Antibody Structure
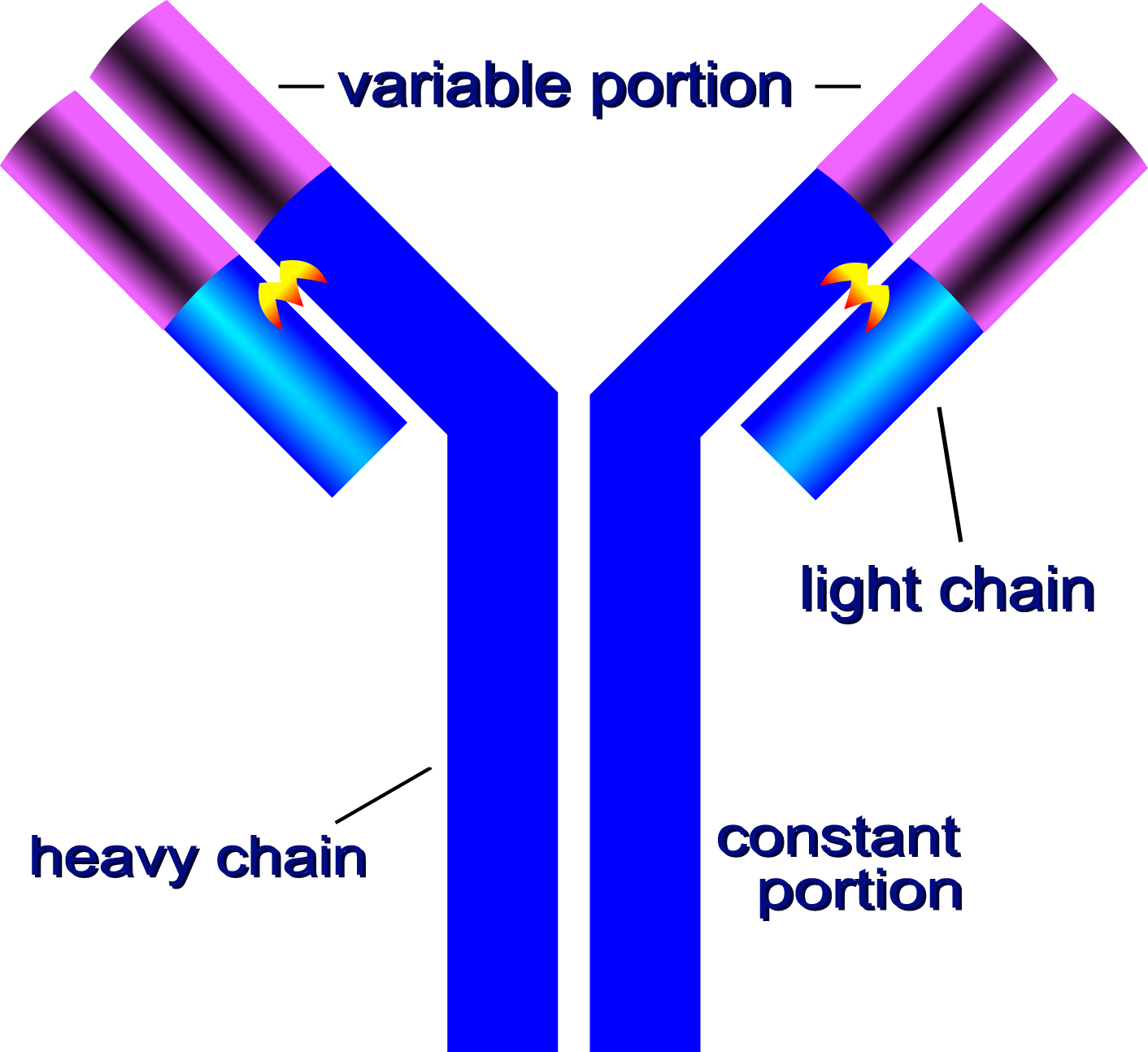
Label The Diagram Of An Antibody Structure Antibodies are y shaped proteins that bind to specific antigens and trigger immune responses. learn about their structure, function, classes, subclasses, and how they are produced and regulated by b cells. Antibodies are protective proteins produced by b cells in response to antigens. learn how antibodies work, how they are structured, and how they differ in function and type.

Monoclonal Antibody Definition Hybridoma Human Monoclonal The igg antibody molecule is made up of four polypeptide chains, comprising two identical light chains and two identical heavy chains, and can be thought of as forming a flexible y shaped structure. each of the four chains has a variable (v) region at its amino terminus, which contributes to the antigen binding site, and a constant (c) region. Learn about antibodies, protein molecules produced by b lymphocytes that recognize and bind to antigens. explore their forms, structure, functions, isotypes, and applications in immunology and research. The general features of antibodies described below will focus on the igg1 framework. our knowledge of how antibody structure relates to function is being exploited to create antibodies and antibody related biologics with the appropriate functional and biophysical properties to address specific therapeutic needs. Antibodies are immune system related proteins called immunoglobulins. each antibody consists of four polypeptides– two heavy chains and two light chains joined to form a "y" shaped molecule. the amino acid sequence in the tips of the "y" varies greatly among different antibodies. this variable region, composed of 110 130 amino acids, give the.

Comments are closed.