Anatomy Ear Overview

Human Ear Anatomy Parts Of Ear Structure Diagram And Ear Problems The ear is a complex part of an even more complex sensory system. it is situated bilaterally on the human skull, at the same level as the nose. the main functions of the ear are, of course, hearing, as well as constantly maintaining balance. the ear is anatomically divided into three portions: external ear. middle ear. The human ear picks up and interprets high frequency vibrations of air, while the sound sensing organs of aquatic animals are designed to pick up high frequency vibrations in water. most vertebrates have two ears: one on either side of the head. in some animals, including most mammals, the ear is also used for balance.

Instant Anatomy Head And Neck Areas Organs Ear General Overview The ear is a multifaceted organ that connects the central nervous system to the external head and neck. this structure as a whole can be thought of as 3 separate organs that work in a collective to coordinate certain functions, such as hearing and balance. any disharmony in this continuum may disrupt the ear's functionality. [1, 2, 3, 5] the. Your inner ear contains two main parts: the cochlea and the semicircular canals. your cochlea is the hearing organ. this snail shaped structure contains two fluid filled chambers lined with tiny hairs. when sound enters, the fluid inside of your cochlea causes the tiny hairs to vibrate, sending electrical impulses to your brain. The ear anatomy consists of three parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. the outer ear is the part you can see, including the flap of skin called the pinna and the tube like ear canal. the middle ear is inside your head, and there is a space called the middle ear. it has three tiny bones called ossicles and a cavity called the. Human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction and maintains the sense of balance. anatomically, the ear has three distinguishable parts: the outer, middle, and inner ear. learn about the anatomy and physiology of the human ear in this article.
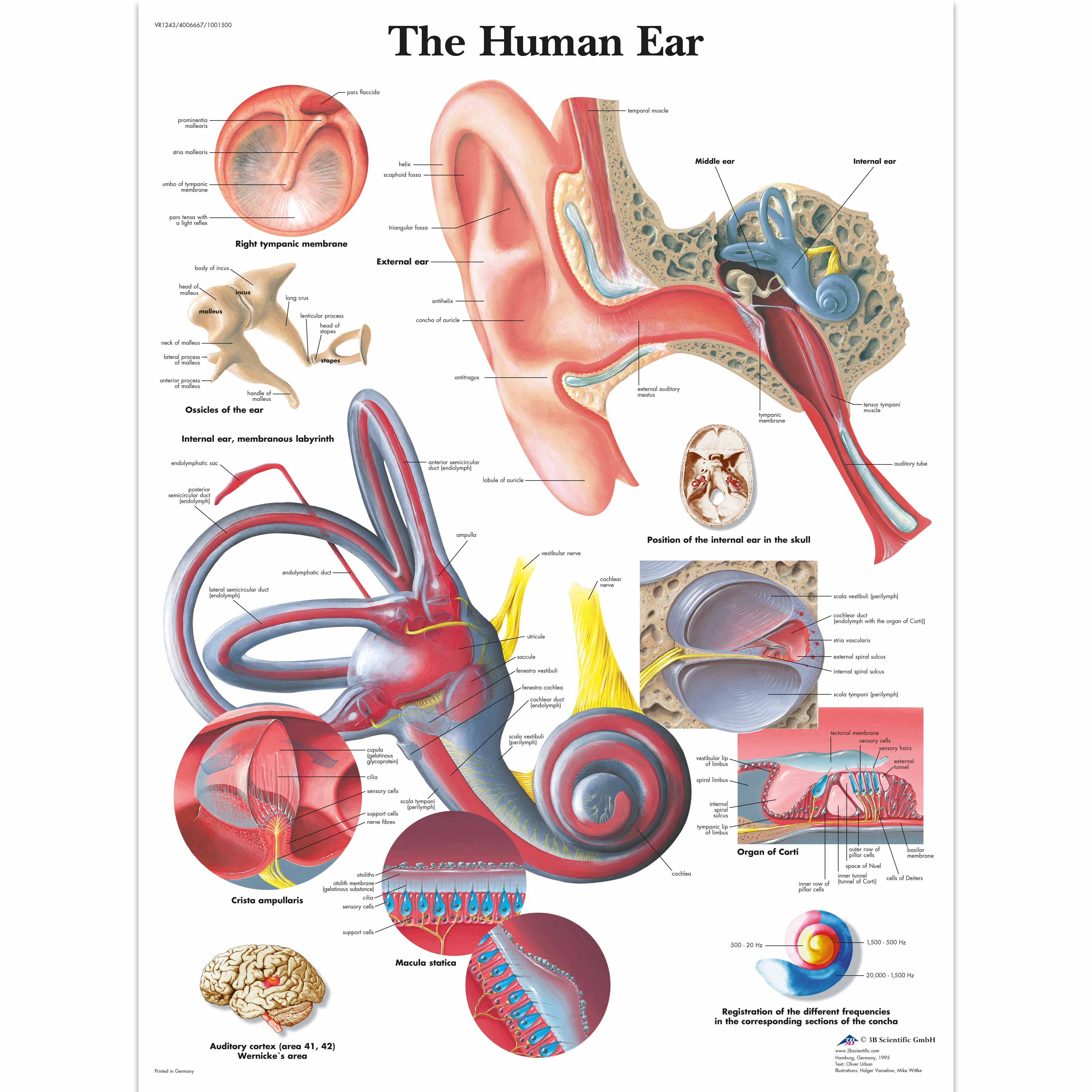
Anatomical Charts And Posters Anatomy Charts The Human Ear The ear anatomy consists of three parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. the outer ear is the part you can see, including the flap of skin called the pinna and the tube like ear canal. the middle ear is inside your head, and there is a space called the middle ear. it has three tiny bones called ossicles and a cavity called the. Human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction and maintains the sense of balance. anatomically, the ear has three distinguishable parts: the outer, middle, and inner ear. learn about the anatomy and physiology of the human ear in this article. Figure 1.anatomy of the external ear. 4 innervation of the auricle. the auricle has several sources of sensory innervation:. the superficial surface is supplied by the great auricular nerve and lesser occipital nerve, both of which are branches of the cervical plexus (c2 & c3), and the auriculotemporal branch of the mandibular nerve, which is a branch of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve v). Organs of human hearing are located on either side of the head. essential for hearing and balance, each ear has an intricate structure of bones, nerves, and muscles. the ears can be affected by bacterial infections, viral infections, hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), meniere’s disease, and more.

Human Ear Structure Function Parts Britannica Figure 1.anatomy of the external ear. 4 innervation of the auricle. the auricle has several sources of sensory innervation:. the superficial surface is supplied by the great auricular nerve and lesser occipital nerve, both of which are branches of the cervical plexus (c2 & c3), and the auriculotemporal branch of the mandibular nerve, which is a branch of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve v). Organs of human hearing are located on either side of the head. essential for hearing and balance, each ear has an intricate structure of bones, nerves, and muscles. the ears can be affected by bacterial infections, viral infections, hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), meniere’s disease, and more.

Parts Of The Ear Diagram Labeled

Comments are closed.