Basic Simple Human Cell Diagram
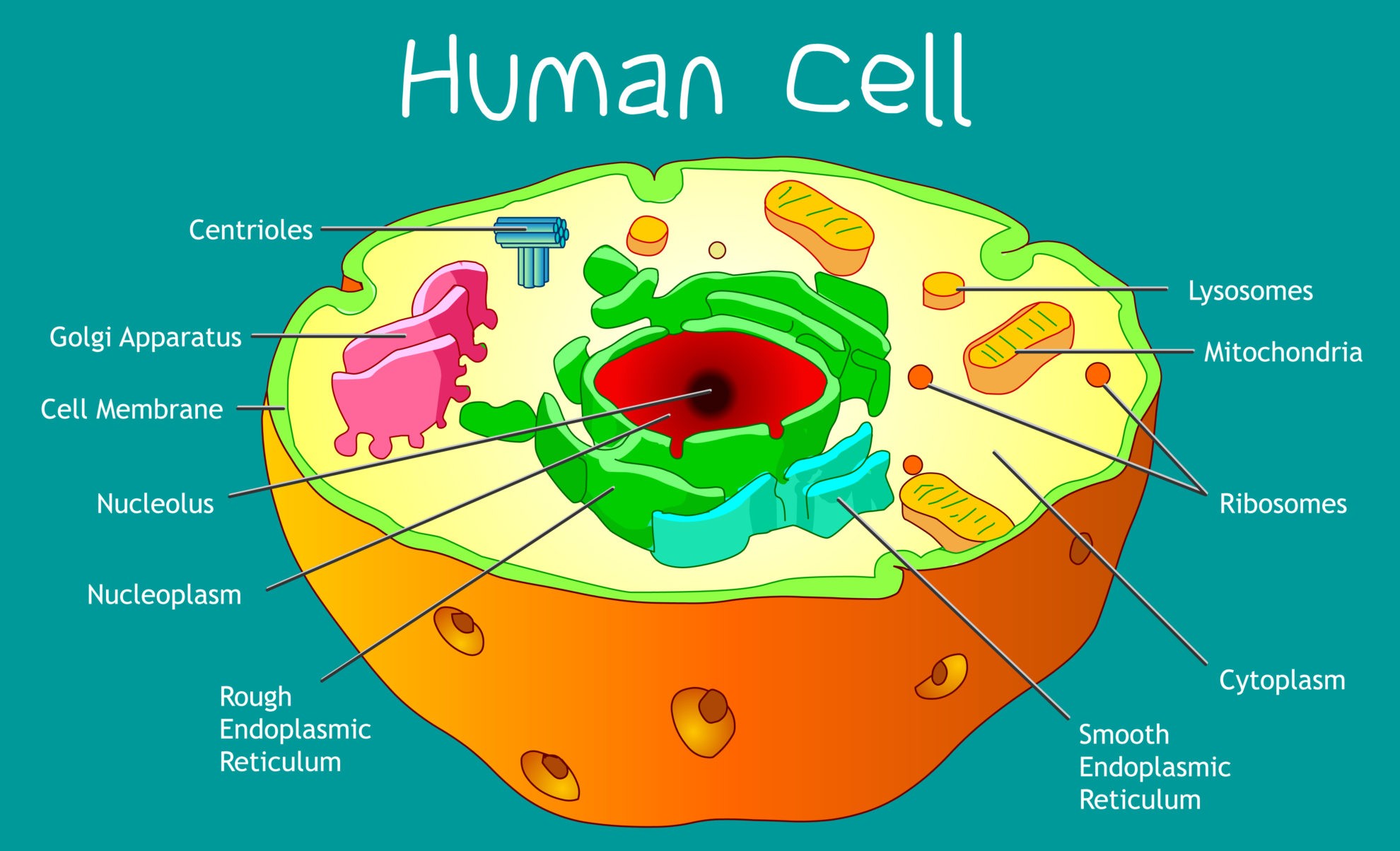
Simple Human Cell Diagram Figure 4.1.2 4.1. 2 phospholipids form the basic structure of a cell membrane. hydrophobic tails of phospholipids are facing the core of the membrane, avoiding contact with the inner and outer watery environment. hydrophilic heads are facing the surface of the membrane in contact with intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid. Human cell diagram, parts, pictures, structure and functions. the cell is the basic functional in a human meaning that it is a self contained and fully operational living entity. humans are multicellular organisms with various different types of cells that work together to sustain life. other non cellular components in the body include water.
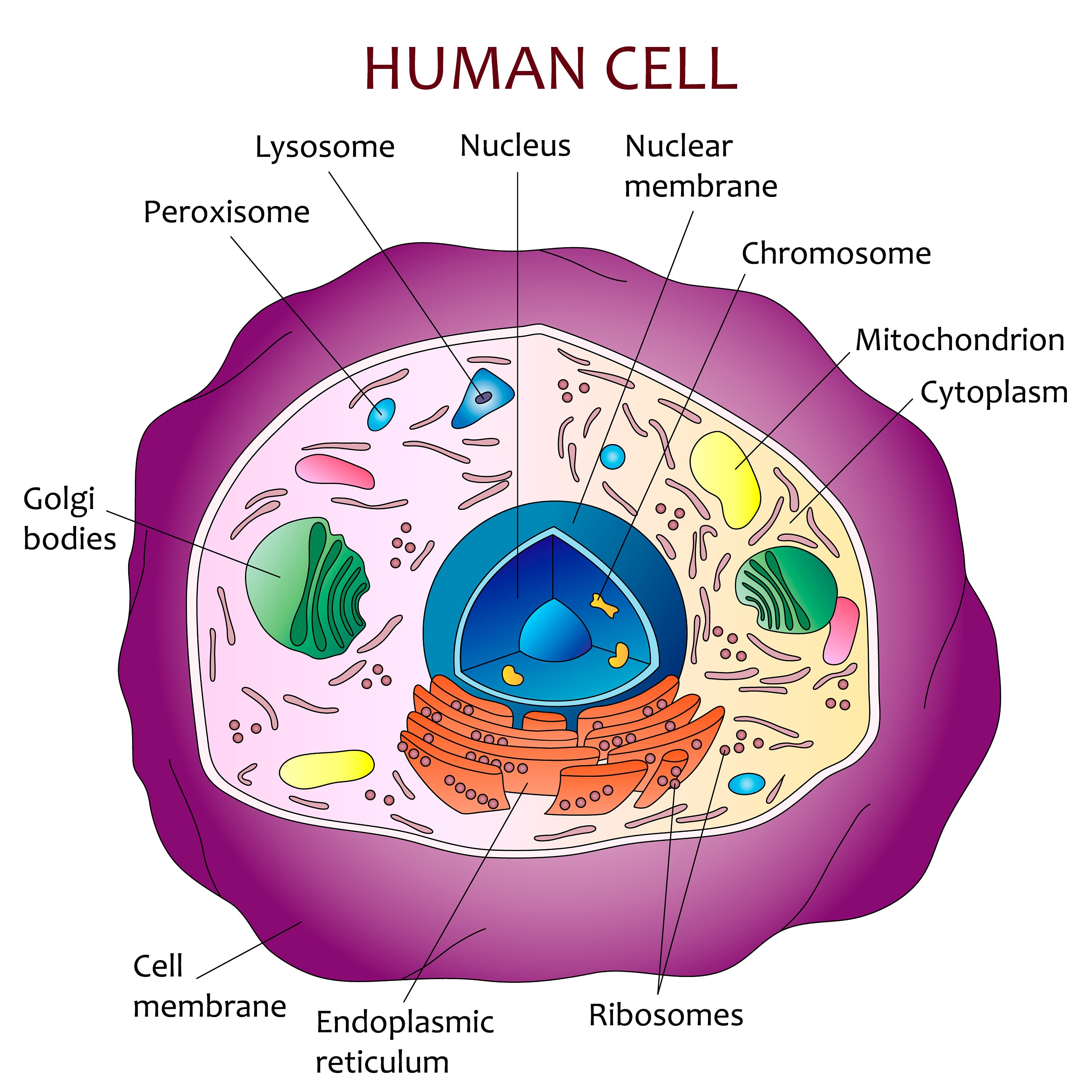
Basic Human Cell Diagram The nucleus is a large organelle that contains the cell’s genetic information. the nucleolus is the largest structure within a nucleus, and contains a cluster of protein and ribonucleic acid (rna). it is involved with ribosome formation and the ribosomal rna synthesis. nucleolus fun fact #1: most cells have at least one nucleus, and some. The nucleus is a large organelle that contains the cell’s genetic information. most cells have only one nucleus, but some have more than one, and others—like mature red blood cells—don’t have one at all. within the nucleus is a spherical body known as the nucleolus, which contains clusters of protein, dna, and rna. It is semisolid, which aids in the movement of the cell organs to other places. it contains four molecules: carbohydrates, proteins phospholipids, and cholesterol. the functions of the cell membranes are: it protects the cell. it regulates the exchange of substances in and out of the cell. (1, 2, 3) diagram 2: the human cell membrane. Learning objectives. at the end of this unit, you should be able to: i. specify the characteristics associated with life and explain why the cell is the basic unit of life. ii. describe the levels of structural organization in the body. iii. describe the structure and the functions of the major components of a cell. iv.

Comments are closed.