Abg Nursing Cheat Sheet With A Step By Step Study Guide On Blood Gas
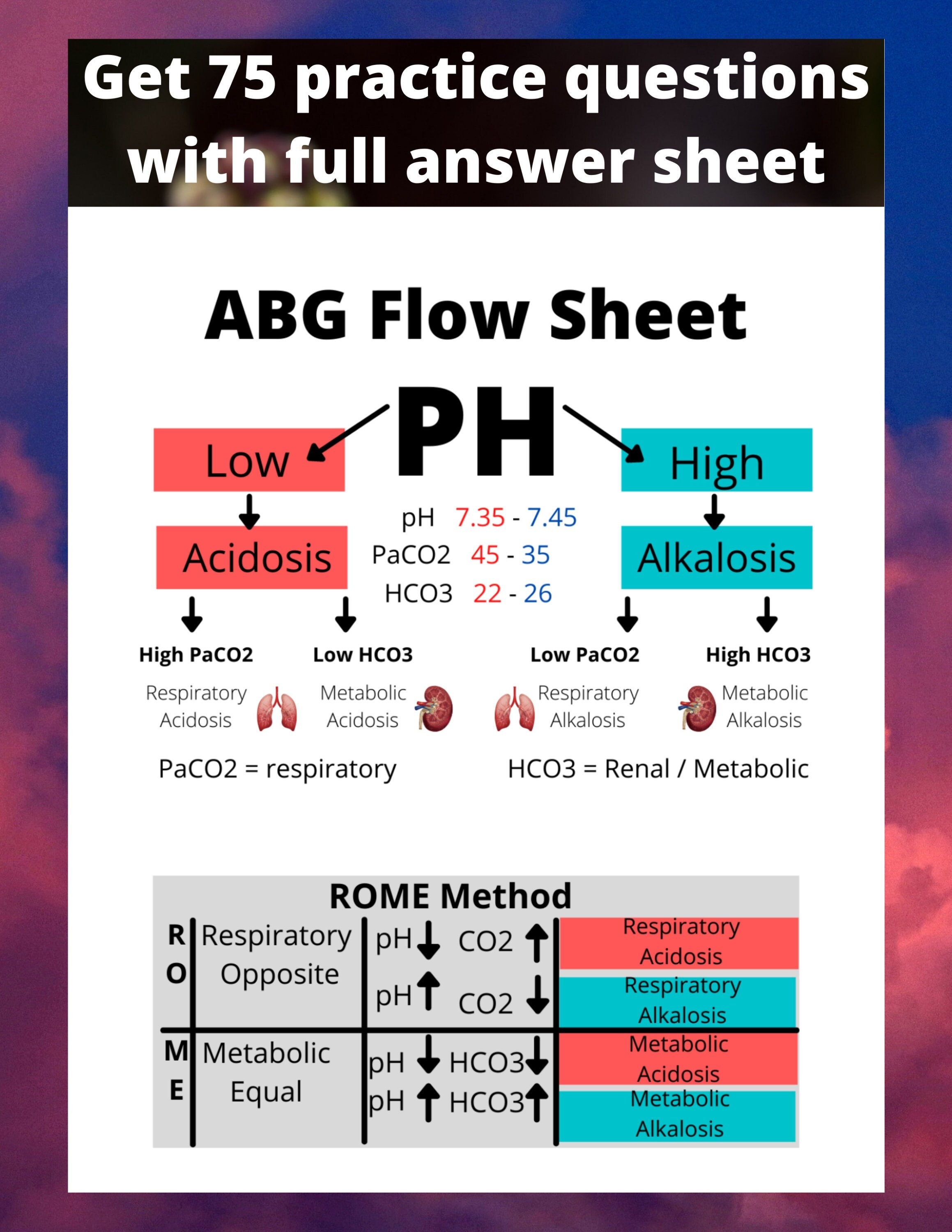
Abg Nursing Cheat Sheet With A Step By Step Study Guide On Blood Gas There are eight (8) steps simple steps you need to know if you want to interpret arterial blood gases (abgs) results using the tic tac toe technique. 1. memorize the normal values. the first step is you need to familiarize yourself with the normal and abnormal abg values when you review the lab results. Abg interpretation guide. interpreting abgs accurately is a crucial skill for nurses to recognize respiratory or metabolic acid base disorders. find a comprehensive guide to arterial blood gas (abg) interpretation below. it covers the normal abg values, compensatory mechanisms, and the ph scale to diagnose respiratory and metabolic acid base.
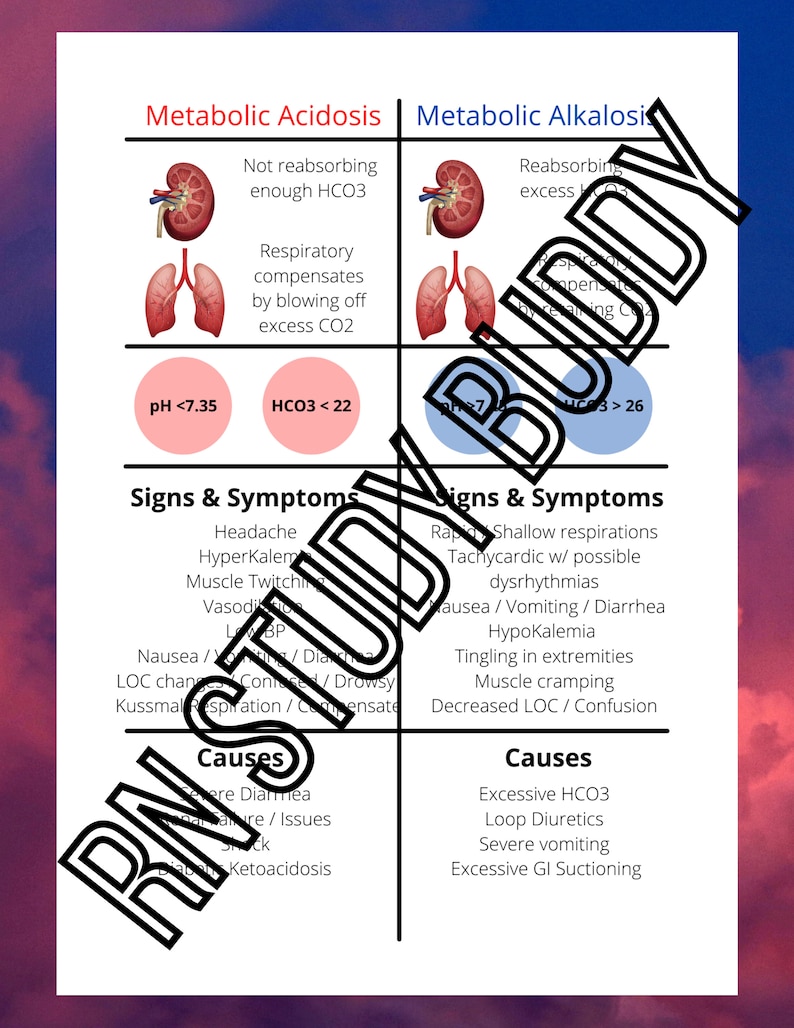
Abg Nursing Cheat Sheet With A Step By Step Study Guide On Blood Gas An abg test checks the acid base balance in your blood as well as the partial pressure of oxygen (pao 2) and carbon dioxide (paco 2). the components include: ph: this is the measure of acids and bases in the blood. basically, if it’s lower than normal, it’s acidic. if it’s higher, it’s basic. Causes: identify the common causes of various acid base imbalances. our abgs and acid base imbalance cheat sheet outlines the triggers you need to know. memory tricks: retaining complex information with ease. our cheat sheet includes clever memory aids to help you remember critical concepts. key players: familiarize yourself with the key. Interpreting an arterial blood gas (abg) involves a step by step approach to make accurate and timely clinical decisions. the simplified steps for abg interpretation include: collect and run an arterial blood sample. determine if the ph is alkalosis or acidosis. determine if the issue is respiratory or metabolic. Anion gap formula: na – (cl – hco 3–) the anion gap (ag) is a derived variable primarily used for the evaluation of metabolic acidosis to determine the presence of unmeasured anions (e.g. albumin is the main unmeasured anion). the normal anion gap varies with different assays but is typically between 4 to 12 mmol l.
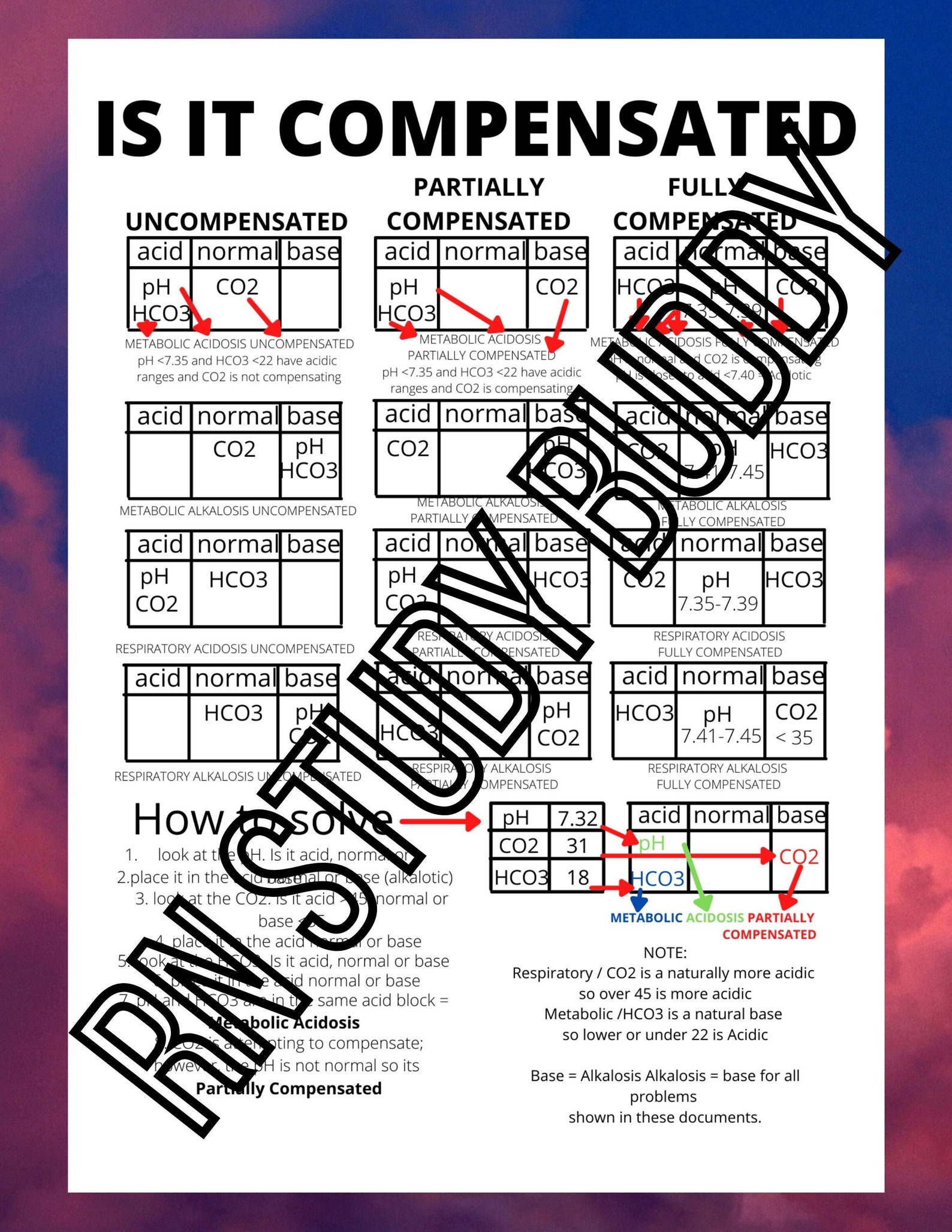
Abg Nursing Cheat Sheet With A Step By Step Study Guide On Blood Gas Interpreting an arterial blood gas (abg) involves a step by step approach to make accurate and timely clinical decisions. the simplified steps for abg interpretation include: collect and run an arterial blood sample. determine if the ph is alkalosis or acidosis. determine if the issue is respiratory or metabolic. Anion gap formula: na – (cl – hco 3–) the anion gap (ag) is a derived variable primarily used for the evaluation of metabolic acidosis to determine the presence of unmeasured anions (e.g. albumin is the main unmeasured anion). the normal anion gap varies with different assays but is typically between 4 to 12 mmol l. Hco3 : this is bicarbonate, a chemical buffer made in the kidneys to neutralize acids. it is the metabolic component of the abg. normal is 22 28 meq l. sao2: this is a measure of the % of oxygen that is attached to hemoglobin in red blood cells. normal is > 95% in healthy humans (avg is 98% for a healthy pt). Interpreting an arterial blood gas (abg) is a crucial skill for physicians, nurses, respiratory therapists, and other health care personnel. abg interpretation is especially important in critically ill patients. the following six step process helps ensure a complete interpretation of every abg. in addition, you will find tables that list.

Comments are closed.