Problem Solving Course 5 Steps To Eliminate Root Causes With Pdca 6m 5w

Problem Solving Course 5 Steps To Eliminate Root Causes This video explains how to solve problems in 5 steps by eliminating root causes, using the pdca process, 6m fishbone diagram, 5 why analysis, and 3w action p. The beginner problem solving training helps anyone to get started with systematic problem solving. within a few days, you will learn the basic methods and tools, and apply them to solve a difficult situation in five steps: (1) describe gap, (2) analyze issues, (3) identify causes, (4) address causes, (5) evaluate results.
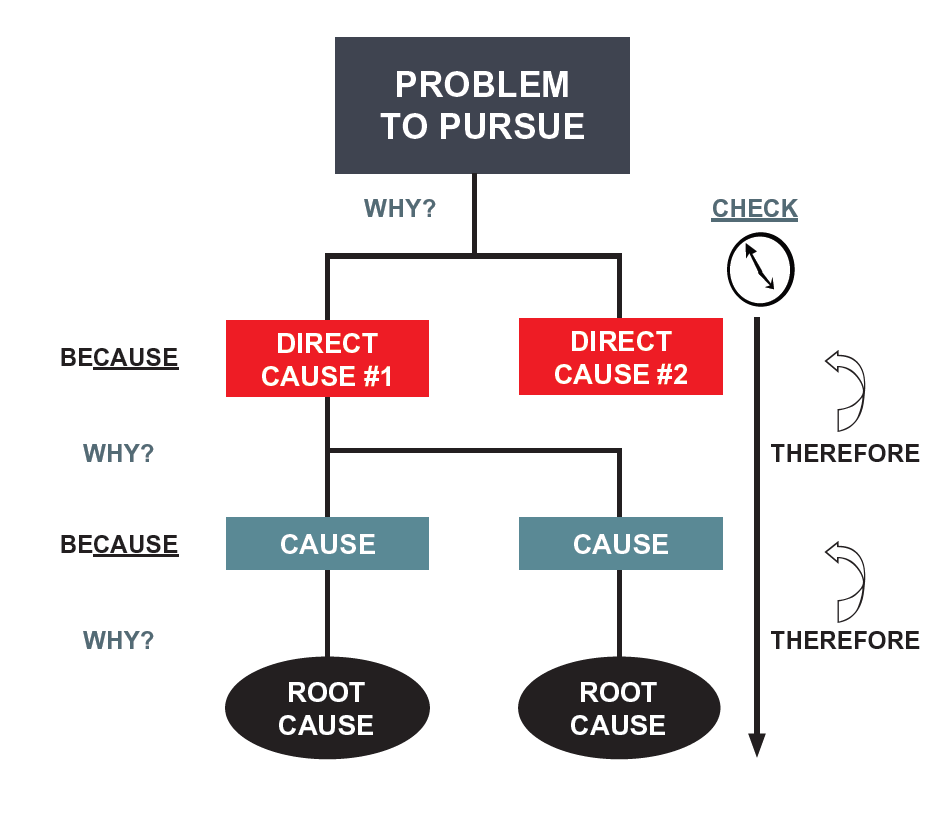
A3 Practical Problem Solving Lean Enterprise Academy The 5 why method is simply asking the question “why” enough times until you get past all the symptoms of a problem and down to the root cause. the 5 why method is often used during the analyze phase of the dmaic process and the plan phase of pdca activities. it is often used in coordination with other analysis tools such as the cause and. Step 1: identify the problem. before diving into a 5 whys analysis, it’s crucial to clearly identify the problem or issue at hand. this step sets the stage for the entire process and ensures that the focus remains on addressing the right concern. take the time to gather relevant data, observe patterns, and consult with team members or. Definition. root cause analysis (rca) is a systematic approach to identify the underlying cause of a problem. by focusing on the root cause, you can effectively address the issue and prevent recurrence. generally, rca is used to investigate incidents, eliminate defects, and enhance systems or processes. When there are many possible causes to a problem: pareto chart: prioritizes problem areas based on impact: when trying to identify the most significant causes: 5 whys: simple, iterative problem solving technique: when the problem is straightforward and the solution is not immediately apparent: fmea: proactive, preventative approach.

Comments are closed.