Abnormal L5 S1 Facet Joint Orientation As A Harbinger Of D
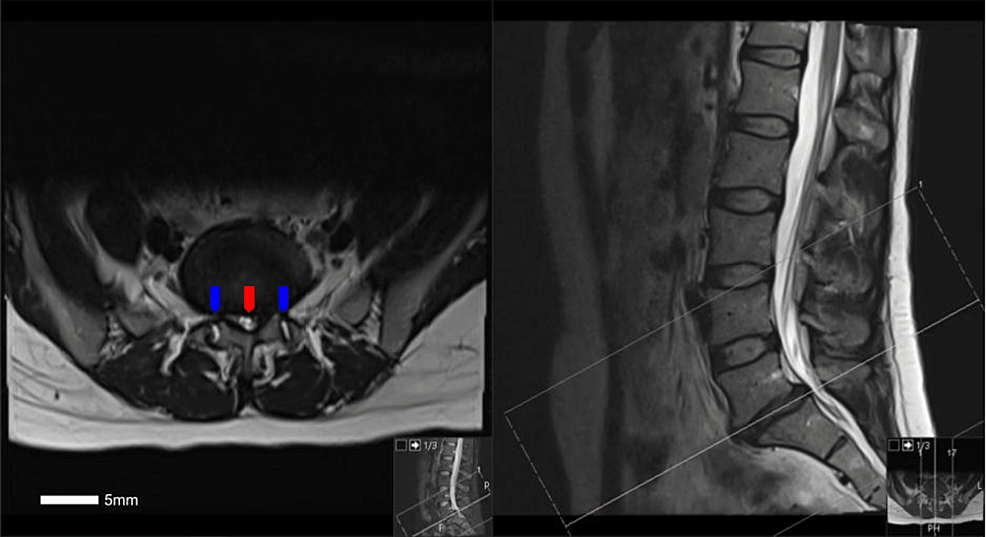
Cureus Abnormal L5 S1 Facet Joint Orientation As A Harbingerо Facet tropism, the variation in facet joint orientation in the sagittal plane, has been sparsely studied and is often overlooked in the development of lumbar degenerative pathology . facet tropism in our patient demonstrated a general increase in angulation until an abruptly sagittal facet joint at the l5 s1 level (table 1). Here, we report a case of a 38 year old female presenting with low back pain and right lower extremity radiculopathy, found to have degenerative l5 s1 spondylolisthesis, which we postulate developed in part due to the sagittal orientation of her l5 s1 facet joints bilaterally.

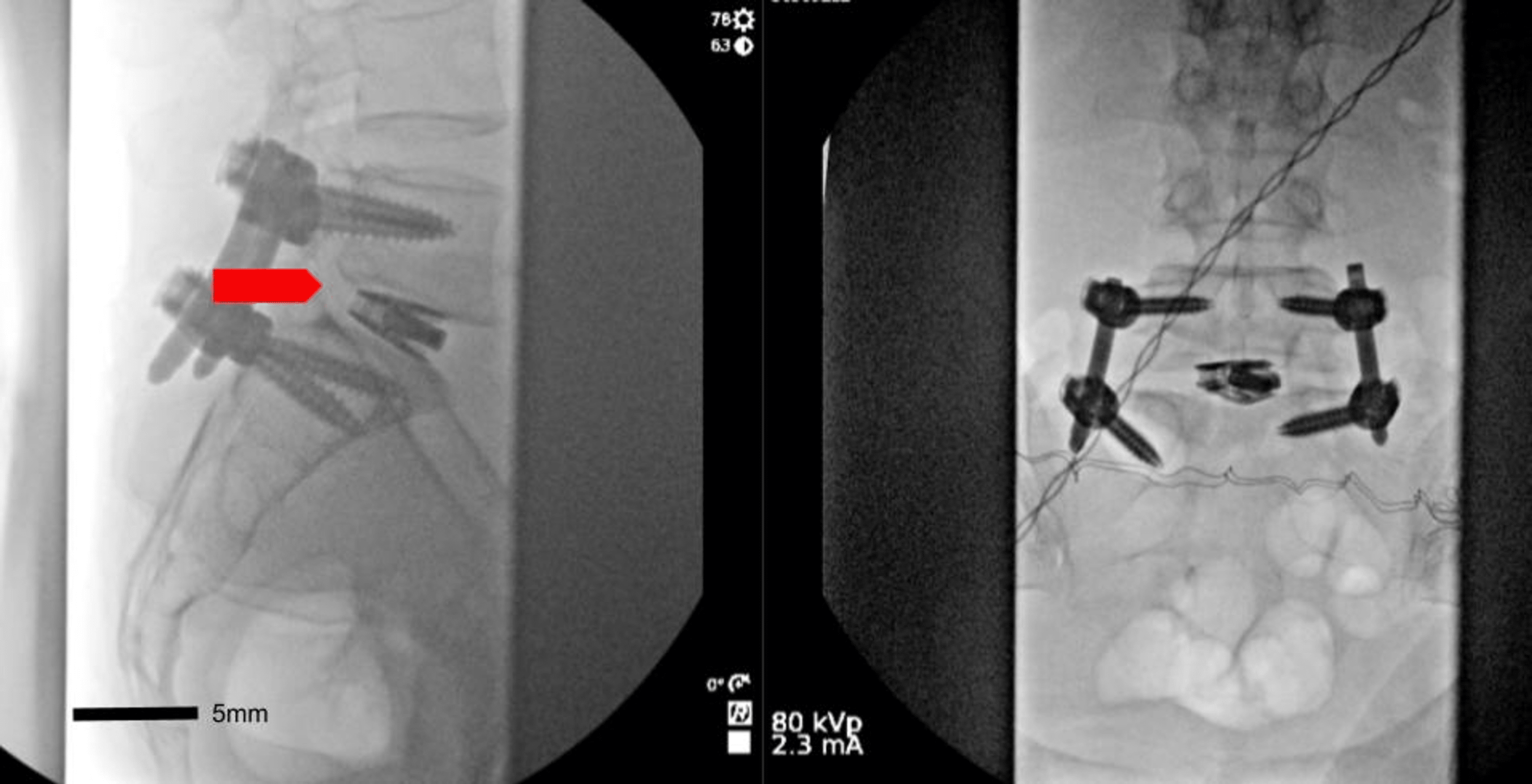
Abnormal L5 S1 Facet Joint Orientation As A Harbinger Of D Degenerative spondylolisthesis is a common cause of low back pain and resultant disability in the adult population. the causes of degenerative spondylolisthesis are not entirely understood, though a combination of anatomic and lifestyle factors likely contributes to the development of this pathology. here, we report a case of a 38 year old female presenting with low back pain and right lower. Note the pars defect on the right (red arrow), as well as the sagittal orientation of the l5 s1 facet joint line (blue lines). the facet joint at l5 s1 demonstrated an angle relative to the midsagittal axis of 1.6°, which is substantially more sagittal than what would be expected of a l5 s1 joint that is typically coronally oriented (table 1). Mri of patients with ddd, ds, and control group at facet joint between l3 4, l4 5, and l5 s1 levels were measured in axial view that can clearly see facet joint (60 subjects in each group). Doi: 10.7759 cureus.40569 corpus id: 259400952; abnormal l5 s1 facet joint orientation as a harbinger of degenerative spondylolisthesis: a case report @article{labak2023abnormallf, title={abnormal l5 s1 facet joint orientation as a harbinger of degenerative spondylolisthesis: a case report}, author={collin m. labak and rohit mauria and eric herring and michael d. shost and manish k. kasliwal.

Figure 3 From Abnormal L5 S1 Facet Joint Orientation As A Har Mri of patients with ddd, ds, and control group at facet joint between l3 4, l4 5, and l5 s1 levels were measured in axial view that can clearly see facet joint (60 subjects in each group). Doi: 10.7759 cureus.40569 corpus id: 259400952; abnormal l5 s1 facet joint orientation as a harbinger of degenerative spondylolisthesis: a case report @article{labak2023abnormallf, title={abnormal l5 s1 facet joint orientation as a harbinger of degenerative spondylolisthesis: a case report}, author={collin m. labak and rohit mauria and eric herring and michael d. shost and manish k. kasliwal. Summary of background data: facet joints at the l5 s1 play an important role in load sharing and imparting stability at this area as well as are involved in conditions such as isthmic spondylolysis, degenerative spondylolisthesis, and osteoarthritis, giving rise to low back pain situations. several morphologic variations at the lumbosacral. See good posture helps reduce back pain. disorders of the lumbar facets typically occur due to degenerative changes within the joint or as a progression of disc degeneration, and less commonly due to direct trauma to the joint. conditions affecting the facets can cause instability in the spinal motion segment, resulting in pain and stiffness in.
Abnormal L5 S1 Facet Joint Orientation As A Harbinger Of D Summary of background data: facet joints at the l5 s1 play an important role in load sharing and imparting stability at this area as well as are involved in conditions such as isthmic spondylolysis, degenerative spondylolisthesis, and osteoarthritis, giving rise to low back pain situations. several morphologic variations at the lumbosacral. See good posture helps reduce back pain. disorders of the lumbar facets typically occur due to degenerative changes within the joint or as a progression of disc degeneration, and less commonly due to direct trauma to the joint. conditions affecting the facets can cause instability in the spinal motion segment, resulting in pain and stiffness in.

Comments are closed.