the value of the multiplier, as the eventual change in real gdp divided by the change in autonomous expenditures (planned investment, in this case): with a multiplier of 4, each $1 increase in planned investment (or any other autonomous expenditure) eventually increases equilibrium real gdp by $4. Figure 28.7 autonomous and induced consumption. consumption has an autonomous component and an induced component. in panel (a), autonomous consumption c a equals $300 billion at every level of real gdp. panel (b) shows induced consumption c i. total consumption c is shown in panel (c). Autonomous consumption vs. induced consumption: an overview. the key difference between autonomous consumption and induced consumption lies in the factor of income. those with little to no income. This is consumption that is influenced by levels of income. with rising income, people can spend more. in the diagram above, induced consumption is given by formula b (y) where b equals the marginal propensity to consume. related. definition of autonomous consumption the level of consumption which does not depend on income.
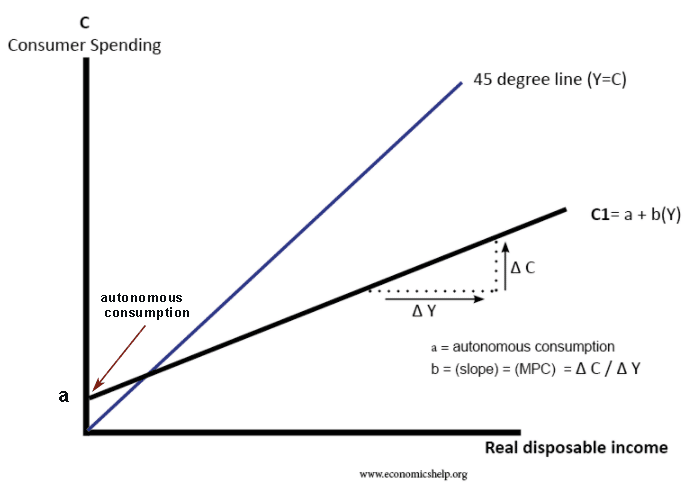
Autonomous Consumption Economics Help Autonomous consumption vs. induced consumption: an overview. the key difference between autonomous consumption and induced consumption lies in the factor of income. those with little to no income. This is consumption that is influenced by levels of income. with rising income, people can spend more. in the diagram above, induced consumption is given by formula b (y) where b equals the marginal propensity to consume. related. definition of autonomous consumption the level of consumption which does not depend on income. The difference between autonomous consumption and induced consumption is that the latter should fluctuate depending on income. induced consumption is the portion of spending that varies depending. Figure 28.7 autonomous and induced consumption consumption has an autonomous component and an induced component. in panel (a), autonomous consumption c a equals $300 billion at every level of real gdp. panel (b) shows induced consumption c i. total consumption c is shown in panel (c).

How To Calculate Autonomous Consumption Induced Consumption Total The difference between autonomous consumption and induced consumption is that the latter should fluctuate depending on income. induced consumption is the portion of spending that varies depending. Figure 28.7 autonomous and induced consumption consumption has an autonomous component and an induced component. in panel (a), autonomous consumption c a equals $300 billion at every level of real gdp. panel (b) shows induced consumption c i. total consumption c is shown in panel (c).

Comments are closed.