Audio Bit Depth And Sample Rate Explained

Sample Rate And Bit Depth Explained Digital Audio Hsr The bit depth shows the number of possible amplitude values in a sample. you can calculate the number of possible amplitude values of a given bit depth. this is done using equation 2 to the power of n (substitute n with the bit depth). using the equation; a bit depth of 16 will be 2^16 = 65536 possible values. A higher sample rate, measured in hertz (hz), allows for a greater number of samples per second. this means that more accurate representations of sound waves are captured, resulting in a more detailed and refined audio signal. on the other hand, bit depth, measured in bits, determines the number of possible values each sample can take.
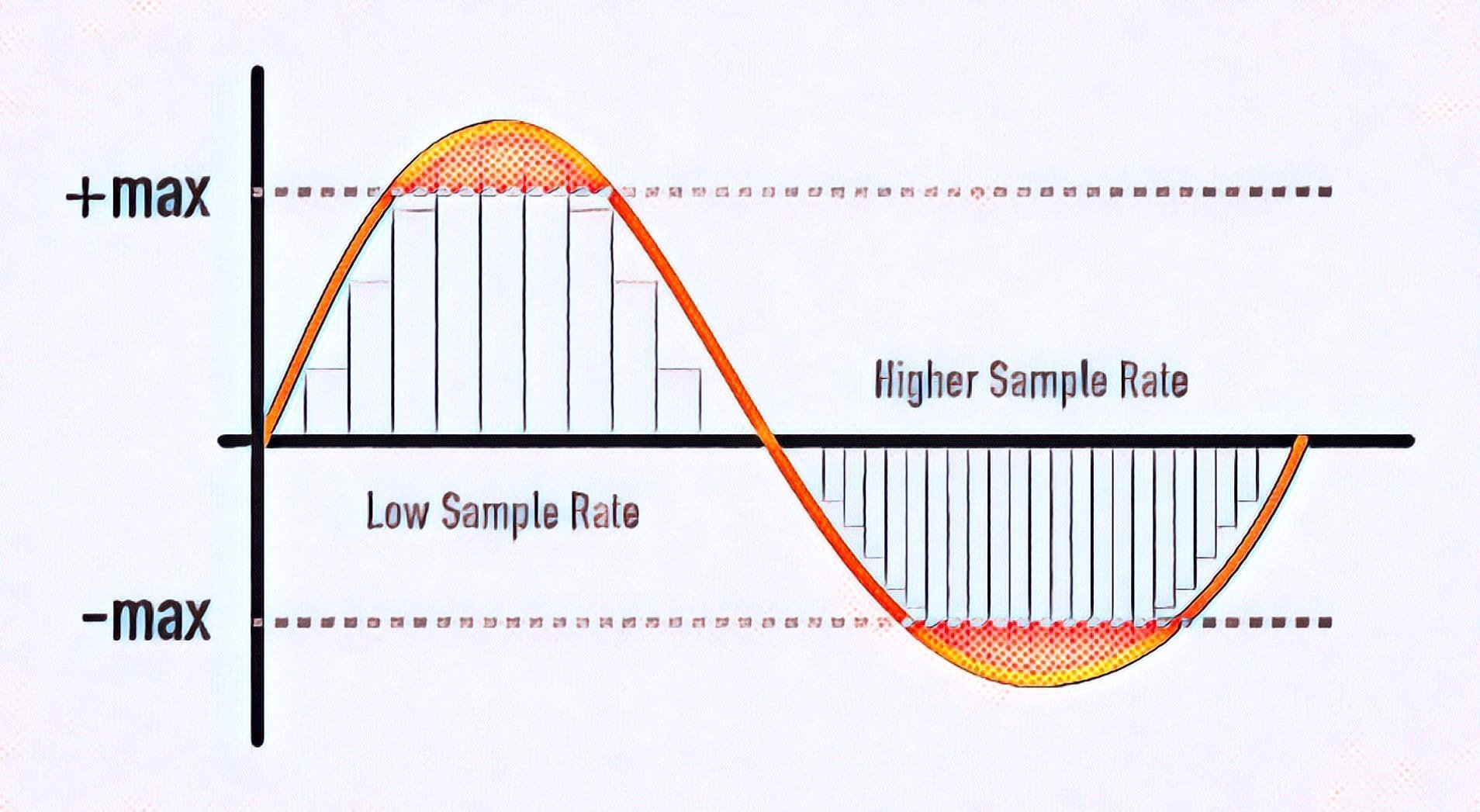
Understanding Sample Rate Bit Depth And Bit Rate Headphonesty The audio sample rate is measured in kilohertz (khz) and it determines the range of frequencies captured in digital audio. in most daws, you’ll find an adjustable sample rate in your audio preferences. this controls the sample rate for audio in your project. the options you see in the average daw—44.1 khz, 48 khz—may seem a bit random. A bit depth of 16 bit for a sample rate of 44.1khz is enough to reproduce the audible frequency and dynamic range for the average person, which is why it became the standard cd format. should you always record in 192khz 24 bit? although there are no limits to sample rate and bit depth, 192khz 24 bit is the gold standard for hi res audio. (there. In digital audio, a bit is a binary unit of information that can have a value of either 0 or 1. the bit depth determines the number of possible amplitude values that can be assigned to each sample. the higher the bit depth, the greater the resolution and dynamic range of the audio. common bit depths used in music production and podcasting range. Sample rate reveals how many times per second an analog audio signal was sampled (on a horizontal axis). nyquist frequency theorem states that to sample a song accurately, you must use twice the highest frequency for the sample rate. bit depth determines how close samples are placed on an analog signal (on a vertical axis).

Sample Rate And Bit Depth Explained Digital Audio Hsr In digital audio, a bit is a binary unit of information that can have a value of either 0 or 1. the bit depth determines the number of possible amplitude values that can be assigned to each sample. the higher the bit depth, the greater the resolution and dynamic range of the audio. common bit depths used in music production and podcasting range. Sample rate reveals how many times per second an analog audio signal was sampled (on a horizontal axis). nyquist frequency theorem states that to sample a song accurately, you must use twice the highest frequency for the sample rate. bit depth determines how close samples are placed on an analog signal (on a vertical axis). Sample rate deals with the audio clarity, whereas the bit depth deals with the amount of noise in the audio. circling back, each sample is assigned a sequence of binary digits by the adc. the number of binary digits per sample is called the bit depth. the adc assigns each sample the binary digits based on the amplitude of the audio (the. Sample rate refers to the number of times an audio signal is sampled per second, usually measured in hertz (hz) or kilohertz (khz). consider sample rate as the speed of a camera's shutter, capturing multiple images in a brief period. in the audiophile community, this metric is crucial because it directly affects the range of frequencies that.

Digital Audio Basics Sample Rate And Bit Depth Presonus Sample rate deals with the audio clarity, whereas the bit depth deals with the amount of noise in the audio. circling back, each sample is assigned a sequence of binary digits by the adc. the number of binary digits per sample is called the bit depth. the adc assigns each sample the binary digits based on the amplitude of the audio (the. Sample rate refers to the number of times an audio signal is sampled per second, usually measured in hertz (hz) or kilohertz (khz). consider sample rate as the speed of a camera's shutter, capturing multiple images in a brief period. in the audiophile community, this metric is crucial because it directly affects the range of frequencies that.

Comments are closed.