Blood Buffer System

Buffer Action In The Blood Youtube Learn how blood maintains its ph between 7.35 and 7.45 using carbonic acid and bicarbonate anion as a buffer system. explore the effects of o2 and co2 on blood buffer and other biological buffers in research. Learn how blood buffers resist dramatic ph changes by using weak acids and bases. explore the composition, capacity and examples of blood buffers and their role in maintaining homeostasis.
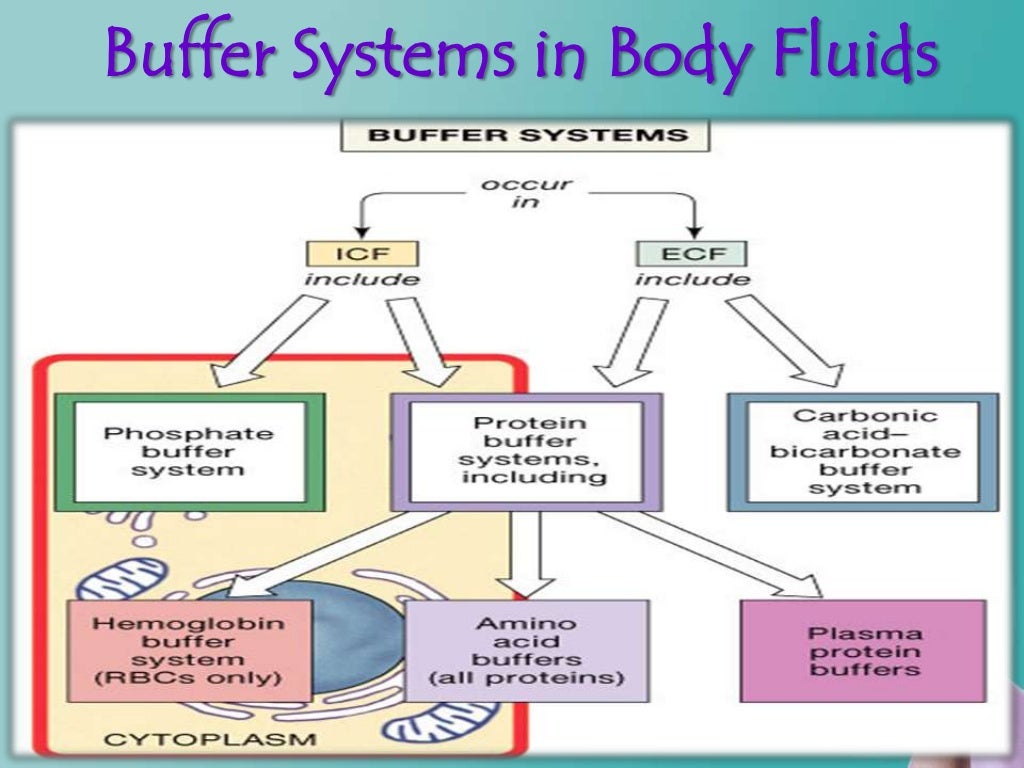
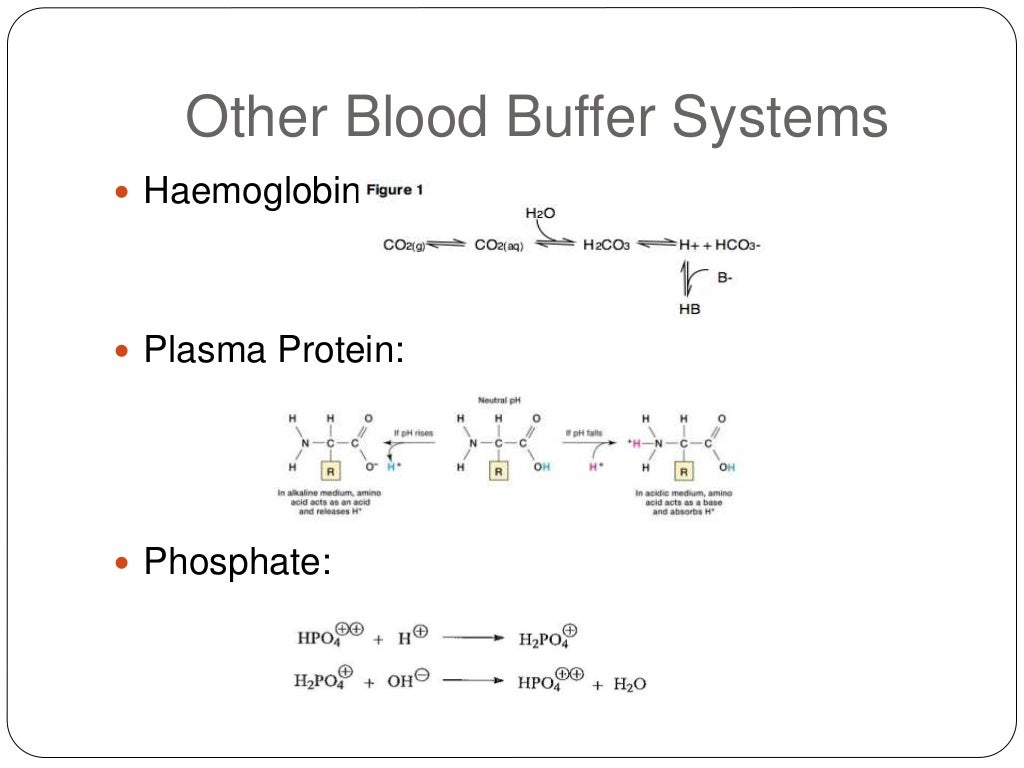
Buffer System Learn how proteins, phosphates, bicarbonate, and carbonic acid work as buffers to maintain blood ph within a normal range. understand how the respiratory and renal systems regulate acid base balance and how co2 affects blood ph. Blood ph buffer systems. buffer systems work by neutralising added acid or base to resist changes to ph. for example, when h is added, the buffer system acts to ‘mop up’ excess h . when h is low, or excess base is added, the buffer can ‘donate’ its own h to the solution to try and minimise the ph change. bicarbonate buffer system. Learn how blood buffers resist changes in ph and how blood glucose is regulated by insulin and glucagon. perform experiments to test the buffering capacity of different solutions and measure your blood glucose level. The bicarbonate buffer system is an acid base homeostatic mechanism involving the balance of carbonic acid (h 2 co 3), bicarbonate ion (hco −. 3), and carbon dioxide (co 2) in order to maintain ph in the blood and duodenum, among other tissues, to support proper metabolic function. [1] .
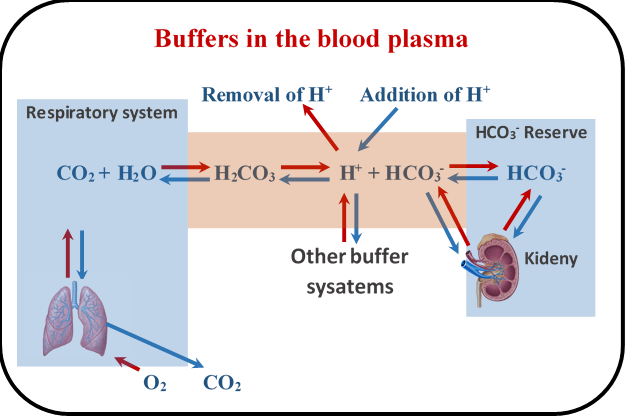
6 8 Ph Buffers Chemistry Libretexts Learn how blood buffers resist changes in ph and how blood glucose is regulated by insulin and glucagon. perform experiments to test the buffering capacity of different solutions and measure your blood glucose level. The bicarbonate buffer system is an acid base homeostatic mechanism involving the balance of carbonic acid (h 2 co 3), bicarbonate ion (hco −. 3), and carbon dioxide (co 2) in order to maintain ph in the blood and duodenum, among other tissues, to support proper metabolic function. [1] . Introduction. to maintain homeostasis, the human body employs many physiological adaptations. one of these is maintaining an acid base balance. in the absence of pathological states, the ph of the human body ranges between 7.35 to 7.45, with the average at 7.40. why this number? why not a neutral number of 7.0 instead of a slightly alkaline 7.40?. Learn how buffers maintain ph balance in our blood and other solutions with khan academy's interactive videos and exercises.

Bicarbonate Buffer System Example Of Multiple Equilibria Teaching Introduction. to maintain homeostasis, the human body employs many physiological adaptations. one of these is maintaining an acid base balance. in the absence of pathological states, the ph of the human body ranges between 7.35 to 7.45, with the average at 7.40. why this number? why not a neutral number of 7.0 instead of a slightly alkaline 7.40?. Learn how buffers maintain ph balance in our blood and other solutions with khan academy's interactive videos and exercises.
Blood Buffer System

Comments are closed.