A Electromagnetically Pumped Liquid Metal Cooling Technique B

A Electromagnetically Pumped Liquid Metal Cooling Technique B The successful design of a liquid rocket engine is strictly linked to the development of efficient cooling systems, able to dissipate huge thermal loads coming from the combustion in the thrust. Fig. 1 (a) electromagnetically pumped liquid metal cooling technique; (b) schematic diagram of a dc emp. the formulation describing the emp model was derived from maxwell equations coupled with.

A Electromagnetically Pumped Liquid Metal Cooling Technique B A) electromagnetically pumped liquid metal cooling technique; (b) schematic diagram of a dc emp. the curve of pressure difference flow rate for the dc electromagnetic pump under different currents. Abstract. in this study, both the numerical simulations and experiments are carried out to investigate the flow and heat transfer performance of liquid metal (ga 61 in 25 sn 13 zn 1) in a dc emp (direct current electromagnetic pump). the numerical results indicate that flatter and higher channel lead to higher pressure heads and larger flow. This study offers an optimization method for manufacturing a new compact structure of emp towards driving metal coolant and will further promote the development of the liquid metal heat transfer techniques. ab electromagnetically pumped liquid metal cooling is a powerful method for the thermal management of extremely high heat flux devices. Furthermore, the pressure drop inside the electromagnetic pump is another significant factor that affects the pump driving performance. kim et al. [60] conducted measurements on the pressure drop of an electromagnetic pump and studied the effects of magnetic field intensity and liquid metal flow velocity on the flow pressure drop of electrically conductive liquid sodium, as shown in fig. 3 (c).

A Electromagnetically Pumped Liquid Metal Cooling Technique B This study offers an optimization method for manufacturing a new compact structure of emp towards driving metal coolant and will further promote the development of the liquid metal heat transfer techniques. ab electromagnetically pumped liquid metal cooling is a powerful method for the thermal management of extremely high heat flux devices. Furthermore, the pressure drop inside the electromagnetic pump is another significant factor that affects the pump driving performance. kim et al. [60] conducted measurements on the pressure drop of an electromagnetic pump and studied the effects of magnetic field intensity and liquid metal flow velocity on the flow pressure drop of electrically conductive liquid sodium, as shown in fig. 3 (c). V. t. e. an electromagnetic pump is a pump that moves liquid metal, molten salt, brine, or other electrically conductive liquid using electromagnetism. a magnetic field is set at right angles to the direction the liquid moves in, and a current is passed through it. this causes an electromagnetic force that moves the liquid. In these systems, the em pump acted as a mechanism to provide fine adjustment of the mer cury pressme head at the propellant vaporizer. one such pump produced a pressure differential of 0.6 atm at a 20 a current level4 the piimary designs used for electromagnetically pumping liquid metals ase direct current (dc) and.

A D Schematics For Liquid Metal Cooling Experiment System A V. t. e. an electromagnetic pump is a pump that moves liquid metal, molten salt, brine, or other electrically conductive liquid using electromagnetism. a magnetic field is set at right angles to the direction the liquid moves in, and a current is passed through it. this causes an electromagnetic force that moves the liquid. In these systems, the em pump acted as a mechanism to provide fine adjustment of the mer cury pressme head at the propellant vaporizer. one such pump produced a pressure differential of 0.6 atm at a 20 a current level4 the piimary designs used for electromagnetically pumping liquid metals ase direct current (dc) and.
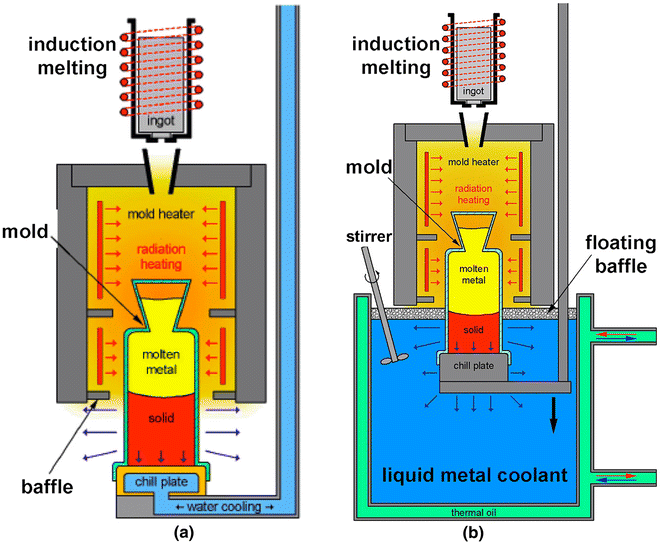
Structure Refinement By A Liquid Metal Cooling Solidification Process

Comments are closed.