Boiling Atmospheric Pressure And Vapor Pressure
How Does Atmospheric Pressure Affect Boiling Point A video about the phenomenon of boiling for the khan academy talent search contest, july 2016.images:image of earth from space (1:12): commons.wikime. Boiling. boiling is the process by which a liquid turns into a vapor when it is heated to its boiling point. the change from a liquid phase to a gaseous phase occurs when the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to the atmospheric pressure exerted on the liquid. boiling is a physical change and molecules are not chemically altered during the.

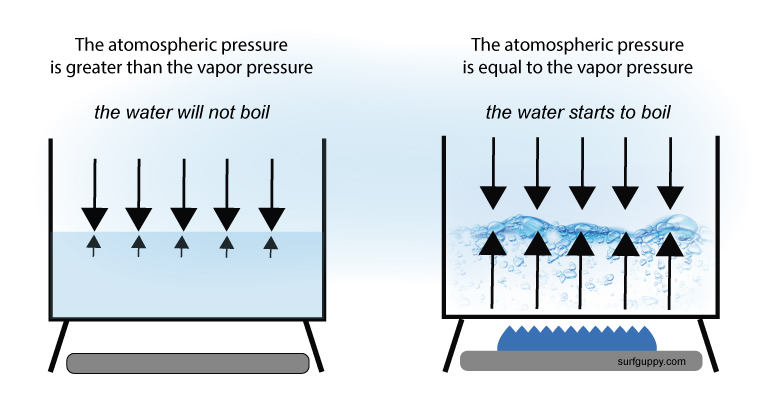
Difference Between Vapor Pressure And Boiling Point Definition A few key ideas: to understand pressure you need to visualize the atoms molecules colliding. these collisions create pressure and are the basis of collision theory. boiling occurs when the atmospheric pressure and the vapor pressure are equal. the bubbles in a boiling liqued are not air. they are the liquid that has changed states to a gas. So, at 1 atm of pressure, the saturated vapor pressure of water occurs at 100 ° c (212 ° f). in other words, vapor pressure equals atmospheric pressure at a liquid’s boiling point. a substance with a high vapor pressure is said to be volatile. examples of volatile substances include gasoline and rubbing alcohol (liquids) and. When the vapor pressure increases enough to equal the external atmospheric pressure, the liquid reaches its boiling point. the boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which its equilibrium vapor pressure is equal to the pressure exerted on the liquid by its gaseous surroundings. for liquids in open containers, this pressure is that due. For water, the vapor pressure reaches the standard sea level atmospheric pressure of 760 mmhg at 100°c. since the vapor pressure increases with temperature, it follows that for pressure greater than 760 mmhg (e.g., in a pressure cooker), the boiling point is above 100°c and for pressure less than 760 mmhg (e.g., at altitudes above sea level.

Comments are closed.