2 Igneous Rocks F2021 1 Pdf At The End Of This Lab You Will Be Able

2 Igneous Rocks F2021 1 Pdf At The End Of This Lab You Will Be Able This is the igneous rock lab from the 2021 fall semester. 2 igneous rocks f2021 1. course: at the end of this lab, you will be able to identify some common. Lab 2: igneous rocks and environments (50 pts) at the end of this lab, you will be able to identify some common igneous rocks based on their mineral composition and texture. we will concentrate on the different textures based on mode of formation and compositions based on relative amounts of ferromagnesian and non ferromagnesian minerals.
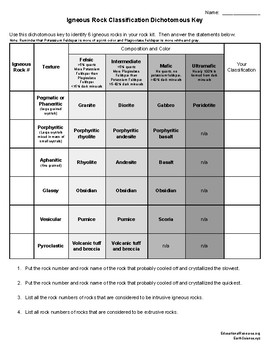
Igneous Rock Identification Lab By Educationalresource Tpt For example, if it contains holes, it is considered vesicular. 5.you will find the rock name where the color column and the texture row come together on the igneous rock identification table. 6 plete the data table 1 and answer the questions that follow. save your work, and submit the completed lab worksheet in canvas. The 7 minerals that you need to be able to identify in order to classify igneous rocks are quartz, potassium feldspar (sometimes called alkali feldspar), plagioclase feldspar, mica, amphibole, pyroxene, and olivine. the hints from last week for identifying these minerals is attached to the end of this lab handout. Lab activity 5.2 crystal textures of igneous rocks in activity 5.2, you explored the properties and formation conditions of various crystal textures of igneous rocks. in this exercise, you will compare and contrast these textures to each other, and then relate their appearances to the locations of the formations of rocks with these textures. Figure 6. rhyolite is a felsic, extrusive igneous rock. it has the same chemistry & mineralogy as granite, but is very finely crystalline (aphanitic texture; crystals <1 mm in size) due to cooling of high viscosity lava. rhyolites are often light gray to pinkish to somewhat reddish in color.

Igneous Rocks Lab Pdf Mercedes Sheets Igneous Rock Identificatio Lab activity 5.2 crystal textures of igneous rocks in activity 5.2, you explored the properties and formation conditions of various crystal textures of igneous rocks. in this exercise, you will compare and contrast these textures to each other, and then relate their appearances to the locations of the formations of rocks with these textures. Figure 6. rhyolite is a felsic, extrusive igneous rock. it has the same chemistry & mineralogy as granite, but is very finely crystalline (aphanitic texture; crystals <1 mm in size) due to cooling of high viscosity lava. rhyolites are often light gray to pinkish to somewhat reddish in color. Phaneritic: coarse grained texture due to slow cooling (typical of plutonic rocks). granite is a common example of a phaneritic igneous rock. this rock has large, visible crystals of minerals such as quartz, feldspar, and mica. aphanitic: fine grained texture due to rapid cooling (typical of volcanic rocks). Please hold on to your lab notes to help you prepare for the rock and mineral quiz and your lab final exam. 3.2 igneous rock origin 3.2.1 magma composition. before any igneous rock can form, there must be molten material, known as magma, produced; therefore, you must have a rock to melt to make the magma, which then cools to become an igneous rock.

Comments are closed.