Atomic Radius Basic Introduction Periodic Table Trends Chemistry
.PNG)
Periodic Trends Presentation Chemistry This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into atomic radius which is one of the four main periodic table trends you need to know. atomic. The atomic radius is defined as one half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together. figure 6.15.2 6.15. 2: the atomic radius (r) (r) of an atom can be defined as one half the distance (d) (d) between two nuclei in a diatomic molecule.

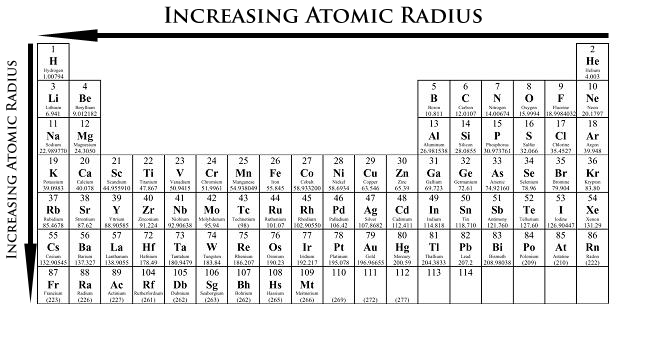
Atomic Radius Basic Introduction Periodic Table Trends Chemistry Periodic trends are specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of a certain element, including its size and its electronic properties. major periodic trends include: electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radius, melting point, and metallic character. The atomic radius is defined as one half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together. the units for atomic radii are picometers, equal to 10−12 10 − 12 meters. as an example, the internuclear distance between the two hydrogen atoms in an h2 h 2 molecule is measured to be 74pm 74 pm. Many periodic trends are general. there may be a few points where an opposite trend is seen, but there is an overall trend when considered across a whole row or down a whole column of the periodic table. atomic radii. the atomic radius is an indication of the size of an atom. although the concept of a definite radius of an atom is a bit fuzzy. The organization of the periodic table shows the periodic trends of six different physical properties of the elements: atomic radius, electron affinity, electronegativity, ionization energy, and metallic nonmetallic character. atomic radius is half the distance between two identical atoms touching each other. atomic radius increases as you move.
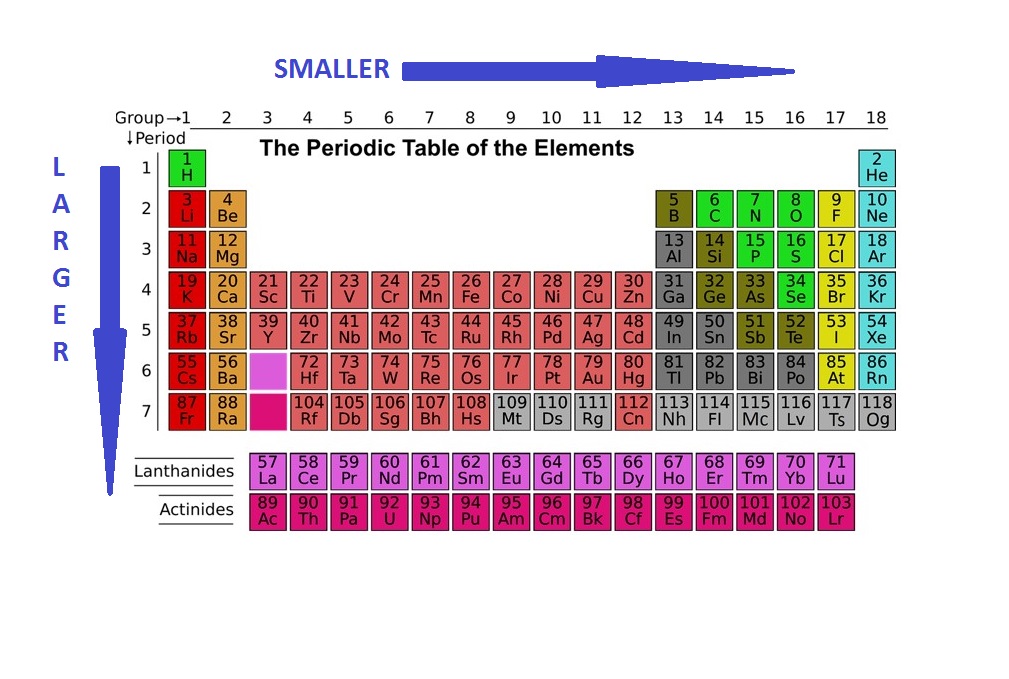
Atomic Radius Periodic Table Trend Cabinets Matttroy Many periodic trends are general. there may be a few points where an opposite trend is seen, but there is an overall trend when considered across a whole row or down a whole column of the periodic table. atomic radii. the atomic radius is an indication of the size of an atom. although the concept of a definite radius of an atom is a bit fuzzy. The organization of the periodic table shows the periodic trends of six different physical properties of the elements: atomic radius, electron affinity, electronegativity, ionization energy, and metallic nonmetallic character. atomic radius is half the distance between two identical atoms touching each other. atomic radius increases as you move. Period trends. there are many trends on the periodic table. for example, ionization energy, electronegativity, and of course atomic radius which we will discuss now. across a period, atomic radii decrease. this is because while the number of electrons increases down the period, they only add to the same main energy level, and therefore do not. Atomic radius trend 1: atomic radii decrease from left to right across a period. the first atomic radius periodic trend is that atomic size decreases as you move left to right across a period. within a period of elements, each new electron is added to the same shell. when an electron is added, a new proton is also added to the nucleus, which.
/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)
Atomic Radius Periodic Table Electronegativity Periodic Table Ti Period trends. there are many trends on the periodic table. for example, ionization energy, electronegativity, and of course atomic radius which we will discuss now. across a period, atomic radii decrease. this is because while the number of electrons increases down the period, they only add to the same main energy level, and therefore do not. Atomic radius trend 1: atomic radii decrease from left to right across a period. the first atomic radius periodic trend is that atomic size decreases as you move left to right across a period. within a period of elements, each new electron is added to the same shell. when an electron is added, a new proton is also added to the nucleus, which.
Periodic Trends Chemistry Libretexts

Comments are closed.