489 Functional Anatomy Of The Knee And Leg

Functional Anatomy Of The Knee And Leg Functional Anatomy Of The A narrated powerpoint presentation by dr. mary lloyd ireland, dept. of orthopaedic surgery & sports medicine, university of kentucky, lexington, kentucky usa. Knee passive range of motion refers to how far the knee can be moved by an external force (e.g. another person) when the leg muscles are relaxed. to assess passive knee flexion: the patient is in supine lying. flex the patient’s leg to 90° at the hip and maintain this position by holding the distal femur with one hand.
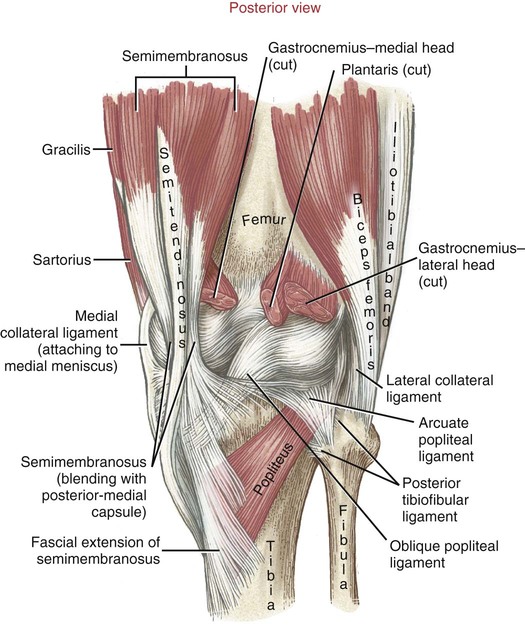
Structure And Function Of The Knee Musculoskeletal Key The knee is the joint that connects your thigh to your lower leg. it’s the biggest joint in your body. like all joints, your knees are part of your skeletal system. your knees also contain cartilage, muscles, ligaments and nerves. your knees help support your weight and let your legs bend and move. almost any movement that uses your legs. Knee anatomy involves more than just muscles and bones. ligaments, tendons, and cartilage work together to connect the thigh bone, shin bone, and knee cap and allow the leg to bend back and forth like a hinge. the largest joint in the body, the knee is also one of the most easily injured. problems with any part of the knee's anatomy can result. Fibula: the outer shin bone. the knee bones work together to support the entire body and transfer forces between the hip and foot, allowing the leg to move smoothly and efficiently. human knee joint anatomy actually comprises of two joints, the. tibiofemoral joint: the main knee joint between the thigh and shin bones. The main parts of the knee joint are the femur, tibia, patella, and supporting ligaments. the condyles of the femur and of the tibia come in close proximity to form the main structure of the joint. the patella, commonly known as the ‘kneecap’, is a sesamoid bone that sits within the tendon of the quadriceps femoris.
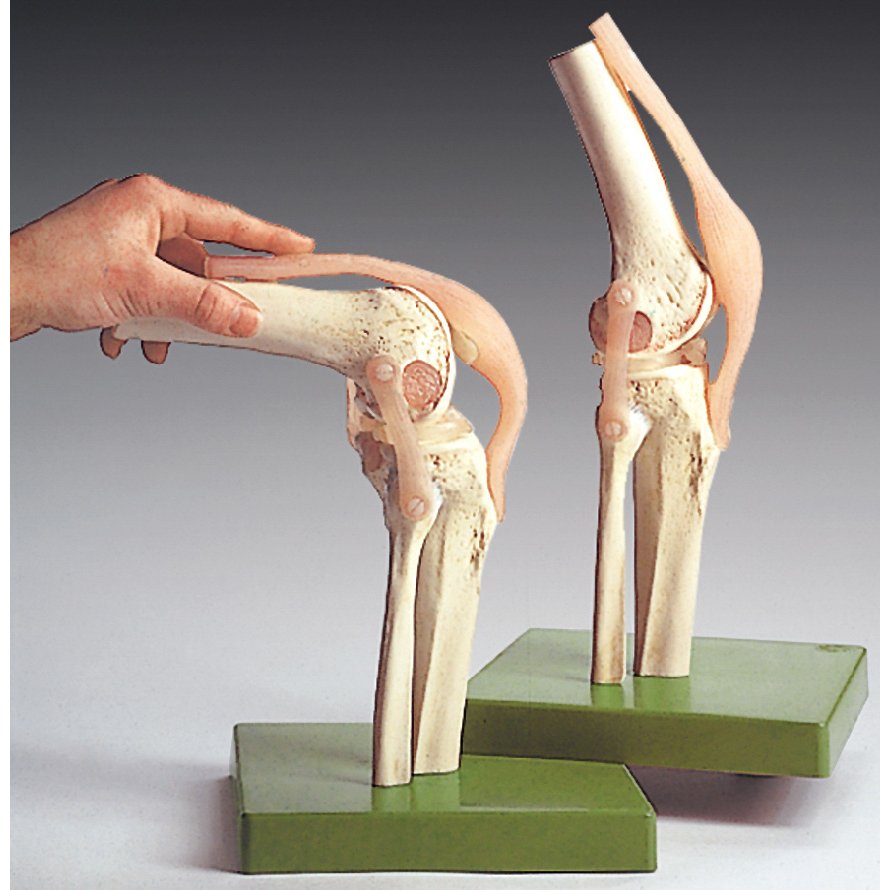
Functional Model Of The Knee Joint Anatomical Chart Company Ns 50 Fibula: the outer shin bone. the knee bones work together to support the entire body and transfer forces between the hip and foot, allowing the leg to move smoothly and efficiently. human knee joint anatomy actually comprises of two joints, the. tibiofemoral joint: the main knee joint between the thigh and shin bones. The main parts of the knee joint are the femur, tibia, patella, and supporting ligaments. the condyles of the femur and of the tibia come in close proximity to form the main structure of the joint. the patella, commonly known as the ‘kneecap’, is a sesamoid bone that sits within the tendon of the quadriceps femoris. The tibia, or shinbone, is a key bone in the lower leg. it is located at the front and closer to the midline of the body. it works with the fibula and is linked by a tough membrane that allows limited movement. the main function of the tibia is to connect the knee joint to the ankle. The knee is a type of synovial hinge joint. the knee is formed by the articulation of the femur bone in the thigh with the tibia in the lower leg. a patella or knee cap covers the front of the joint. a synovium surrounding the knee joint produces synovial fluid that nourishes, protects, and supports the joint.

Functional Anatomy Of The Knee Movement And Stability Interactive The tibia, or shinbone, is a key bone in the lower leg. it is located at the front and closer to the midline of the body. it works with the fibula and is linked by a tough membrane that allows limited movement. the main function of the tibia is to connect the knee joint to the ankle. The knee is a type of synovial hinge joint. the knee is formed by the articulation of the femur bone in the thigh with the tibia in the lower leg. a patella or knee cap covers the front of the joint. a synovium surrounding the knee joint produces synovial fluid that nourishes, protects, and supports the joint.
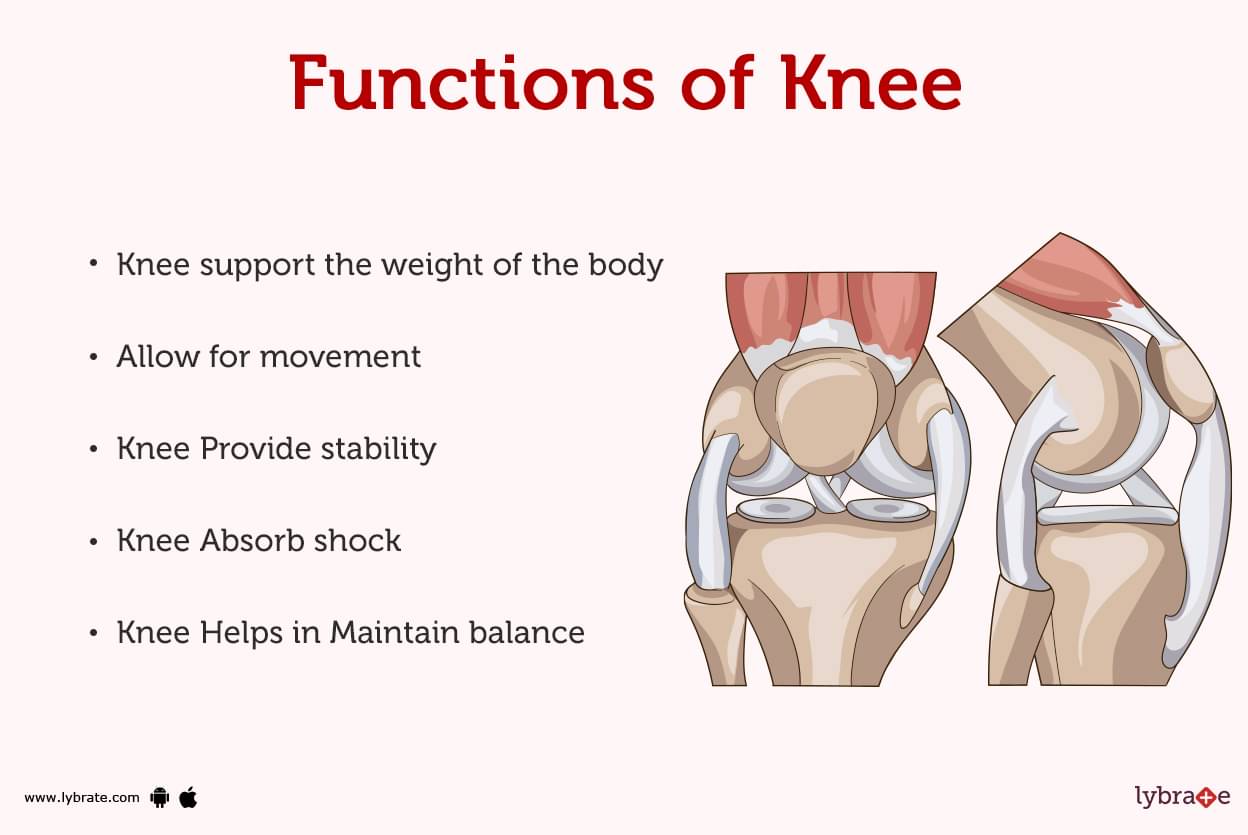
Knee Human Anatomy Function Parts Diseases Treatments

Comments are closed.