20 Examples Of Analog Computer

7 Examples Of Analogue Computers In Real Life вђ Studiousguy January 23, 2024. analog computer examples are slide rule, ammeter, voltmeter, astrolabe, torquetum, nomogram, planimeter, and more. an analog computer is a form of computer that works on continuous physical variables such as voltage, fluid flow, or mechanical motion by manipulating those variables to solve problems. A speedometer is another example of an analog computer used in vehicles. it uses a system of gears and a flexible cable to measure the speed of the vehicle. the input to the system is the rotation of the wheels, and the output is the speed reading on the scale. a seismometer is an analog computer that is used to measure earthquakes.
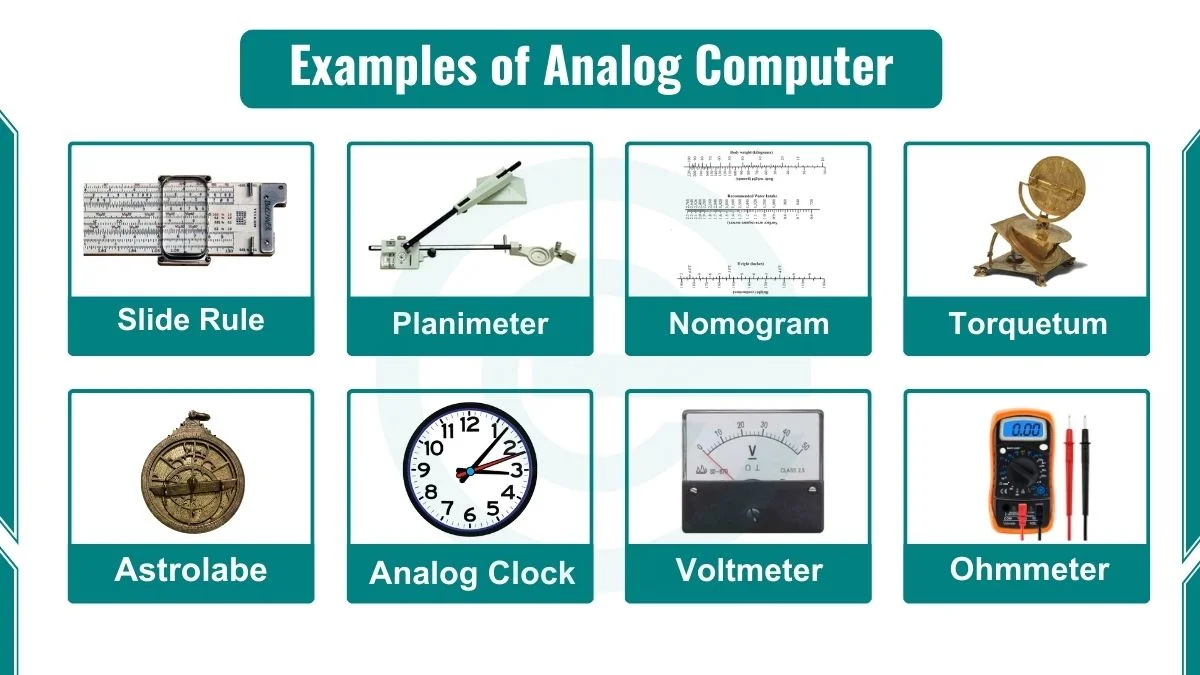
20 Examples Of Analog Computer Various examples of electronic analogue computers include spectrometer, oscilloscope, etc. 5. mechanical analogue computers. mechanical analog computers, as the name suggests, make use of mechanical parts like gears, shafts, cams, etc. to perform the computations such as multiplication, division, etc. these type of computers are rough and tough. For example, sound waves and light waves are analog streams of information that can be measured at greater and greater precision that feels almost infinite. this can be contrasted with digital information used by machines that consists of sequences of 0s and 1s that have a finite and well defined precision. Analog devices are machines or equipment that consume or produce continuous signals or media. this is contrasted with digital devices based on modern digital computers that use binary signals of 0s and 1s. in many cases, analog is also used to refer to the old version of a machine that now has some digital equivalent. Computer. analog computer, any of a class of devices in which continuously variable physical quantities, such as electrical potential, fluid pressure, or mechanical motion, are represented in a way analogous to the corresponding quantities in the problem to be solved. the analog system is set up according to initial conditions and then allowed.

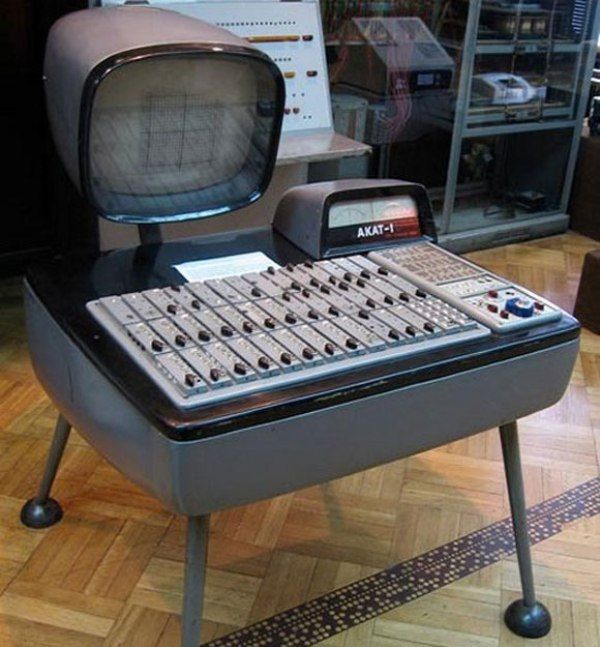
Analog Computer Definition Examples Facts Britannica Analog devices are machines or equipment that consume or produce continuous signals or media. this is contrasted with digital devices based on modern digital computers that use binary signals of 0s and 1s. in many cases, analog is also used to refer to the old version of a machine that now has some digital equivalent. Computer. analog computer, any of a class of devices in which continuously variable physical quantities, such as electrical potential, fluid pressure, or mechanical motion, are represented in a way analogous to the corresponding quantities in the problem to be solved. the analog system is set up according to initial conditions and then allowed. Tr 10 desktop analog computer of the late 1960s and early 1970s. an analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computation machine (computer) that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (analog signals) to model the problem being solved. A computer that processes analog data is called an analog computer. analog computers use measurements to execute computations and store data in a continuous form of physical values. compared to a digital computer, which represents outcomes using symbolic numbers, it is very different. when data has to be measured directly without being.

Comments are closed.