Intermediate Macroeconomics The Keynesian Model
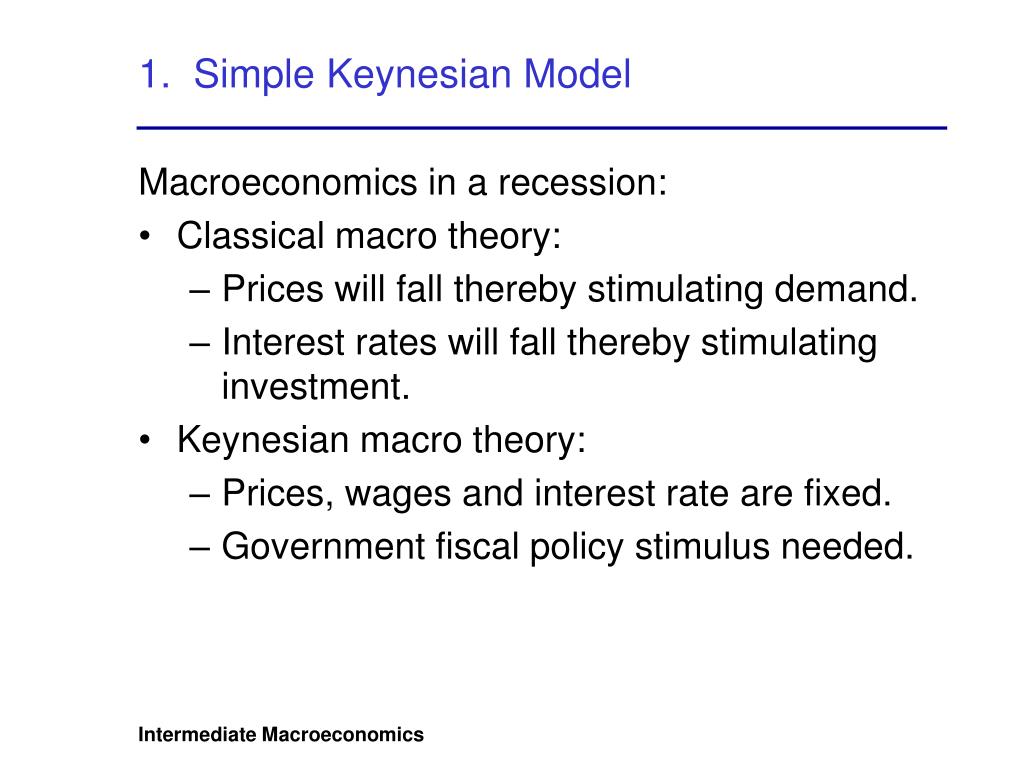
Intermediate Macroeconomics The Keynesian Model The components of the keynesian model (the equilibrium condition and the aggregate expenditures equation) have been established. note that we have really only defined spending. this characterizes the keynesian model as strictly a model of demand. the supply side is essentially ignored. This graph should make clear why the model is called a “keynesian cross”. this is because the (zz) and (yy) curves cross to determine output. this pedagogical device to visualize the keynesian multiplier was introduced in 1948 by paul samuelson in his famous economics textbook, to provide a geometric intuitive interpretation of keynes’ ideas.
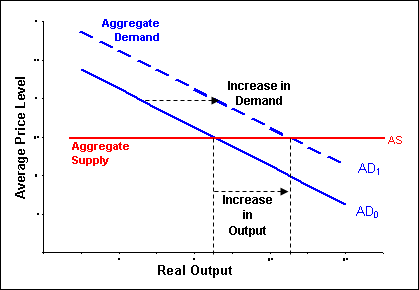
Ppt Intermediate Macroeconomics Powerpoint Presentation Free Much teaching of intermediate macroeconomics uses the is lm asor ad asapproach. this is far removed both from the practice of interest rate setting, inflation targeting central banks and from the models that are taught in graduate courses. modern monetary macroeconomics is based on what is increasingly known as the 3 equation new keynesian. Macroeconomics keynes and the classics keynesian macroeconomic model in his famous book the general theory of employment, interest, and money (1936), keynes rejected the classical model. in 1936 the world was in depression. the allocation of resources was not efficient, with much idle capital and labor. instead the economy was in crisis. 13. Intermediate macroeconomics london school of economics, 2023 2nd year undergraduates. syllabus. lecture 2: new keynesian model in continuous time. lecture 3:. The ad as model can be used to illustrate both say’s law that supply creates its own demand and keynes’ law that demand creates its own supply. consider the three zones of the sras curve as identified in figure 1: the keynesian zone, the neoclassical zone, and the intermediate zone. figure 1.

Comments are closed.