A Meat Eater That Eats Primary Consumers

Ppt Guess Who S Coming To Dinner Powerpoint Presentation Free The network of all the inter related food chains in a biological community. autotroph. an organism that makes its food from light or chemical energy without eating. heterotroph. an organism that gets its energy by eating other organisms. carnivore. an organism that eats meat. herbivore. an organism that eats plants. Secondary consumers feed on smaller, plant eating animals (primary consumers). examples of secondary consumers include bluegill, small fish, crayfish and frogs. top predators top predators are at the top of the food chain. top predators eat plants, primary consumers and or secondary consumers. they can be carnivores or omnivores.
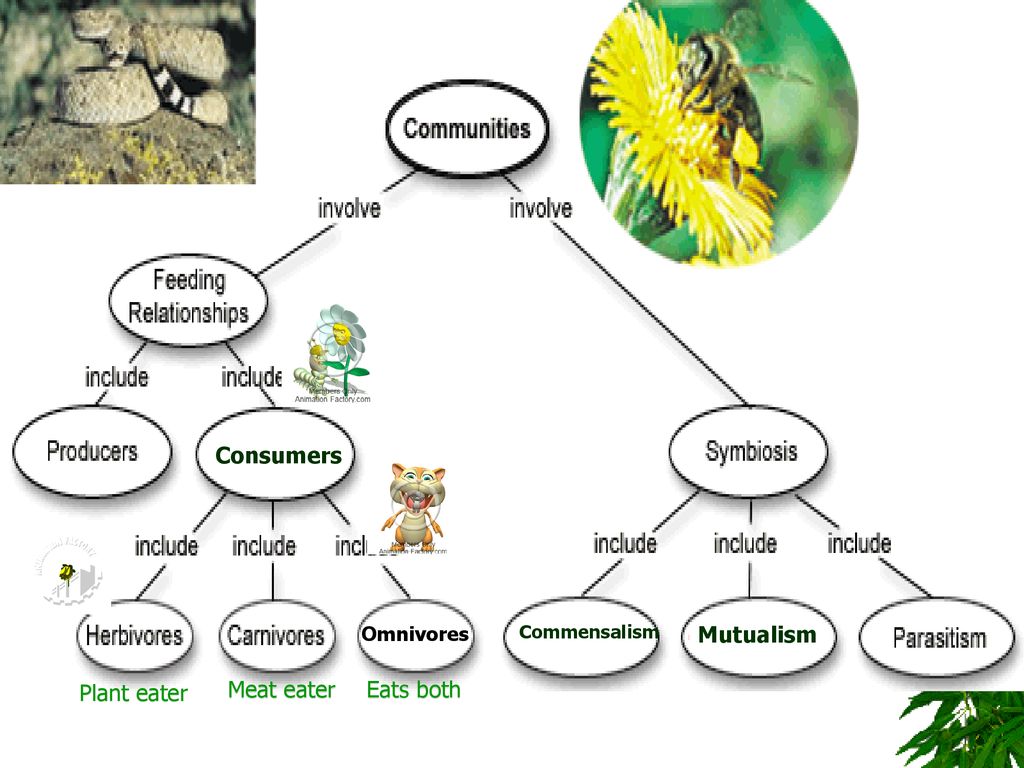
Ecology Notes Ppt Download The organisms that eat the producers are the primary consumers. they tend to be small in size and there are many of them. the primary consumers are herbivores (vegetarians). the organisms that eat the primary consumers are meat eaters (carnivores) and are called the secondary consumers. Consumers the next trophic levels are made up of animals that eat producers. these organisms are called consumers. consumers can be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores eat meat, while omnivores eat various organisms, including both meat and plants. primary consumers are herbivores, which eat plants, algae, and other producers. Higher level consumers (i.e., secondary, tertiary, and above) can be carnivores (animals that eat other animals) or omnivores (animals that eat both plants and animals). omnivores, like people, consume many types of foods. people eat plants, such as vegetables and fruits. we also eat animals and animal products, such as meat, milk, and eggs. we. It will not eat animals. secondary consumers eat the primary consumers. a mouse might be a primary consumer and a cat might be the secondary. secondary consumers are also called carnivores. carnivore means "meat eater." in some ecosystems, there is a third level of consumer called the tertiary consumer (that means third level).
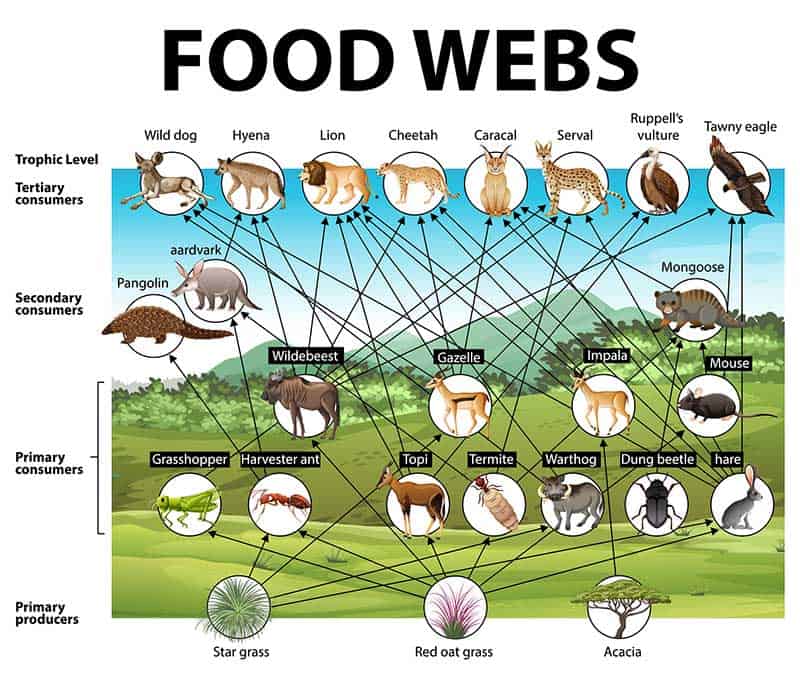
12 Examples Of Primary Consumers Pictures Diagram Wildlife Informer Higher level consumers (i.e., secondary, tertiary, and above) can be carnivores (animals that eat other animals) or omnivores (animals that eat both plants and animals). omnivores, like people, consume many types of foods. people eat plants, such as vegetables and fruits. we also eat animals and animal products, such as meat, milk, and eggs. we. It will not eat animals. secondary consumers eat the primary consumers. a mouse might be a primary consumer and a cat might be the secondary. secondary consumers are also called carnivores. carnivore means "meat eater." in some ecosystems, there is a third level of consumer called the tertiary consumer (that means third level). If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. if you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. The primary consumer plays an important role in the ecosystem by facilitating the flow of energy through the food chain. its main job is to consume plants, converting the energy stored in them into a form that can be used by other consumers in the ecosystem. primary consumers are vital in the trophic structure as they directly consume.

Educa T Natural Science 3º If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. if you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. The primary consumer plays an important role in the ecosystem by facilitating the flow of energy through the food chain. its main job is to consume plants, converting the energy stored in them into a form that can be used by other consumers in the ecosystem. primary consumers are vital in the trophic structure as they directly consume.

Comments are closed.