Air Pressure Wind Earth Science
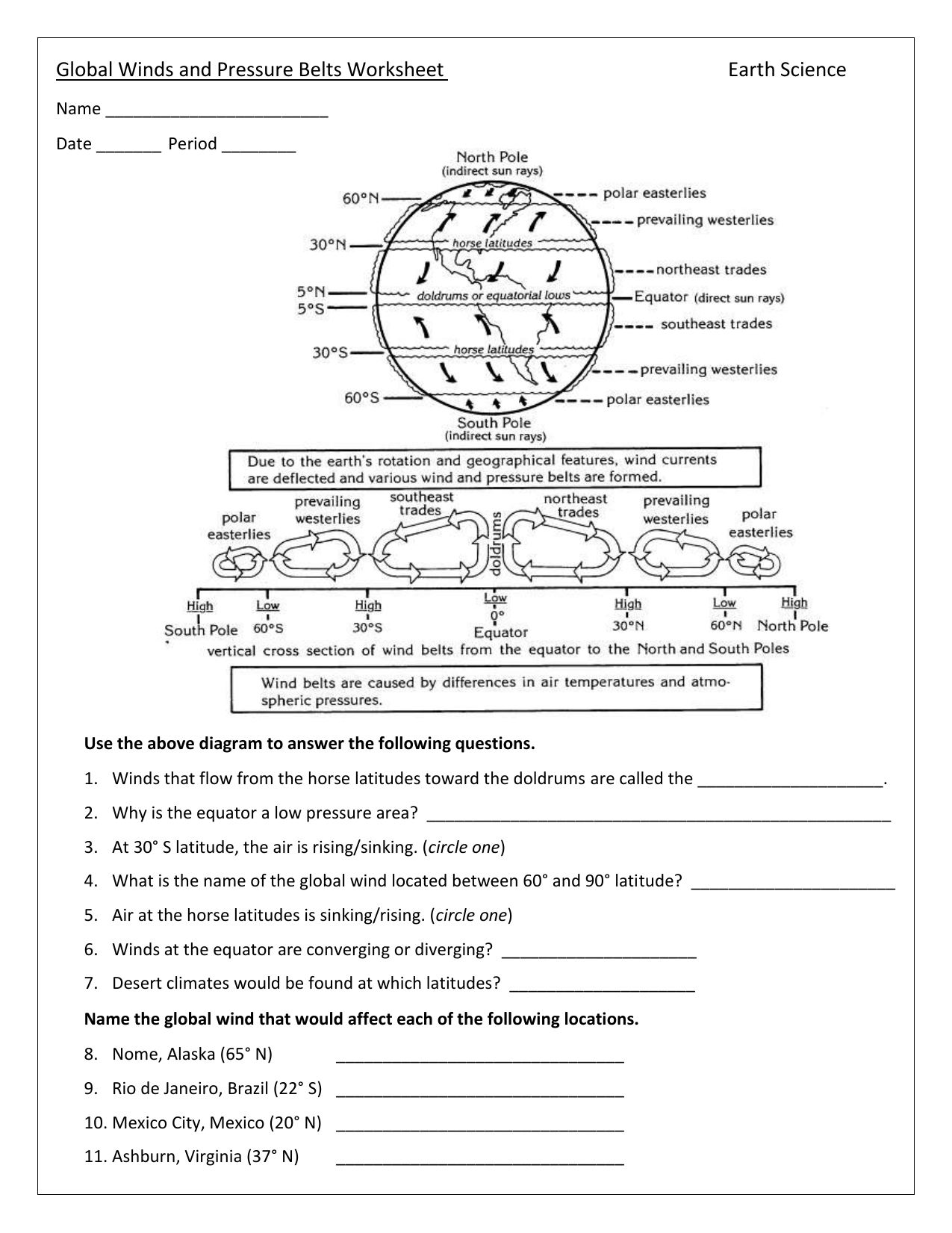
Global Winds And Pressure Belts Worksheet Earth Science Air that moves horizontally between high and low pressure zones makes wind. the greater the pressure difference between the pressure zones the faster the wind moves. convection in the atmosphere creates the planet’s weather. when warm air rises and cools in a low pressure zone, it may not be able to hold all the water it contains as vapor. Climate pressure, wind, air: atmospheric pressure and wind are both significant controlling factors of earth’s weather and climate. although these two physical variables may at first glance appear to be quite different, they are in fact closely related. wind exists because of horizontal and vertical differences (gradients) in pressure, yielding a correspondence that often makes it possible.

Chapter 18 Air Pressure And Wind Earth Science Phys 102 Youtube An atmosphere (atm) is a unit of measurement equal to the average air pressure at sea level at a temperature of 15 degrees celsius (59 degrees fahrenheit). one atmosphere is 1,013 millibars, or 760 millimeters (29.92 inches) of mercury. atmospheric pressure drops as altitude increases. Wind wind results from a horizontal difference in air pressure and since the sun heats different parts of the earth differently, causing pressure differences, the sun is the driving force for most winds. the wind is a result of forces acting on the atmosphere: 1. pressure gradient force (pgf) causes horizontal pressure differences and winds 2. Above every square inch on the surface of the earth is 14.7 pounds of air. that means air exerts 14.7 pounds per square inch (psi) of pressure at earth’s surface. high in the atmosphere, air pressure decreases. with fewer air molecules above, there is less pressure from the weight of the air above. Air pressure is defined as the amount of force that these molecules impart on a given area. in general, the more air molecules present, the greater the air pressure. wind, in turn, is driven by.

What Is Atmospheric Air Pressure And Wind Hadleys Cell Diagram And Above every square inch on the surface of the earth is 14.7 pounds of air. that means air exerts 14.7 pounds per square inch (psi) of pressure at earth’s surface. high in the atmosphere, air pressure decreases. with fewer air molecules above, there is less pressure from the weight of the air above. Air pressure is defined as the amount of force that these molecules impart on a given area. in general, the more air molecules present, the greater the air pressure. wind, in turn, is driven by. Wind is caused by differences of pressure in the earth's atmosphere. air from a high pressure area will move towards an area of low pressure. high winds are caused when air moves between areas with large differences in air pressure. on earth, the main differences in air pressure are caused by differences in temperature. Answers: wind is the movement of the air through the earth’s atmosphere. the atmosphere controls the pressure of the earth’s surface by first controlling the temperature. high pressure areas arise from cooler temperatures, and low pressure areas arise from warmer temperatures. wind is measured in terms of its direction and its speed of travel.

Comments are closed.