Arterial Blood Gas Abg Interpretation вђў Ag Non Ag Grepmed

Arterial Blood Gas Abg Interpretation вђў Ag Non Ag Anion gap formula: na – (cl – hco 3–) the anion gap (ag) is a derived variable primarily used for the evaluation of metabolic acidosis to determine the presence of unmeasured anions (e.g. albumin is the main unmeasured anion). the normal anion gap varies with different assays but is typically between 4 to 12 mmol l. Interpreting an arterial blood gas (abg) involves a step by step approach to make accurate and timely clinical decisions. the simplified steps for abg interpretation include: collect and run an arterial blood sample. determine if the ph is alkalosis or acidosis. determine if the issue is respiratory or metabolic.
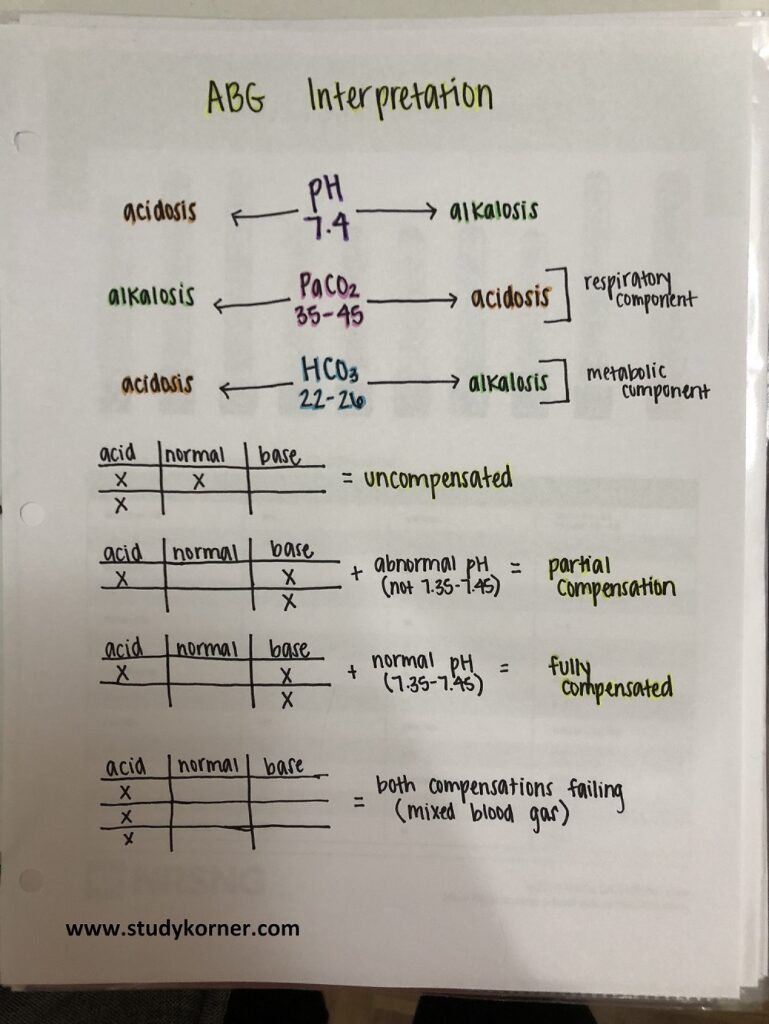
Arterial Blood Gas Abg Interpretation Made Easy Chart Studypk The aforementioned components all have different normal values and represent different aspects of the blood gas. according to the national institute of health, typical normal values are: ph: 7.35 7.45. partial pressure of oxygen (pao2): 75 to 100 mmhg. partial pressure of carbon dioxide (paco2): 35 45 mmhg. bicarbonate (hco3): 22 26 meq l. Interpreting an arterial blood gas (abg) is a crucial skill for physicians, nurses, respiratory therapists, and other health care personnel. abg interpretation is especially important in critically ill patients. the following six step process helps ensure a complete interpretation of every abg. in addition, you will find tables that list. Introduction. an arterial blood gas (abg) is a test that measures the oxygen tension (pao 2), carbon dioxide tension (paco 2), acidity (ph), oxyhemoglobin saturation (sao 2), and bicarbonate (hco 3) concentration in arterial blood. some blood gas analyzers also measure the methemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin, and hemoglobin levels. They are easy to remember: for ph, the normal range is 7.35 to 7.45. for paco 2, the normal range is 35 to 45. for hco 3, the normal range is 22 to 26. normal blood ph scale diagram for the tic tac toe method for abg analysis. the recommended way of memorizing it is by drawing the diagram of normal values above.
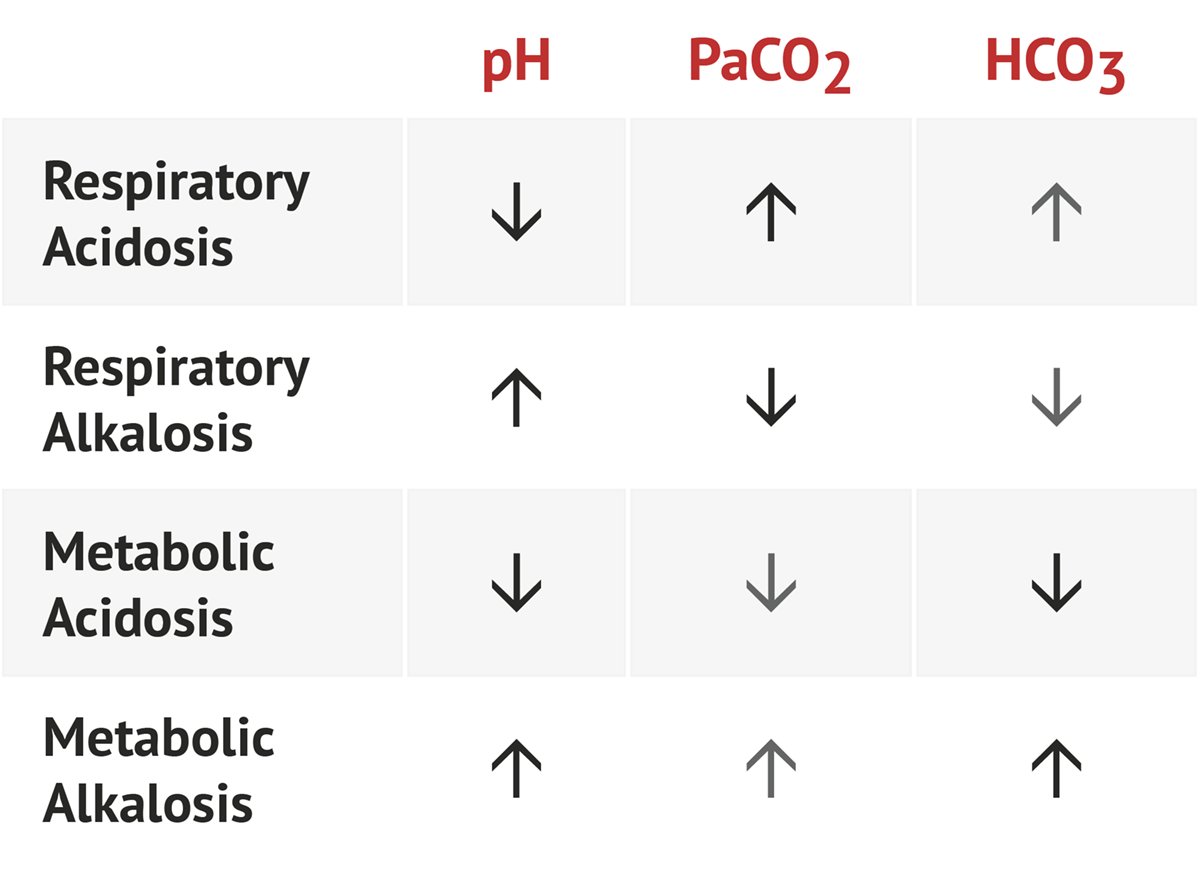
Arterial Blood Gas Interpretation Medschool Introduction. an arterial blood gas (abg) is a test that measures the oxygen tension (pao 2), carbon dioxide tension (paco 2), acidity (ph), oxyhemoglobin saturation (sao 2), and bicarbonate (hco 3) concentration in arterial blood. some blood gas analyzers also measure the methemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin, and hemoglobin levels. They are easy to remember: for ph, the normal range is 7.35 to 7.45. for paco 2, the normal range is 35 to 45. for hco 3, the normal range is 22 to 26. normal blood ph scale diagram for the tic tac toe method for abg analysis. the recommended way of memorizing it is by drawing the diagram of normal values above. An arterial blood gas (abg) test is a blood test that requires a sample from an artery in your body to measure the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your blood. the test also checks the balance of acids and bases, known as the ph balance, in your blood. your body normally tightly regulates the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your. Instructions. this analyzer should not substitute for clinical context. sodium and chloride are required for anion gap calculation. note: normal albumin levels are typically 4 g dl in us units and 40 g l in si units.

Arterial Blood Gases Abg Interpretation A Simplified Approach Ppt An arterial blood gas (abg) test is a blood test that requires a sample from an artery in your body to measure the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your blood. the test also checks the balance of acids and bases, known as the ph balance, in your blood. your body normally tightly regulates the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your. Instructions. this analyzer should not substitute for clinical context. sodium and chloride are required for anion gap calculation. note: normal albumin levels are typically 4 g dl in us units and 40 g l in si units.

Comments are closed.