Muscle Lab Muscles Of The Back

Diagrams Of Back Muscles 101 Diagrams The muscles of the back can be arranged into 3 categories based on their location: superficial back muscles, intermediate back muscles and intrinsic back muscles.the intrinsic muscles are named as such because their embryological development begins in the back, oppose to the superficial and intermediate back muscles which develop elsewhere and are therefore classed as extrinsic muscles. Your lat muscles are the largest muscles in the upper half of your body. they start below your shoulder blades and extend to your spine in your lower back. levator scapulae: these are smaller muscles that start at the side of your neck and extend to your shoulder blades. rhomboids: the rhomboid muscles connect your shoulder blades to your spine.
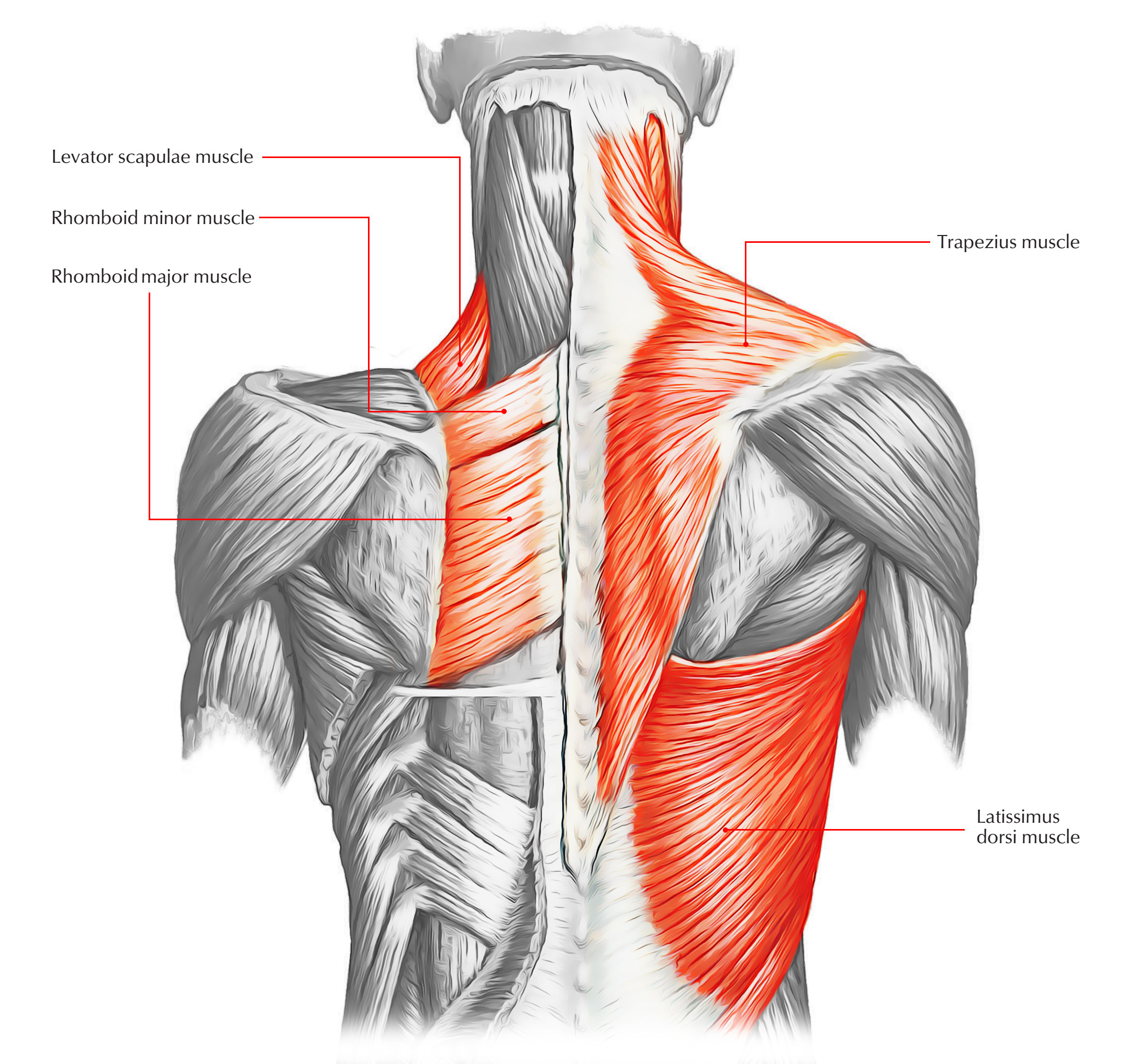
88 Muscles Of The Back L2sanpiero The muscles of the back are a group of strong, paired muscles that lie on the posterior aspect of the trunk. they provide movements of the spine, stability to the trunk, as well as the coordination between the movements of the limbs and trunk. the extrinsic (superficial) back muscles, which lie most superficially on the back. Semispinalis, multifidus and rotatores make up the transversospinal muscle group. semispinalis. transverse processes of c7 t12. capitis: back of skull between nuchal lines; cervicis & thoracis: spines 4 6 vertebrae above origin. extends the trunk and laterally bends the trunk, rotates the trunk to the opposite side. Deep group of back muscles. the deep or intrinsic muscles of the back extend from the pelvis to the skull and are innervated by segmental branches of the posterior rami of spinal nerves. they consist of: the extensors and rotators of the head and neck: the splenius capitis and cervicis (spinotransversales muscles). There are three major groups of back muscles: superficial: attached to the shoulder girdle. intermediate: attached to the posterior thorax. deep: attached to the vertebral column, also known as the intrinsic muscle group [1] these groups serve to allow: flexion extension, rotation, and side bending of the back; movement of the limbs; locomotor.

Back Muscle Diagrams Labeled Levator Scapulae Healing Healthy Deep group of back muscles. the deep or intrinsic muscles of the back extend from the pelvis to the skull and are innervated by segmental branches of the posterior rami of spinal nerves. they consist of: the extensors and rotators of the head and neck: the splenius capitis and cervicis (spinotransversales muscles). There are three major groups of back muscles: superficial: attached to the shoulder girdle. intermediate: attached to the posterior thorax. deep: attached to the vertebral column, also known as the intrinsic muscle group [1] these groups serve to allow: flexion extension, rotation, and side bending of the back; movement of the limbs; locomotor. Back anatomy. the back is the body region between the neck and the gluteal regions. it comprises the vertebral column (spine) and two compartments of back muscles; extrinsic and intrinsic. the back functions are many, such as to house and protect the spinal cord, hold the body and head upright, and adjust the movements of the upper and lower limbs. The deep back muscles act together to provide support and maintain the body’s posture, as well as to produce movements of the head, neck, and trunk. the main functions of these muscles are flexion, extension, lateral flexion and axial rotation of the vertebral column. all of these muscles are innervated by the segmental branches of the.
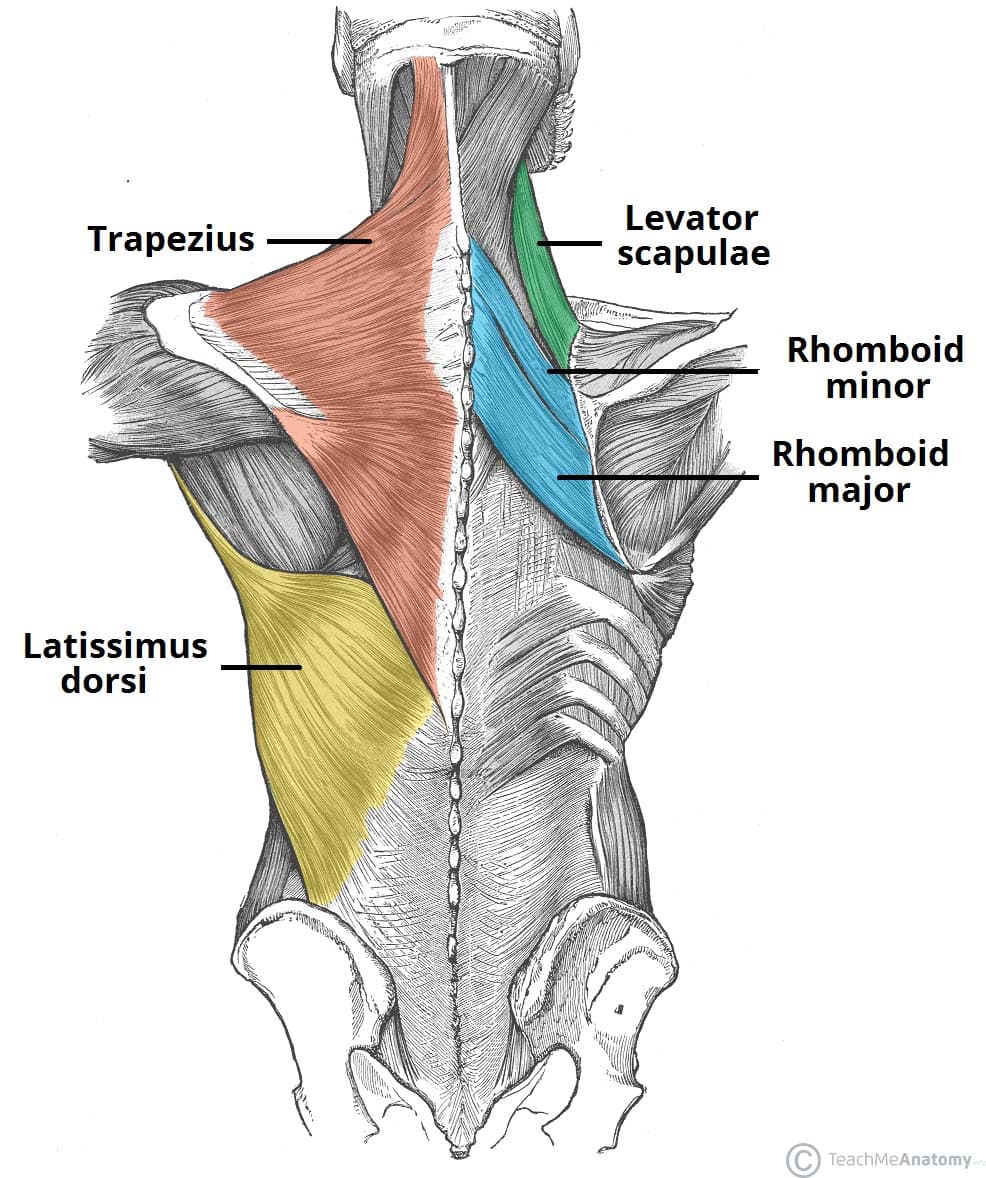
The Superficial Back Muscles Attachments Actions Teachmeanatomy Back anatomy. the back is the body region between the neck and the gluteal regions. it comprises the vertebral column (spine) and two compartments of back muscles; extrinsic and intrinsic. the back functions are many, such as to house and protect the spinal cord, hold the body and head upright, and adjust the movements of the upper and lower limbs. The deep back muscles act together to provide support and maintain the body’s posture, as well as to produce movements of the head, neck, and trunk. the main functions of these muscles are flexion, extension, lateral flexion and axial rotation of the vertebral column. all of these muscles are innervated by the segmental branches of the.

Gross Lab Muscles Of The Deep Back Flashcards Quizlet

Comments are closed.