Active Transport In Cell Membrane Ppt Transport Informations Lane
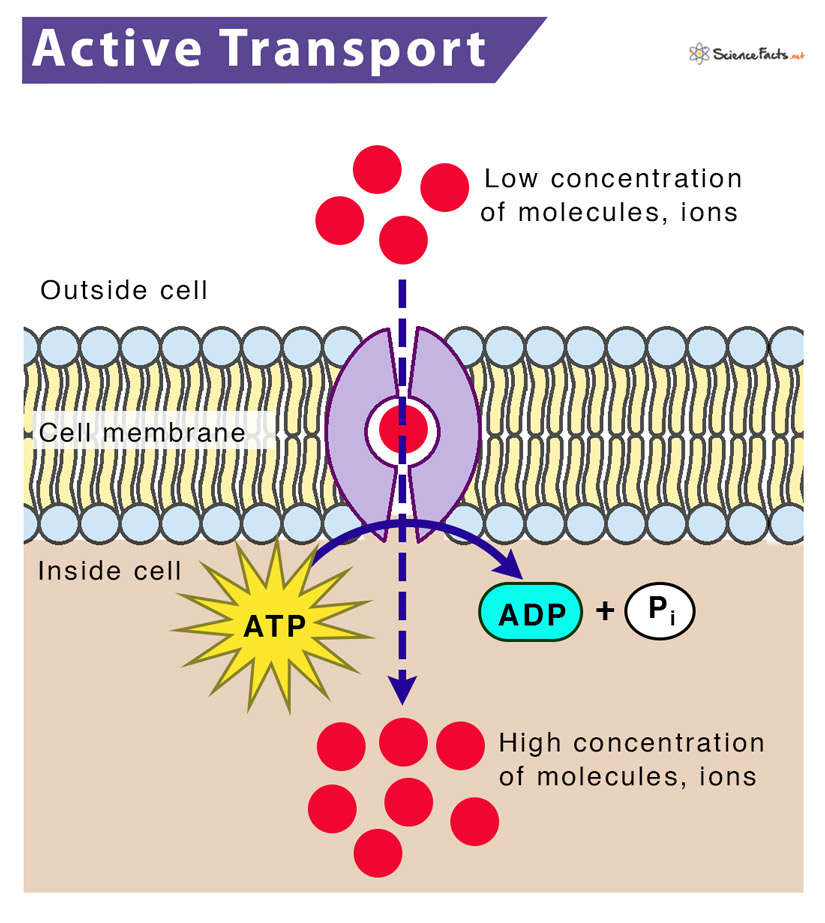
Cell Membrane And Transport Labeled Transport Informations Lane Transport across cell membrane. this document discusses cell membrane transport mechanisms. it begins by outlining the key topics to be covered, including the importance of cell membranes, types of transport mechanisms, and details on active and primary secondary active transport. it then provides information on the structure of the cell. Active transport requires energy and moves molecules against their concentration gradient. there are two types: primary active transport which directly uses atp hydrolysis for energy, and secondary active transport which utilizes ion gradients established by primary transport. primary transport examples include the sodium potassium pump.
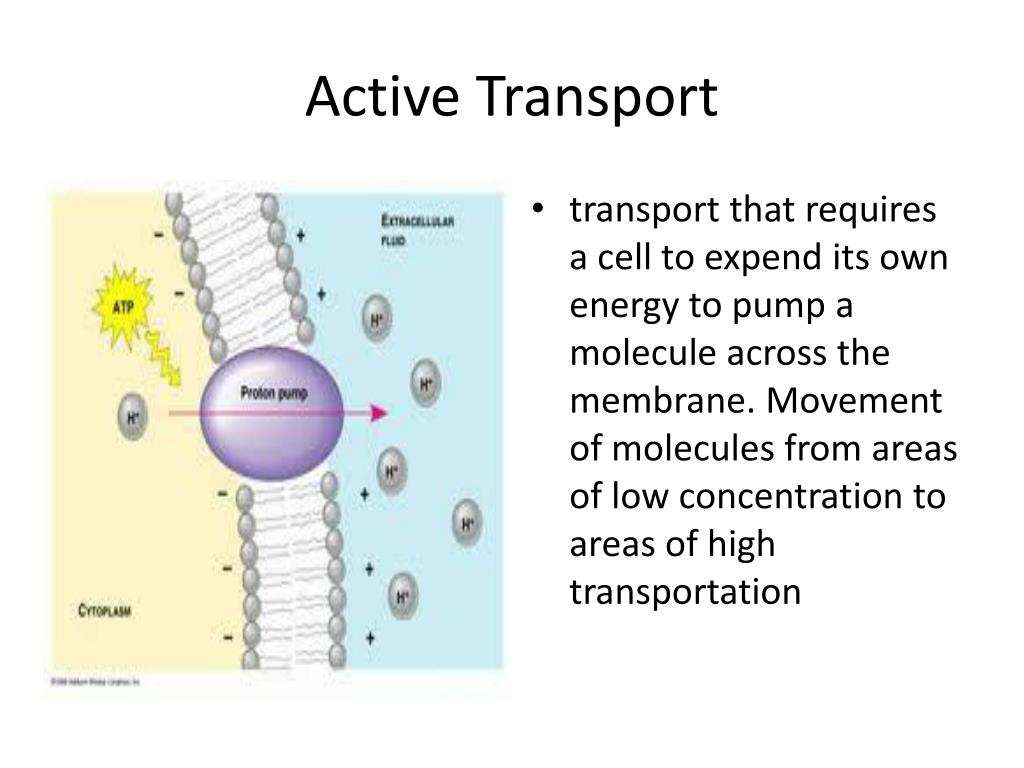
Active Transport In Cell Membrane Ppt Transport Informations Lane 5. cell membrane and membrane transport. the plasma membrane separates the cell from its environment and regulates the transport of substances into and out of the cell. it has a fluid mosaic structure consisting of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. membrane proteins function as ion channels, carriers, receptors, linkers, and cell. 1 passive transport and active transport. chapter 7 section 3. 2 passive transport movement of molecules across a cell membrane without the input of energy 2 types of passive transport: diffusion osmosis. 3 key terms to know concentration: the mass of solute in a given volume of solution equilibrium: concentration of the solute is the same. Transport through cell membranes the phospholipid bilayer is a good barrier around cells, especially to water soluble molecules. however, for the cell to survive some materials need to be able to enter and leave the cell. there are 4 basic mechanisms: diffusion and facilitated diffusion osmosis active transport bulk transport as biology, cell membranes and transport. Slide 1. transport of substance through cell membrane 1 & 2. dr. somia iqbal. learning objectives. classify various modes of transport of substances across the cell membrane. compare and contrast modes of transport of substances across the cell membrane with examples (osmosis, diffusion, facilitated diffusion, primary active transport.
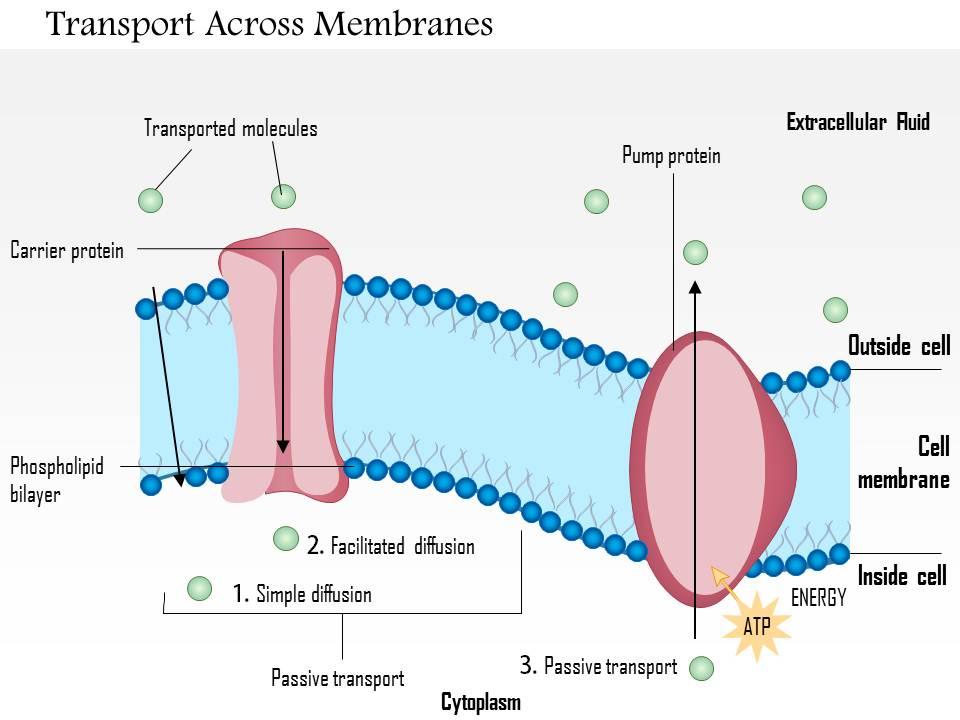
3 Types Of Transport Across Cell Membrane Transport Informations La Transport through cell membranes the phospholipid bilayer is a good barrier around cells, especially to water soluble molecules. however, for the cell to survive some materials need to be able to enter and leave the cell. there are 4 basic mechanisms: diffusion and facilitated diffusion osmosis active transport bulk transport as biology, cell membranes and transport. Slide 1. transport of substance through cell membrane 1 & 2. dr. somia iqbal. learning objectives. classify various modes of transport of substances across the cell membrane. compare and contrast modes of transport of substances across the cell membrane with examples (osmosis, diffusion, facilitated diffusion, primary active transport. Transport across cell membranes chapter 2.2 mcgraw hill ryerson biology 12 (2011). concentration gradient concentration gradient: difference in concentration between one side of a membrane and the other ions and molecules like to move from high to low diffusion: the net movement of ions or molecules from an area of higher concentration to area of lower concentration. If a channel protein exists and is open, the sodium ions will be pulled through the membrane. this movement is used to transport other substances that can attach themselves to the transport protein through the membrane (figure 5.4.4 5.4. 4). many amino acids, as well as glucose, enter a cell this way.

Active Transport Across Cell Membrane Requiresa Gluco Vrogue Co Transport across cell membranes chapter 2.2 mcgraw hill ryerson biology 12 (2011). concentration gradient concentration gradient: difference in concentration between one side of a membrane and the other ions and molecules like to move from high to low diffusion: the net movement of ions or molecules from an area of higher concentration to area of lower concentration. If a channel protein exists and is open, the sodium ions will be pulled through the membrane. this movement is used to transport other substances that can attach themselves to the transport protein through the membrane (figure 5.4.4 5.4. 4). many amino acids, as well as glucose, enter a cell this way.

Ppt Transport Across Cell Membranes Powerpoint Presentation Free

Comments are closed.