Acid Base Equilibria And Buffer Solutions

Acid Base Equilibria Buffer Solution Youtube A solution containing a mixture of an acid and its conjugate base, or of a base and its conjugate acid, is called a buffer solution. unlike in the case of an acid, base, or salt solution, the hydronium ion concentration of a buffer solution does not change greatly when a small amount of acid or base is added to the buffer solution. the base (or. Remember those pesky iceboxes? weak acids and bases establish equilibria, so we have to do iceboxes to figure out things about them. but don't worry, buffers.
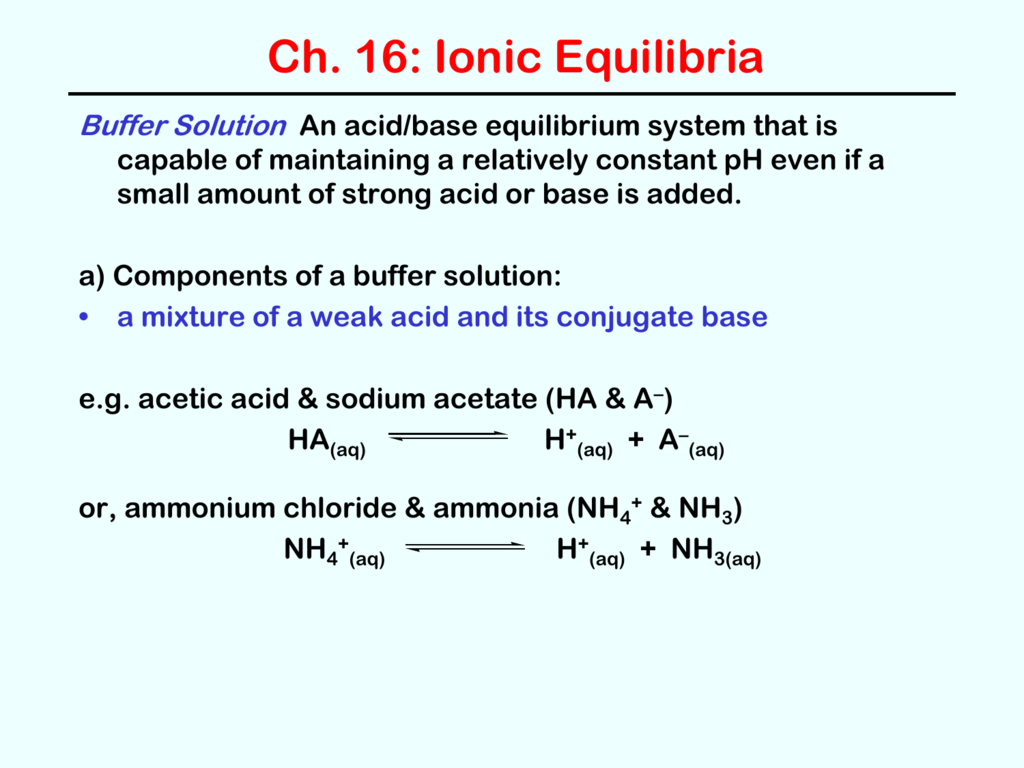
Chapter 1 Fundamental Concepts A solution containing appreciable amounts of a weak conjugate acid base pair is called a buffer solution, or a buffer. buffer solutions resist a change in ph when small amounts of a strong acid or a strong base are added (figure 7.7.1). a solution of acetic acid and sodium acetate (ch 3 cooh ch 3 coona) is an example of a buffer that consists. Substitute values into either form of the henderson hasselbalch approximation (equations 3.2.9 or 3.2.10) to calculate the ph. solution: according to the henderson hasselbalch approximation (equation 3.2.9), the ph of a solution that contains both a weak acid and its conjugate base is. ph = pka log([a −] [ha]). The first regime is a straightforward equilibrium problem. the second regime involves reaction of the acid and base as a limiting reagent problem, followed by straightforward equilibration of the resulting solution. the third regime is handled differently depending on whether the acid (or base) initially present is a weak or strong acid (or base). The reaction between a weak acid and a strong base has a large equilibrium constant and therefore goes essentially to completion. the net ionic equation for the reaction of the weak acid hclo with the strong base naoh (100% ionized in solution) is. hclo(aq) oh–(aq) h2o( ) clo–(aq) k = 1 kb(clo–) = 3.5 106.

Buffer Solutions A Level Chemistrystudent The first regime is a straightforward equilibrium problem. the second regime involves reaction of the acid and base as a limiting reagent problem, followed by straightforward equilibration of the resulting solution. the third regime is handled differently depending on whether the acid (or base) initially present is a weak or strong acid (or base). The reaction between a weak acid and a strong base has a large equilibrium constant and therefore goes essentially to completion. the net ionic equation for the reaction of the weak acid hclo with the strong base naoh (100% ionized in solution) is. hclo(aq) oh–(aq) h2o( ) clo–(aq) k = 1 kb(clo–) = 3.5 106. • if you need to make a buffer for an acidic solution, use acid that’s somewhat stronger (although it still must be a weak acid). you would want k a > 10 7. • if you need a buffer for a basic solution, you would want k a < 10 7. • if you want a buffer for a specific ph, choose a pk a and initial concentrations to satisfy the henderson. A buffer helps to maintain a constant ph. our blood has a natural buffering system to ensure that the ph of our blood stays within a narrow window and that we stay health. in this lecture, we consider how to design a buffer. we also discuss how one can predict the ph of a salt solution.

Ppt Acid Base Equilibria Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id • if you need to make a buffer for an acidic solution, use acid that’s somewhat stronger (although it still must be a weak acid). you would want k a > 10 7. • if you need a buffer for a basic solution, you would want k a < 10 7. • if you want a buffer for a specific ph, choose a pk a and initial concentrations to satisfy the henderson. A buffer helps to maintain a constant ph. our blood has a natural buffering system to ensure that the ph of our blood stays within a narrow window and that we stay health. in this lecture, we consider how to design a buffer. we also discuss how one can predict the ph of a salt solution.

Comments are closed.