211 Newtons 2nd Law Traction On Leg Science Showme
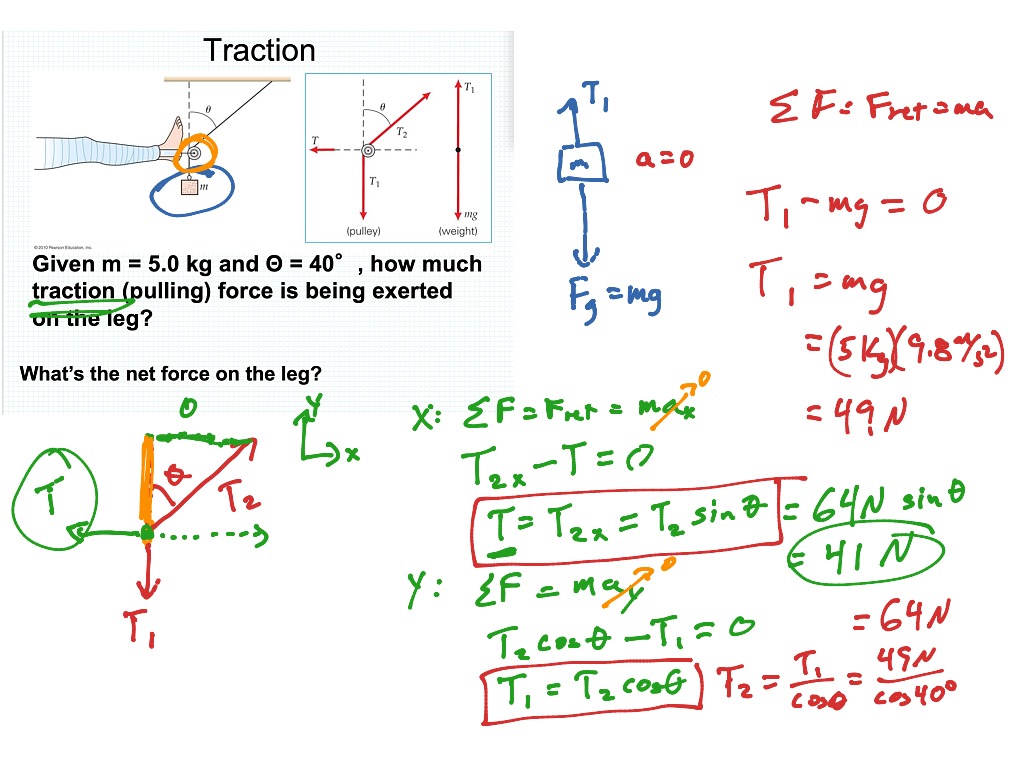
211 Newtons 2nd Law Traction On Leg Science Showme 211 newtons 2nd law atwood machine by matt evans september 29, 2020. The newton's second law of motion states that acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force f acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass m. it is expressed with the following equation: a = f m. where: a [m s²] is the acceleration of an object; f [n] is the force acting on an object; and. m [kg] is the mass of an object.
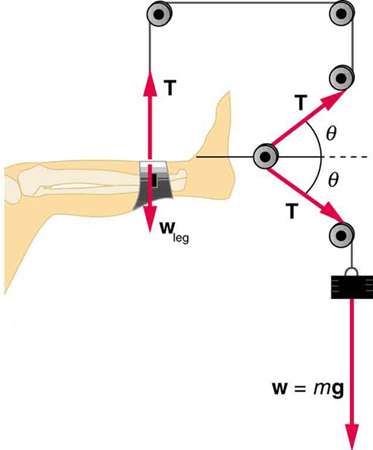
Normal Tension And Other Examples Of Forces Physics Course Hero Newton’s second law – force. the rate of change of an object’s momentum equals the force acting upon it or the applied force equal’s an object’s mass times its acceleration. the two equations for newton’s second law are: f = m*a. f = Δp Δt. here, f is the applied force, m is mass, a is acceleration, p is momentum, and t is time. 5.5 newton’s third law. identify the action and reaction forces in the following situations: earth attracts the moon, a boy kicks a football, a rocket accelerates upward, a car accelerates forward, a high jumper leaps, and. a bullet is shot from a gun. suppose that you are holding a cup of coffee in your hand. Newton’s 2nd law relates an object’s mass, the net force on it, and its acceleration: therefore, we can find the force as follows: fnet = ma. substituting the values, we get. 1000 kg × 4 m s 2 = 4000 n. therefore, the horizontal net force is required to accelerate a 1000 kg car at 4 m s 2 is 4000 n. In equation form, newton’s second law is. a → = f → net m, where a → is the acceleration, f → net is the net force, and m is the mass. this is often written in the more familiar form. f → net = ∑ f → = m a →, 5.3. but the first equation gives more insight into what newton’s second law means.

Newton S Second Law Of Motion Pdf Newton’s 2nd law relates an object’s mass, the net force on it, and its acceleration: therefore, we can find the force as follows: fnet = ma. substituting the values, we get. 1000 kg × 4 m s 2 = 4000 n. therefore, the horizontal net force is required to accelerate a 1000 kg car at 4 m s 2 is 4000 n. In equation form, newton’s second law is. a → = f → net m, where a → is the acceleration, f → net is the net force, and m is the mass. this is often written in the more familiar form. f → net = ∑ f → = m a →, 5.3. but the first equation gives more insight into what newton’s second law means. Newton's second law as a guide to thinking the numerical information in the table above demonstrates some important qualitative relationships between force, mass, and acceleration. comparing the values in rows 1 and 2, it can be seen that a doubling of the net force results in a doubling of the acceleration (if mass is held constant). What is newton's second law? (article) | khan academy. physics archive. course: physics archive > unit 3. lesson 1: newton's laws of motion. newton's first law of motion introduction.

Comments are closed.