Buffers In Blood For A Level Chemistry Ocr A Carbonic Acid Buffer Hydrogencarbonate
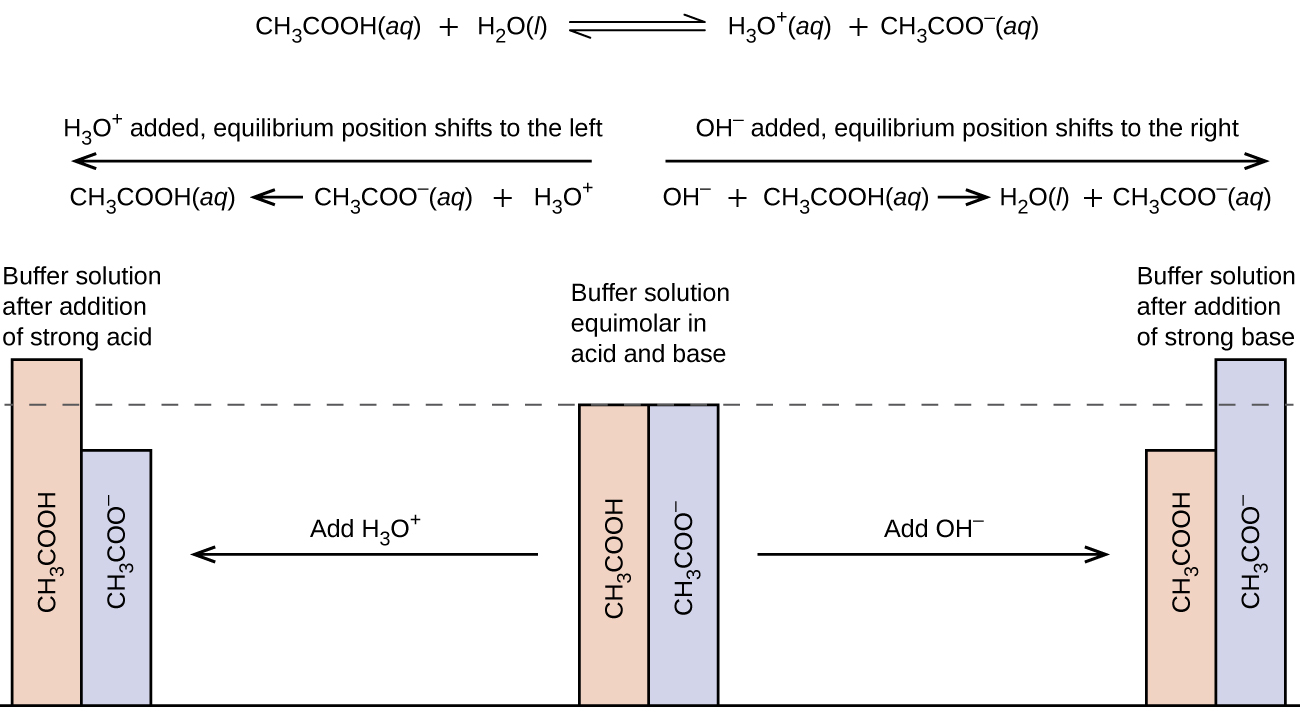
14 6 Buffers Chemistry Libretexts The link to my full video catalogue is here = docs.google spreadsheets d 1qk0ufov1ss5nqgosseobkhed y0aubytu inzlows64 edit?usp=sharingtopics are. Past papers. edexcel. spanish. past papers. cie. spanish language & literature. past papers. other subjects. revision notes on 5.6.5 buffers for the aqa a level chemistry syllabus, written by the chemistry experts at save my exams.
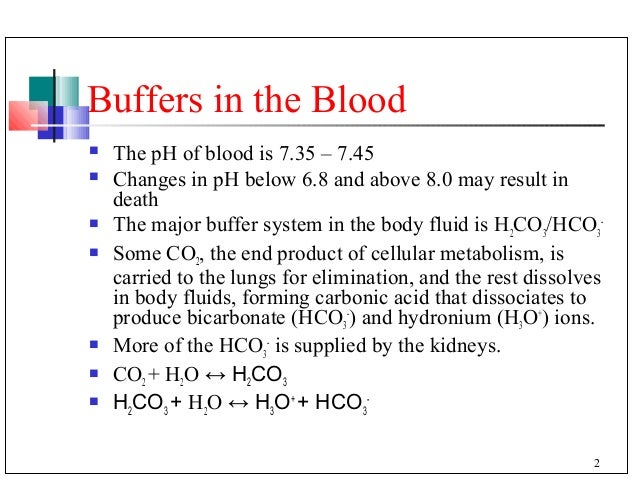
Buffer In The Blood (d) blood contains a mixture of carbonic acid, h2co3, and hydrogencarbonate ions, hco–. 3 explain how the carbonic acid–hydrogencarbonate mixture acts as abuffer. in your answer include the equation for the equilibrium in this buffer solution and explain how this equilibrium system is able to control bloodph.[5] [total:22marks] [4]. (ii) healthy blood at a ph of 7.40 has a hydrogencarbonate : carbonic acid ratio of 10.5 : 1. a patient is admitted to hospital. the patient’s blood ph is measured as 7.20. calculate the hydrogencarbonate : carbonic acid ratio in the patient’sblood. [5] [total22marks] head to savemyexams.co.uk for more awesome resources 7. 66 minutes. butanoic acid, ch3(ch2)2cooh, is the ‘butter acid’, formed when butter turns rancid and tastes sour. a student prepares an aqueous solution of butanoic acid with a concentration of 0.250 mol dm–3. the ka of butanoic acid is 1.51 × 10–5 mol dm–3. (ii) write the expression for the acid dissociation constant of butanoic acid. Carbonic acid, h,co;, is a weak bronsted lowry acid formed when carbon dioxide dissolves in water. healthy blood is buffered to a ph of 7.40. the most important buffer solution in blood is a mixture of carbonic acid and hydrogencarbonate ions, hco; (a) explain how the carbonic acid hydrogencarbonate mixture acts as a buffer in the control of blood ph.

Blood Buffer System 66 minutes. butanoic acid, ch3(ch2)2cooh, is the ‘butter acid’, formed when butter turns rancid and tastes sour. a student prepares an aqueous solution of butanoic acid with a concentration of 0.250 mol dm–3. the ka of butanoic acid is 1.51 × 10–5 mol dm–3. (ii) write the expression for the acid dissociation constant of butanoic acid. Carbonic acid, h,co;, is a weak bronsted lowry acid formed when carbon dioxide dissolves in water. healthy blood is buffered to a ph of 7.40. the most important buffer solution in blood is a mixture of carbonic acid and hydrogencarbonate ions, hco; (a) explain how the carbonic acid hydrogencarbonate mixture acts as a buffer in the control of blood ph. Outlining how blood is able to buffer ph by using carbonic acid and hydrogen carbonate ions dissolved in blood plasma. the effect on position of equilibrium. The levels of carbonic acid (h 2 co 3) in the blood are primarily controlled by respiration. when the body produces excess carbon dioxide (co 2), it reacts with water to form carbonic acid: co 2(aq) h 2 o (l) ⇌ h 2 co 3(aq) to reduce the concentration of carbonic acid, the body can exhale co 2 through the lungs.

A Level Chemistry Ocr Notes Acids Bases And Buffers A Level Note Outlining how blood is able to buffer ph by using carbonic acid and hydrogen carbonate ions dissolved in blood plasma. the effect on position of equilibrium. The levels of carbonic acid (h 2 co 3) in the blood are primarily controlled by respiration. when the body produces excess carbon dioxide (co 2), it reacts with water to form carbonic acid: co 2(aq) h 2 o (l) ⇌ h 2 co 3(aq) to reduce the concentration of carbonic acid, the body can exhale co 2 through the lungs.

Acids And Bases Buffer Calculation Past Paper Exam Question

Comments are closed.