Antibodies Free Full Text Antibody Drug Conjugates As Cancer
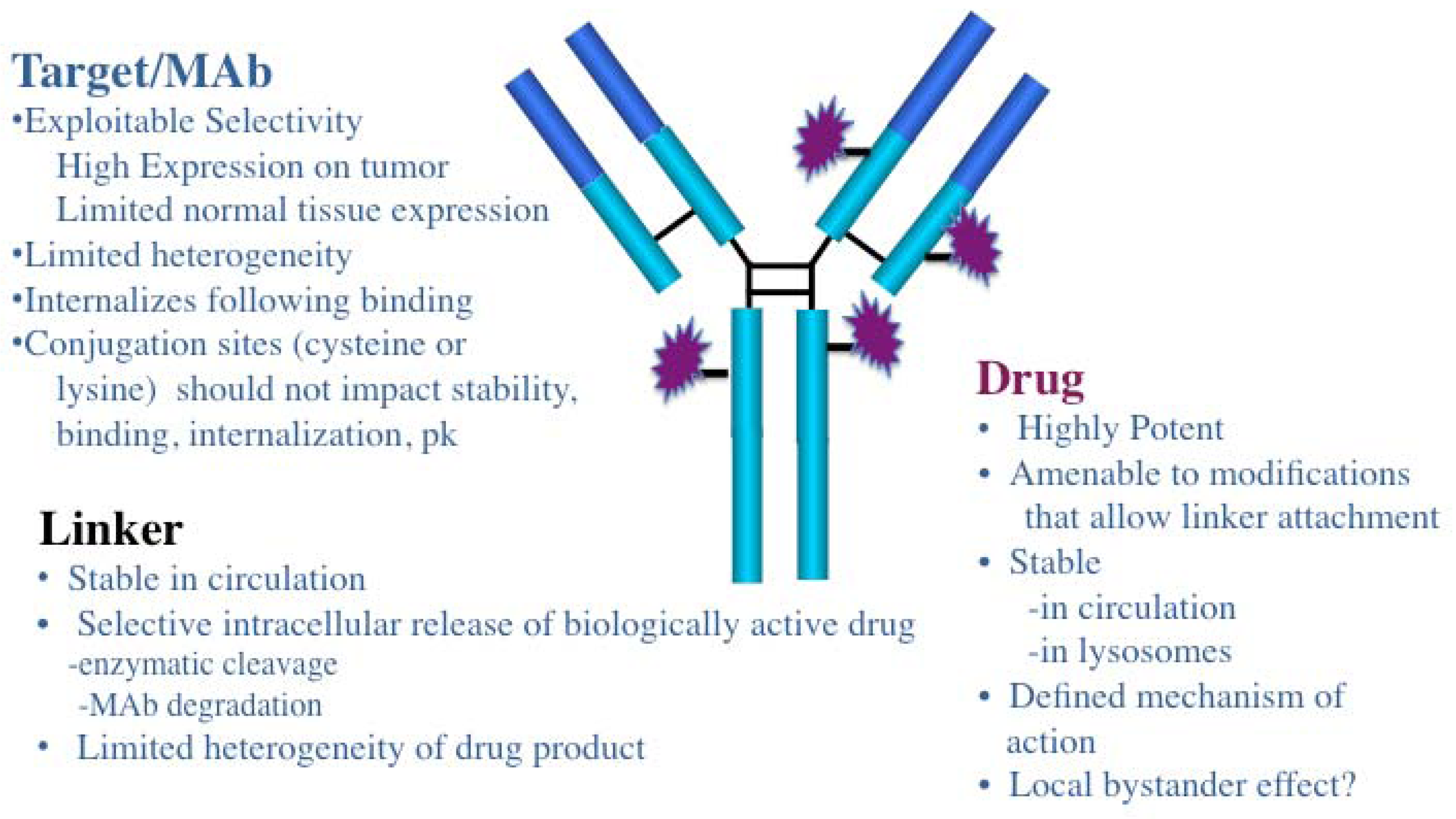
Antibodies Free Full Text Antibody Drug Conjugates As Cancer Monoclonal antibody (mab) based therapies have achieved considerable success in oncology, primarily when used in combination with cytotoxic drugs. antibody drug conjugates (adcs) are a class of therapeutics that harness the antigen selectivity of mabs to deliver highly potent cytotoxic drugs to antigen expressing tumor cells. the use of mab directed delivery can confer a therapeutic index to. A promising molecular target for aggressive cancers is the urokinase receptor (upar). a fully human, recombinant antibody that binds upar to form a stable complex that blocks upa upar interactions (2g10) and is internalized primarily through endocytosis showed efficacy in a mouse xenograft model of highly aggressive, triple negative breast cancer (tnbc). antibody drug conjugates (adcs) of 2g10.
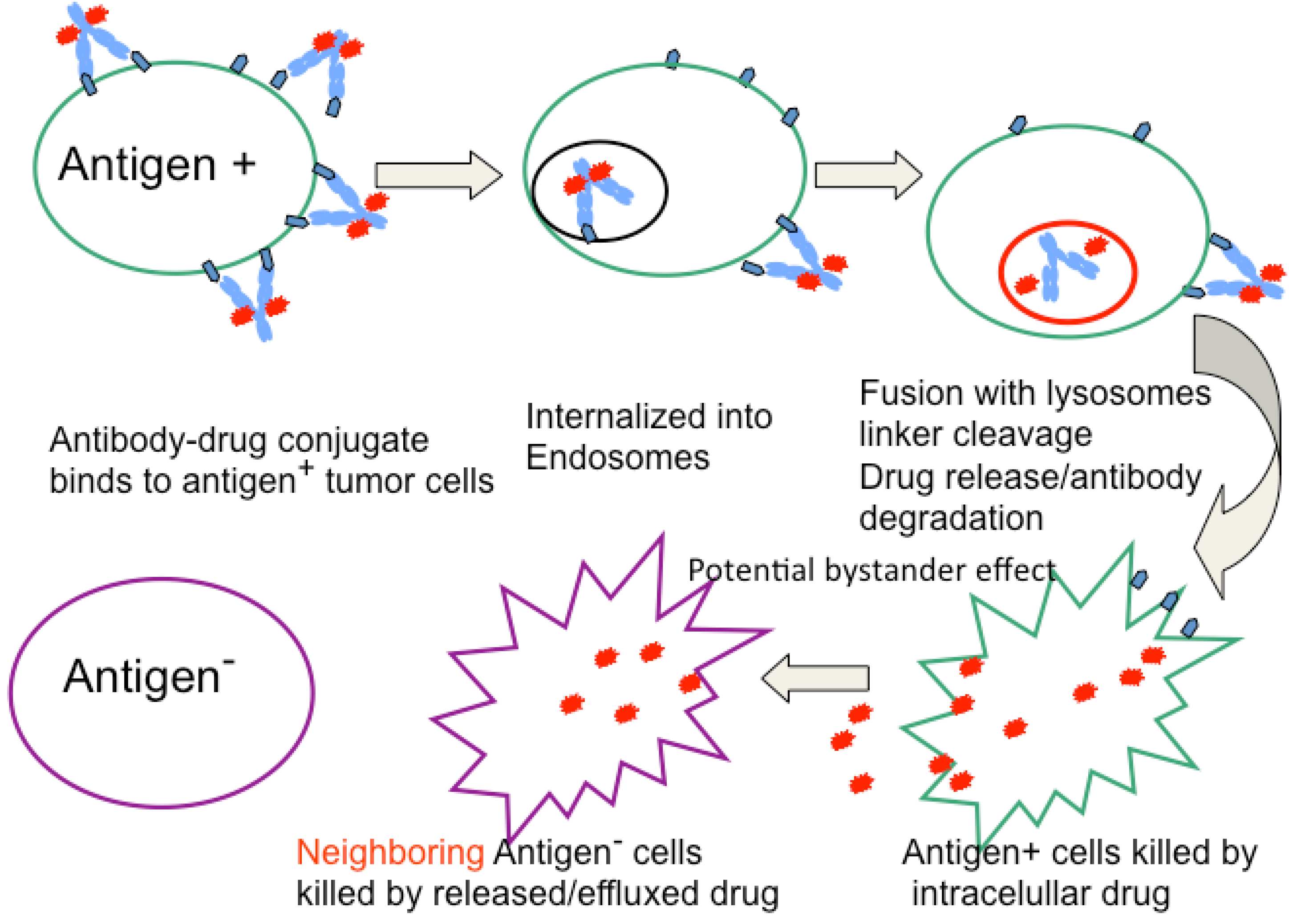
Antibodies Free Full Text Antibody Drug Conjugates As Cancer Learn how antibody drug conjugates, or "biological missiles", target and kill cancer cells with high specificity and potency in this review article. Abstract. antibody–drug conjugates (adcs) are a promising cancer treatment modality that enables the selective delivery of highly cytotoxic payloads to tumours. however, realizing the full. Antibody–drug conjugates (adcs) constitute a rapidly expanding category of biopharmaceuticals that are reshaping the landscape of targeted chemotherapy. the meticulous process of selecting therapeutic targets, aided by specific monoclonal antibodies’ high specificity for binding to designated antigenic epitopes, is pivotal in adc research and development. despite adcs’ intrinsic ability. Bauzon, m. et al. maytansine bearing antibody–drug conjugates induce in vitro hallmarks of immunogenic cell death selectively in antigen positive target cells. oncoimmunology 8, e1565859 (2019.

Biomedicines Free Full Text Antibodyвђ Drug Conjugates For Ca Antibody–drug conjugates (adcs) constitute a rapidly expanding category of biopharmaceuticals that are reshaping the landscape of targeted chemotherapy. the meticulous process of selecting therapeutic targets, aided by specific monoclonal antibodies’ high specificity for binding to designated antigenic epitopes, is pivotal in adc research and development. despite adcs’ intrinsic ability. Bauzon, m. et al. maytansine bearing antibody–drug conjugates induce in vitro hallmarks of immunogenic cell death selectively in antigen positive target cells. oncoimmunology 8, e1565859 (2019. Antibody drug conjugates (adcs) provide effective cancer treatment through the selective delivery of cytotoxic payloads to the cancer cells. they offer unparalleled precision and specificity in directing drugs to cancer cells while minimizing off target effects. despite several advantages, there is a requirement for innovations in the molecular. Antibody–drug conjugates (adcs) are immunoconjugates comprised of a monoclonal antibody tethered to a cytotoxic drug (known as the payload) via a chemical linker. the adc is designed to selectively deliver the ultratoxic payload directly to the target cancer cells. to date, five adcs have received market approval and over 100 are being investigated in various stages of clinical development.
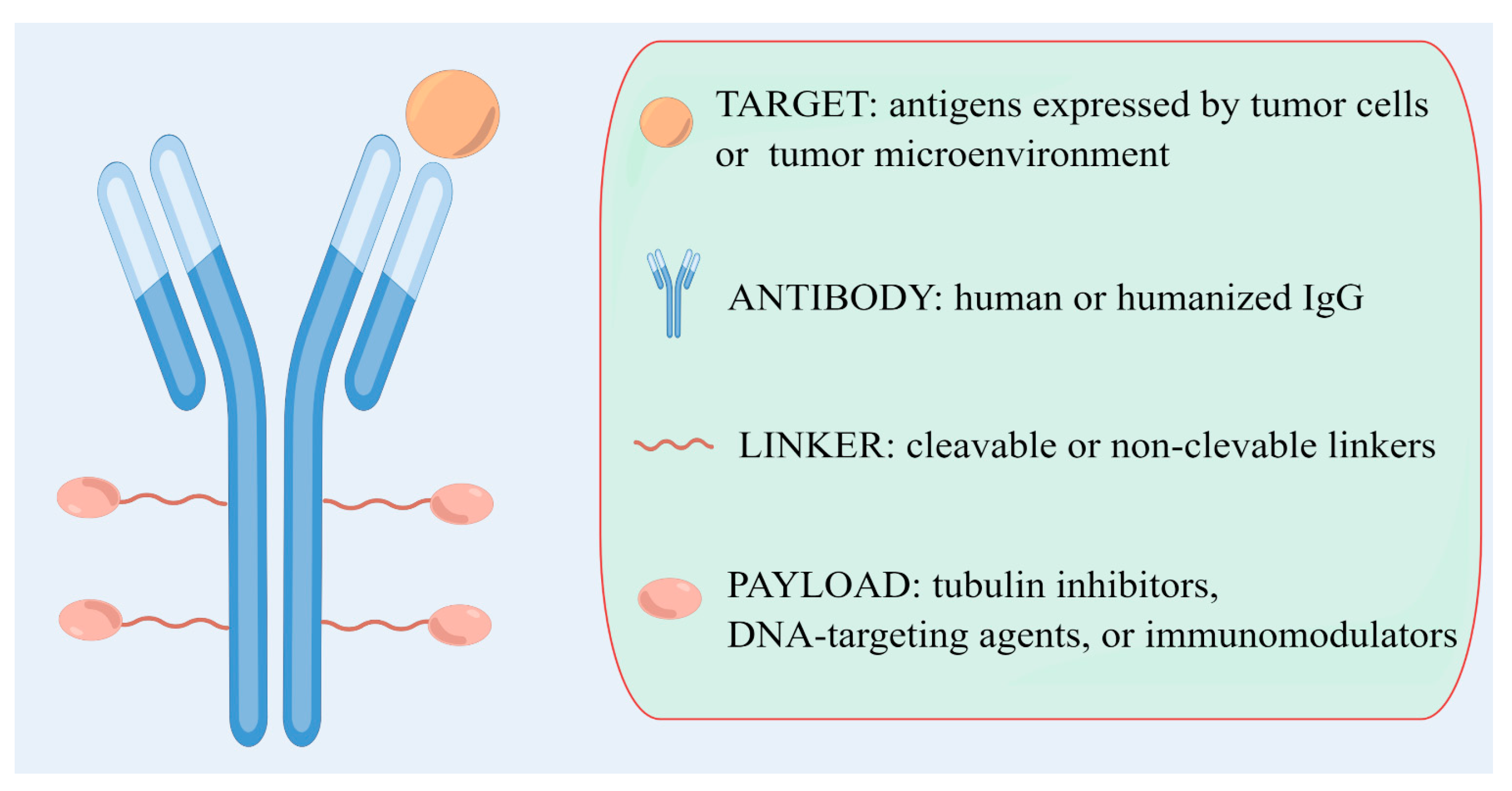
Ijms Free Full Text Antibody Drug Conjugates For Breast Cance Antibody drug conjugates (adcs) provide effective cancer treatment through the selective delivery of cytotoxic payloads to the cancer cells. they offer unparalleled precision and specificity in directing drugs to cancer cells while minimizing off target effects. despite several advantages, there is a requirement for innovations in the molecular. Antibody–drug conjugates (adcs) are immunoconjugates comprised of a monoclonal antibody tethered to a cytotoxic drug (known as the payload) via a chemical linker. the adc is designed to selectively deliver the ultratoxic payload directly to the target cancer cells. to date, five adcs have received market approval and over 100 are being investigated in various stages of clinical development.

Comments are closed.