An Introduction To Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Snp Genetic Educatio
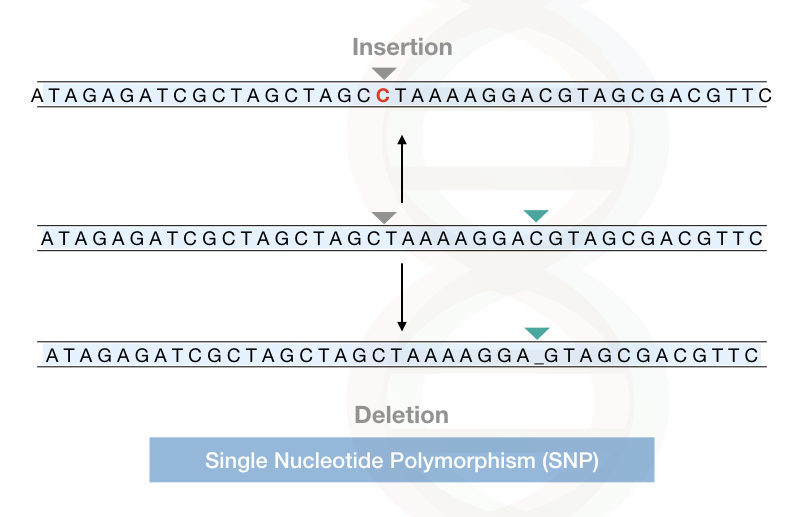
An Introduction To Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Snp Snp is the widely accepted and known term to introduce single nucleotide polymorphism. it is pronounced as ‘snip’ or ‘snips.’. snps are crucial genomic alterations that gained much attention after 1980. however, now in 2023, it’s a major focus of genetic research. Recent news. single nucleotide polymorphism (snp), variation in a genetic sequence that affects only one of the basic building blocks— adenine (a), guanine (g), thymine (t), or cytosine (c)—in a segment of a dna molecule and that occurs in more than 1 percent of a population. an example of an snp is the substitution of a c for a g in the.
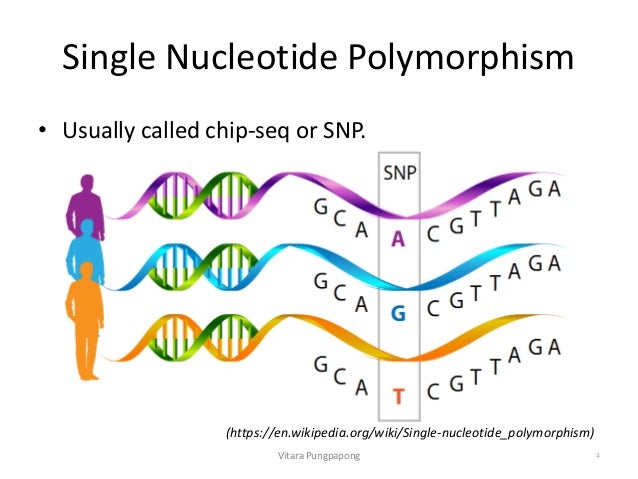
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Analysis Snps Snp. a single nucleotide polymorphism, or snp (pronounced "snip"), is a variation at a single position in a dna sequence among individuals. recall that the dna sequence is formed from a chain of. The upper dna molecule differs from the lower dna molecule at a single base pair location (a g a polymorphism). in genetics and bioinformatics, a single nucleotide polymorphism (snp snɪp ; plural snps snɪps ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. although certain definitions require the. Single nucleotide polymorphism, or snp. if you are reading a news story where it says, for example, scientists find the genetic contributors to diabetes or some other condition or trait, you're probably reading about snps. a snp is a one letter place where your genome varies from another genome sequence. Introduction. single nucleotide polymorphisms (snps), pronounced as “snips,” is the common type of variation found in dna between genes (genetics home reference). each snp differs by a single dna block represented as nucleotide. for example, a snp may be replaced by adenine (a) in place of guanine (g) in a stretch of dna.

Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Snps Are Genetic Mutations That Alter Single nucleotide polymorphism, or snp. if you are reading a news story where it says, for example, scientists find the genetic contributors to diabetes or some other condition or trait, you're probably reading about snps. a snp is a one letter place where your genome varies from another genome sequence. Introduction. single nucleotide polymorphisms (snps), pronounced as “snips,” is the common type of variation found in dna between genes (genetics home reference). each snp differs by a single dna block represented as nucleotide. for example, a snp may be replaced by adenine (a) in place of guanine (g) in a stretch of dna. A single nucleotide polymorphism, or snp, is a single base pair difference in the dna sequence of individual members of a species; not necessarily a pathological mutation, but commonly studied as. In single nucleotide polymorphisms: methods and protocols, second edition, expert researchers explore the latest advances in this area, highlighting the substantial progress that has been made in snp genotyping, examining recent developments in high throughput genotyping approaches, and exploring our new understanding of the impact of snps on.

Comments are closed.