Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear
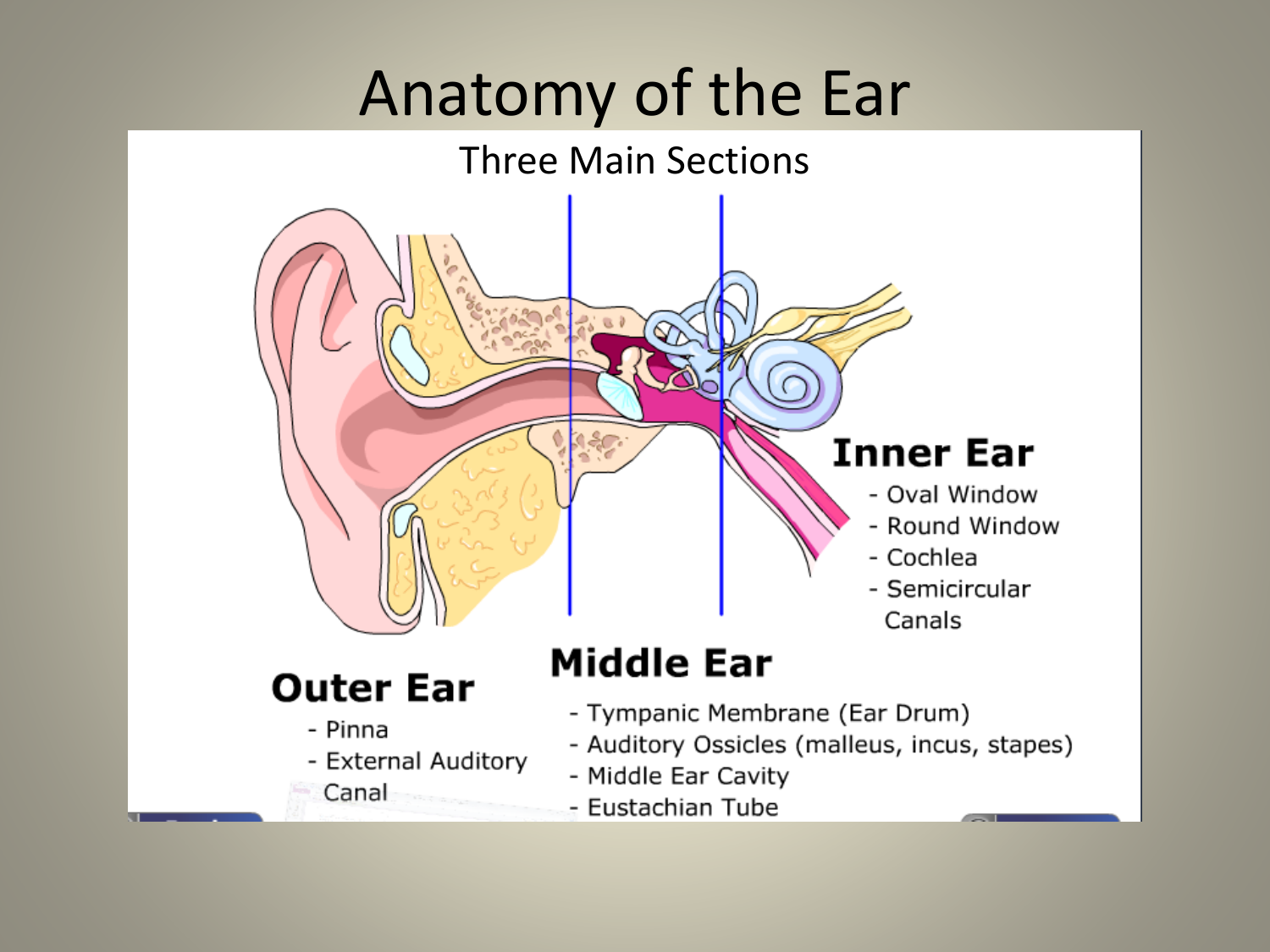
Anatomy Of The Ear The human ear is the organ of hearing and equilibrium. it detects and analyzes sound by the mechanism of transduction, which is the process of converting sound waves into electrochemical impulses. audition cannot take place adequately if the anatomy is abnormal. this article will discuss the mechanisms implied in the conduction of sound waves into the ear, and its integration and transmission. Learn about the external, middle, and internal ear, their structures, functions, and clinical relations. see diagrams, videos, and quizzes to test your knowledge of ear anatomy.
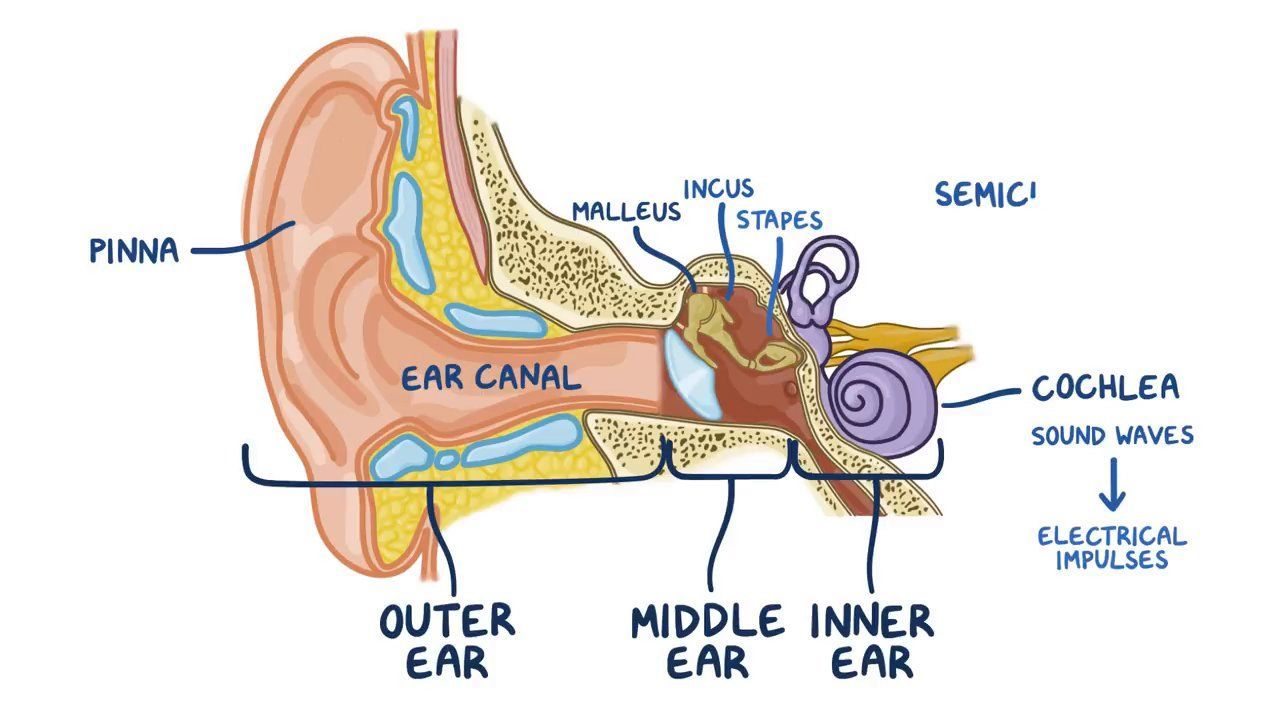
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear Osmosis Learn about the parts and functions of the ear, the organ of hearing and balance. find out how sound waves travel from the outer ear to the inner ear and how they are converted into electrical impulses. Your inner ear contains two main parts: the cochlea and the semicircular canals. your cochlea is the hearing organ. this snail shaped structure contains two fluid filled chambers lined with tiny hairs. when sound enters, the fluid inside of your cochlea causes the tiny hairs to vibrate, sending electrical impulses to your brain. Human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction and maintains the sense of balance. anatomically, the ear has three distinguishable parts: the outer, middle, and inner ear. learn about the anatomy and physiology of the human ear in this article. Human ear hearing, anatomy, physiology: hearing is the process by which the ear transforms sound vibrations in the external environment into nerve impulses that are conveyed to the brain, where they are interpreted as sounds. sounds are produced when vibrating objects, such as the plucked string of a guitar, produce pressure pulses of vibrating air molecules, better known as sound waves. the.

Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear Human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction and maintains the sense of balance. anatomically, the ear has three distinguishable parts: the outer, middle, and inner ear. learn about the anatomy and physiology of the human ear in this article. Human ear hearing, anatomy, physiology: hearing is the process by which the ear transforms sound vibrations in the external environment into nerve impulses that are conveyed to the brain, where they are interpreted as sounds. sounds are produced when vibrating objects, such as the plucked string of a guitar, produce pressure pulses of vibrating air molecules, better known as sound waves. the. The pinna, also called the auricle, is made up of cartilage that gives our ears their various shapes and sizes, and it also has a fleshy bit at the bottom called the ear lobe, or lobule. the pinna directs sound waves towards the opening of the ear canal. the ear canal, or the external acoustic meatus, is a short, curved tube that burrows. The ear is the organ of hearing and balance. the parts of the ear include: external or outer ear, consisting of: pinna or auricle. this is the outside part of the ear. external auditory canal or tube. this is the tube that connects the outer ear to the inside or middle ear. tympanic membrane (eardrum). the tympanic membrane divides the external.

Basic Anatomy Of The Ear The pinna, also called the auricle, is made up of cartilage that gives our ears their various shapes and sizes, and it also has a fleshy bit at the bottom called the ear lobe, or lobule. the pinna directs sound waves towards the opening of the ear canal. the ear canal, or the external acoustic meatus, is a short, curved tube that burrows. The ear is the organ of hearing and balance. the parts of the ear include: external or outer ear, consisting of: pinna or auricle. this is the outside part of the ear. external auditory canal or tube. this is the tube that connects the outer ear to the inside or middle ear. tympanic membrane (eardrum). the tympanic membrane divides the external.

Outer Ear Anatomy Outer Ear Infection Pain Causes Treatment

Comments are closed.