Prim S Ib Economics Hl 16 1 Keynesian Model Ad

Prim S Ib Economics Hl 16 1 Keynesian Model Ad That will happen because there will be little to none spare capacity (e.g. workers) left. firms then offer higher wages than their competitors to hire employees. hence, production costs increase and the price level in an economy rises p1 > p2. 2.2 part of the ib economics syllabus equilibrium. short run equilibrium and long run equilibrium. The multiplier is a factor by which gdp changes following a change in an injection or leakage. the formula for the multiplier: multiplier = 1 (1 – mpc) multiplier = 1 (mps mpt mpm), where: mpc – marginal propensity to consume. mps – marginal propensity to save. mpt – marginal propensity to tax. mpm – marginal propensity to import.

Keynesian Ad As Model What Are The Key Elements Of A Keynesian Ad As Ib hl economics: aggregate demand aggregate supply 2.2. term. 1 13. aggregate demand. click the card to flip 👆. definition. 1 13. total value of goods services demanded by different groups at a given price level in an economy. Diagrams showing how shifts in aggregate demand (ad) and aggregate supply (as) affect macroeconomic equilibrium – real gdp and price level (pl) includes short run aggregate supply (sras) and long run aggregate supply (lras) and classical and keynesian view of lras curves. a simple macroeconomic equilibrium where ad = as. A diagram showing the classical short run equilibrium in an economy resulting in an equilibrium price of ap1 and real output of y1. according to classical theory, this economy is in short run equilibrium at ap1y1. any changes to the components of ad will cause the ad curve to shift left or right creating a new short run equilibrium. Spanish. past papers. cie. spanish language & literature. past papers. revision notes on 3.6.2 the keynesian multiplier for the hl ib economics syllabus, written by the economics experts at save my exams.
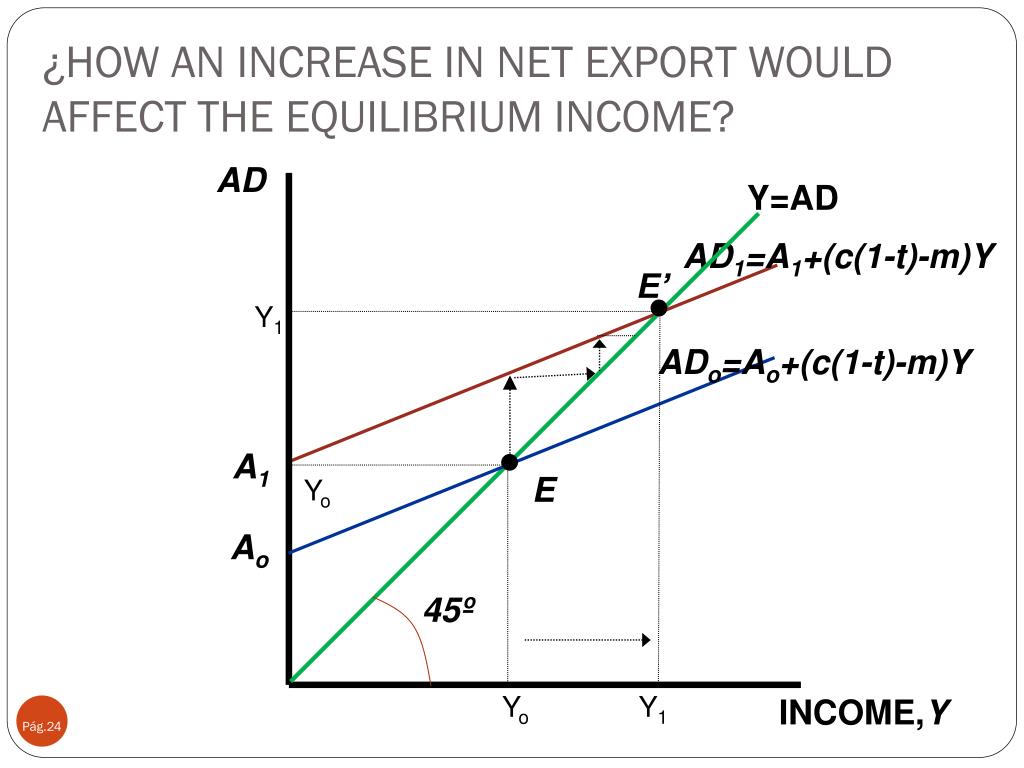
Ppt Basic Keynesian Model Keynesian Cross Diagram Powerpoint A diagram showing the classical short run equilibrium in an economy resulting in an equilibrium price of ap1 and real output of y1. according to classical theory, this economy is in short run equilibrium at ap1y1. any changes to the components of ad will cause the ad curve to shift left or right creating a new short run equilibrium. Spanish. past papers. cie. spanish language & literature. past papers. revision notes on 3.6.2 the keynesian multiplier for the hl ib economics syllabus, written by the economics experts at save my exams. According to the keynesian model, for an economy to be operating under equilibrium, the point where aggregate demand curve meets the curve of aggregate supply should be identified. as there is no distinction between short and long run aggregate supply in keynesian model, equilibrium points are any intersecting regions of the ad and as curves. Ib diploma economics:aggregate demand and aggregate supply. this section of the ib economics course examines economic activity by modeling the the circular flow model, before turning attention to how economy’s total output and income can be measured. growth in output and income are considered. finally, the business cycle, which is a recurring.
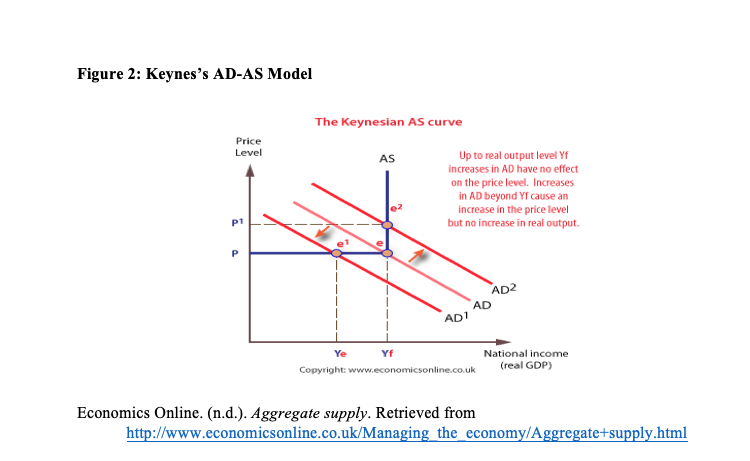
Answered Figure 2 Keynes S Ad As Model Theвђ Bartleby According to the keynesian model, for an economy to be operating under equilibrium, the point where aggregate demand curve meets the curve of aggregate supply should be identified. as there is no distinction between short and long run aggregate supply in keynesian model, equilibrium points are any intersecting regions of the ad and as curves. Ib diploma economics:aggregate demand and aggregate supply. this section of the ib economics course examines economic activity by modeling the the circular flow model, before turning attention to how economy’s total output and income can be measured. growth in output and income are considered. finally, the business cycle, which is a recurring.

Comments are closed.