Blood Circulatory System Veins Doccheck
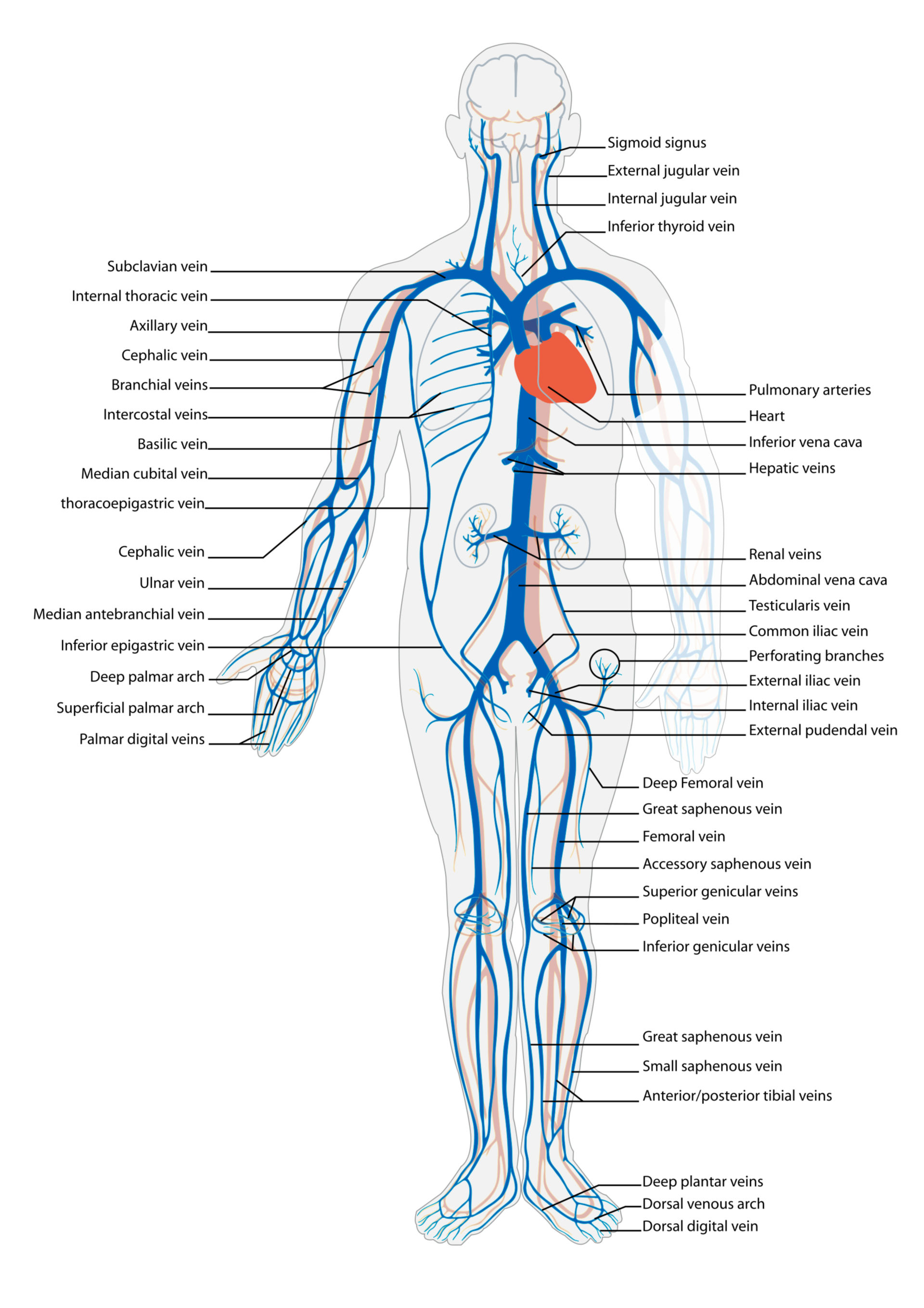
Blood Circulatory System Veins Doccheck The pulmonary cicrulation starts at the right ventricle of the heart. it contracts and pumps de oxygenated bloof into the pulmonary arteries and the connected lung capillaries. from the capillaries the blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary veins and arrives at the left atrium. where it starts the cycle again. (picture: ladyofhats. Veins are blood vessels located throughout your body that collect oxygen poor blood and return it to your heart. veins are part of your circulatory system. they work together with other blood vessels and your heart to keep your blood moving. veins hold most of the blood in your body. in fact, nearly 75% of your blood is in your veins.
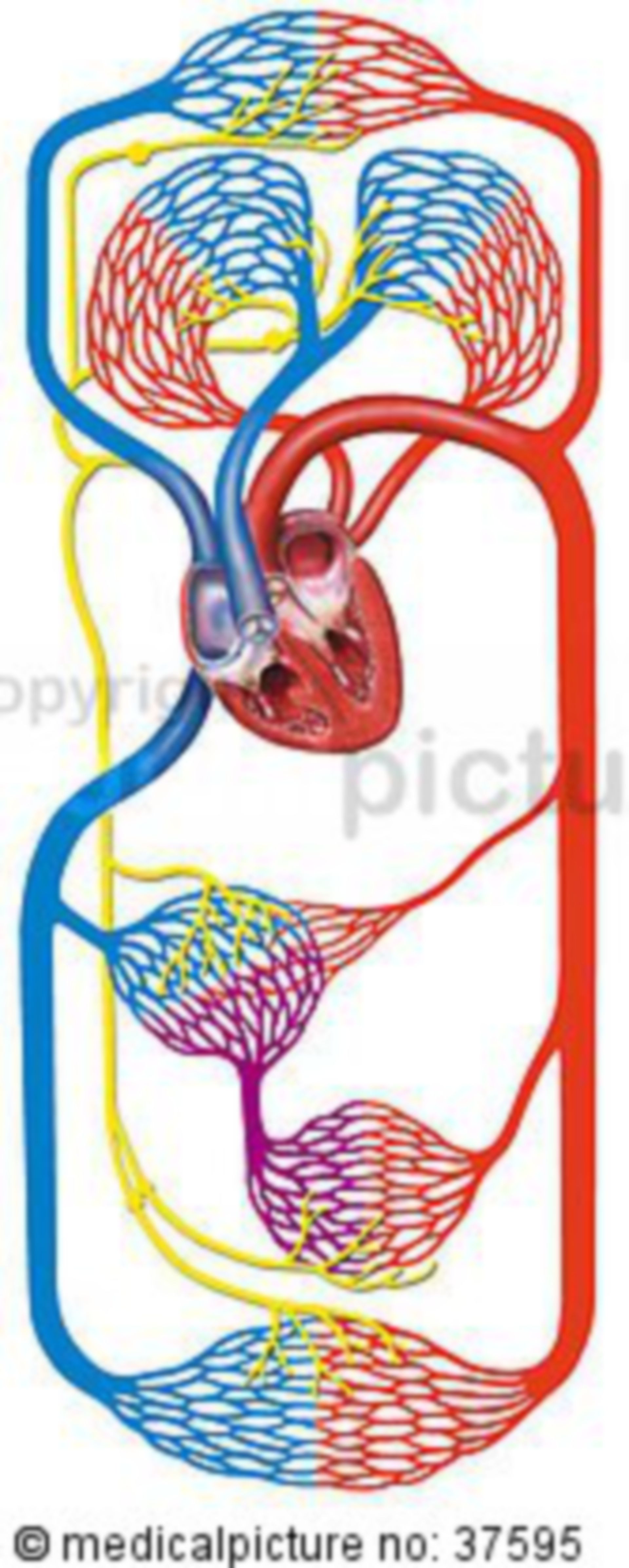
The Human Blood Circulation Doccheck Veins blood flows from venules into larger veins. just like the arterial system, three layers make up the vein walls. but unlike the arteries, the venous pressure is low. veins are thin walled and are less elastic. this feature permits the veins to hold a very high percentage of the blood in circulation. The circulatory system (cardiovascular system) pumps blood from the heart to the lungs to get oxygen. the heart then sends oxygenated blood through arteries to the rest of the body. the veins carry oxygen poor blood back to the heart to start the circulation process over. your circulatory system is critical to healthy organs, muscles and tissues. The walls of most blood vessels have three distinct layers: the tunica externa, the tunica media, and the tunica intima. these layers surround the lumen, the hollow interior through which blood flows. 2. oxygenated blood flows away from the heart through arteries. the left ventricle of the heart pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta. Once the venous blood is in the heart, it will get pumped into the pulmonary circulation for gas exchange. after the gas exchange, the oxygenated blood will return to the body via the arterial system. the veins in the venous system are designed to drain the majority of the blood against gravity. the veins have one way valves.

Blood Circulatory System Veins Doccheck Vrogue Co The walls of most blood vessels have three distinct layers: the tunica externa, the tunica media, and the tunica intima. these layers surround the lumen, the hollow interior through which blood flows. 2. oxygenated blood flows away from the heart through arteries. the left ventricle of the heart pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta. Once the venous blood is in the heart, it will get pumped into the pulmonary circulation for gas exchange. after the gas exchange, the oxygenated blood will return to the body via the arterial system. the veins in the venous system are designed to drain the majority of the blood against gravity. the veins have one way valves. The blood circulatory system (cardiovascular system) delivers nutrients and oxygen to all cells in the body. it consists of the heart and the blood vessels running through the entire body. the arteries carry blood away from the heart; the veins carry it back to the heart. the system of blood vessels resembles a tree: the “trunk” – the main artery (aorta) – branches into large arteries. The vascular system is made up of the vessels that carry blood and lymph fluid through the body. it's also called the circulatory system. the arteries and veins carry blood all over the body. they send oxygen and nutrients to the body tissues. and they take away tissue waste.

Comments are closed.