Average And Marginal Propensities To Save And Consume
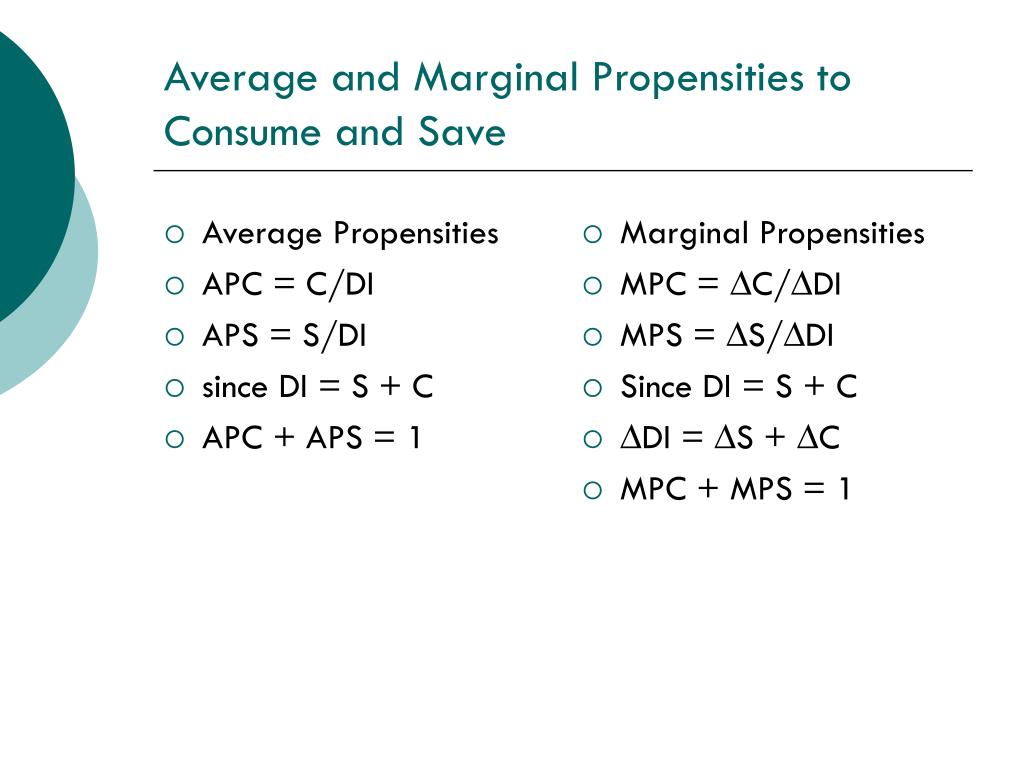
Ppt Basic Macroeconomic Relationships Powerpoint Presentation Free The marginal propensity to save is calculated by dividing the change in savings by the change in income. for example, if consumers saved 20 cents for every $1 increase in income, the mps would be. If you decide to spend $400 of this marginal increase on a new business suit and save the remaining $100, your marginal propensity to save is 0.2. this is calculated by dividing the $100 change in.

Average And Marginal Propensities To Save And Consume Youtube The nation's aps is calculated to be 0.60, or $300 billion $500 billion. this indicates the economy allocated 60% of its disposable income to savings. the average propensity to consume is. An individual’s propensity to consume is calculated as follows: average propensity to consume = $40,000 $70,000 = 0.571. although the average propensity can explain the past consumption pattern of a household, finding out how consumption is affected by any increase in income is determined using the marginal propensity to consume. it makes. The marginal propensity to consume (mpc) measures the proportion of extra income that is spent on consumption. for example, if an individual gains an extra £10, and spends £7.50, then the marginal propensity to consume will be £7.5 10 = 0.75. the mpc will invariably be between 0 and 1. the marginal propensity to consume measures the change. The marginal propensity to consume is measured as the ratio of the change in consumption to the change in income, thus giving us a figure between 0 and 1. the mpc can be more than one if the subject borrowed money or dissaved to finance expenditures higher than their income. the mpc can also be less than zero if an increase in income leads to a.
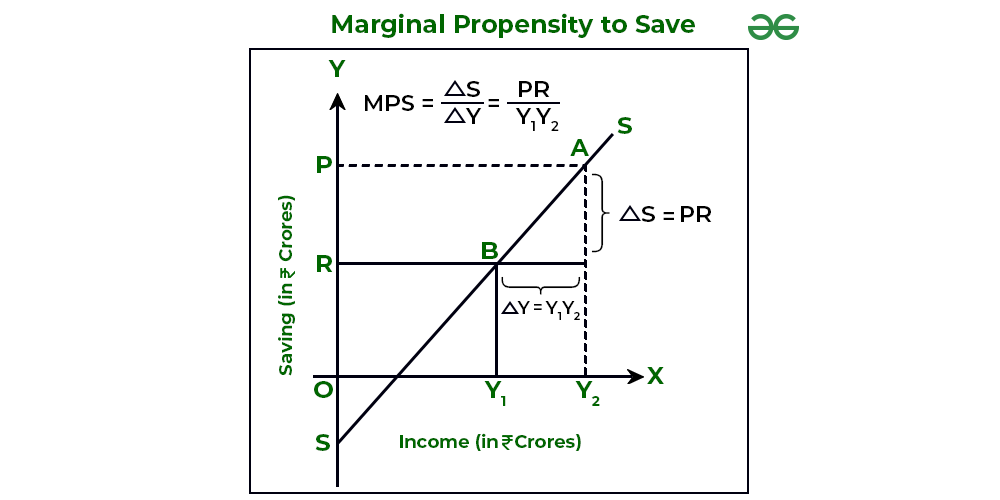
Types Of Propensities To Save Geeksforgeeks The marginal propensity to consume (mpc) measures the proportion of extra income that is spent on consumption. for example, if an individual gains an extra £10, and spends £7.50, then the marginal propensity to consume will be £7.5 10 = 0.75. the mpc will invariably be between 0 and 1. the marginal propensity to consume measures the change. The marginal propensity to consume is measured as the ratio of the change in consumption to the change in income, thus giving us a figure between 0 and 1. the mpc can be more than one if the subject borrowed money or dissaved to finance expenditures higher than their income. the mpc can also be less than zero if an increase in income leads to a. Average propensity to consume (apc) (as well as the marginal propensity to consume) is a concept developed by john maynard keynes to analyze the consumption function, which is a formula where total consumption expenditures (c) of a household consist of autonomous consumption (c a) and income (y) (or disposable income (y d)) multiplied by marginal propensity to consume (c 1 or mpc). The marginal propensity to save (mps) is calculated by dividing the change in saving by the change in income. mps = change in saving (Δs) change in income (Δy) for example, a person's mps would be 0.2, or 20%, if their income and savings rose by $100 and $20, respectively. an example schedule to demonstrate the calculation of mps:.

Average Propensity To Consume What Is It Formula Calculate Average propensity to consume (apc) (as well as the marginal propensity to consume) is a concept developed by john maynard keynes to analyze the consumption function, which is a formula where total consumption expenditures (c) of a household consist of autonomous consumption (c a) and income (y) (or disposable income (y d)) multiplied by marginal propensity to consume (c 1 or mpc). The marginal propensity to save (mps) is calculated by dividing the change in saving by the change in income. mps = change in saving (Δs) change in income (Δy) for example, a person's mps would be 0.2, or 20%, if their income and savings rose by $100 and $20, respectively. an example schedule to demonstrate the calculation of mps:.

Comments are closed.