Buffers In Blood Module 5 Acids Bases And Buffers Chemistry A

Buffers In Blood Module 5 Acids Bases And Buffers Chemistry A N this video we work through the theory behind buffers in blood and calculations of carbonic acid hydrogen carbonate buffers module 5. you may wish to pause. In this video we work through the theory behind buffers, buffer action, and calculations involving buffers in module 5. you may wish to pause the video and t.
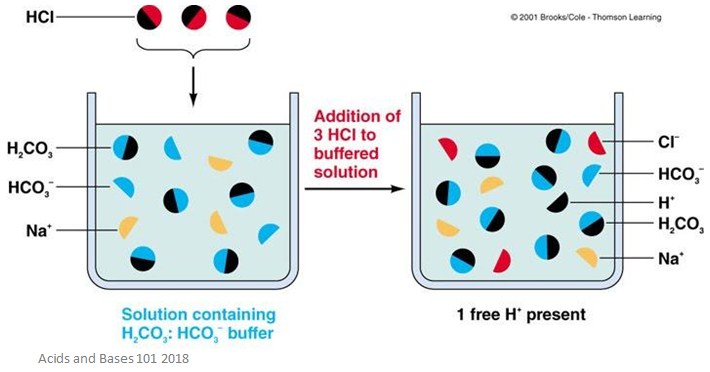
Acid Base Buffers Facts Summary Definition Chemistry Revision A buffer resists sudden changes in ph. it has a weak acid or base and a salt of that weak acid or base. no. combining a strong acid and a strong base will produce salt and water. excess strong acid or strong base will not act as a buffer. not a buffer; buffer; not a buffer; buffer; 4. 1. not a buffer. 2. buffer. 3. not a buffer. 4. not buffer. Conjugate acid base pair. monobasic acid. dibasic acid. tribasic acid. ionic equation for neutralisation. acid metal oxide. acid alkali. acid carbonate. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like bronsted lowry acid, bronsted lowry base, conjugate acid base pair and more. Human blood contains a buffer of carbonic acid (h2co3 h 2 co 3) and bicarbonate anion (hco−3 hco 3 −) in order to maintain blood ph between 7.35 and 7.45, as a value higher than 7.8 or lower than 6.8 can lead to death. in this buffer, hydronium and bicarbonate anion are in equilibrium with carbonic acid. furthermore, the carbonic acid in. Study module 5: acids, bases and buffers v2 flashcards from shakir uddin's al maarifa education class online, or in brainscape's iphone or android app. learn faster with spaced repetition.
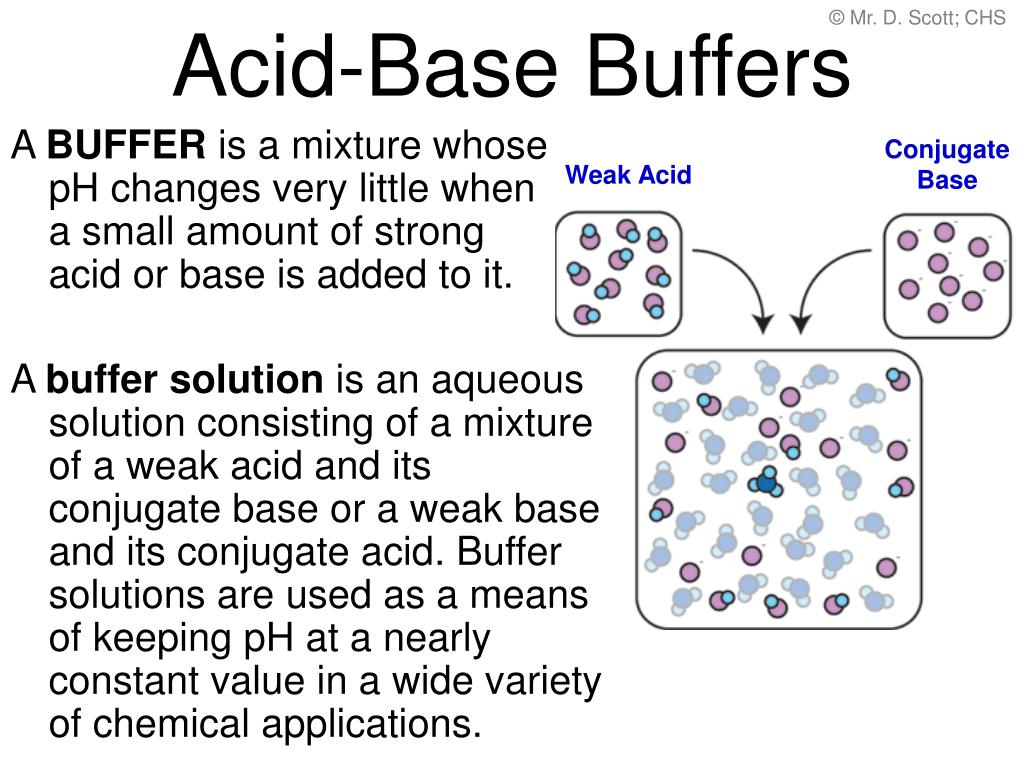
Ppt Acid Base Buffers Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 496487 Human blood contains a buffer of carbonic acid (h2co3 h 2 co 3) and bicarbonate anion (hco−3 hco 3 −) in order to maintain blood ph between 7.35 and 7.45, as a value higher than 7.8 or lower than 6.8 can lead to death. in this buffer, hydronium and bicarbonate anion are in equilibrium with carbonic acid. furthermore, the carbonic acid in. Study module 5: acids, bases and buffers v2 flashcards from shakir uddin's al maarifa education class online, or in brainscape's iphone or android app. learn faster with spaced repetition. For example, a buffer can be composed of dissolved acetic acid (hc 2 h 3 o 2, a weak acid) and sodium acetate (nac 2 h 3 o 2, a salt derived from that acid). another example of a buffer is a solution containing ammonia (nh 3, a weak base) and ammonium chloride (nh 4 cl, a salt derived from that base). let us use an acetic acid–sodium acetate. The bicarbonate buffer system is an acid base homeostatic mechanism involving the balance of carbonic acid (h 2 co 3), bicarbonate ion (hco −. 3), and carbon dioxide (co 2) in order to maintain ph in the blood and duodenum, among other tissues, to support proper metabolic function. [1] catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase, carbon dioxide (co 2.
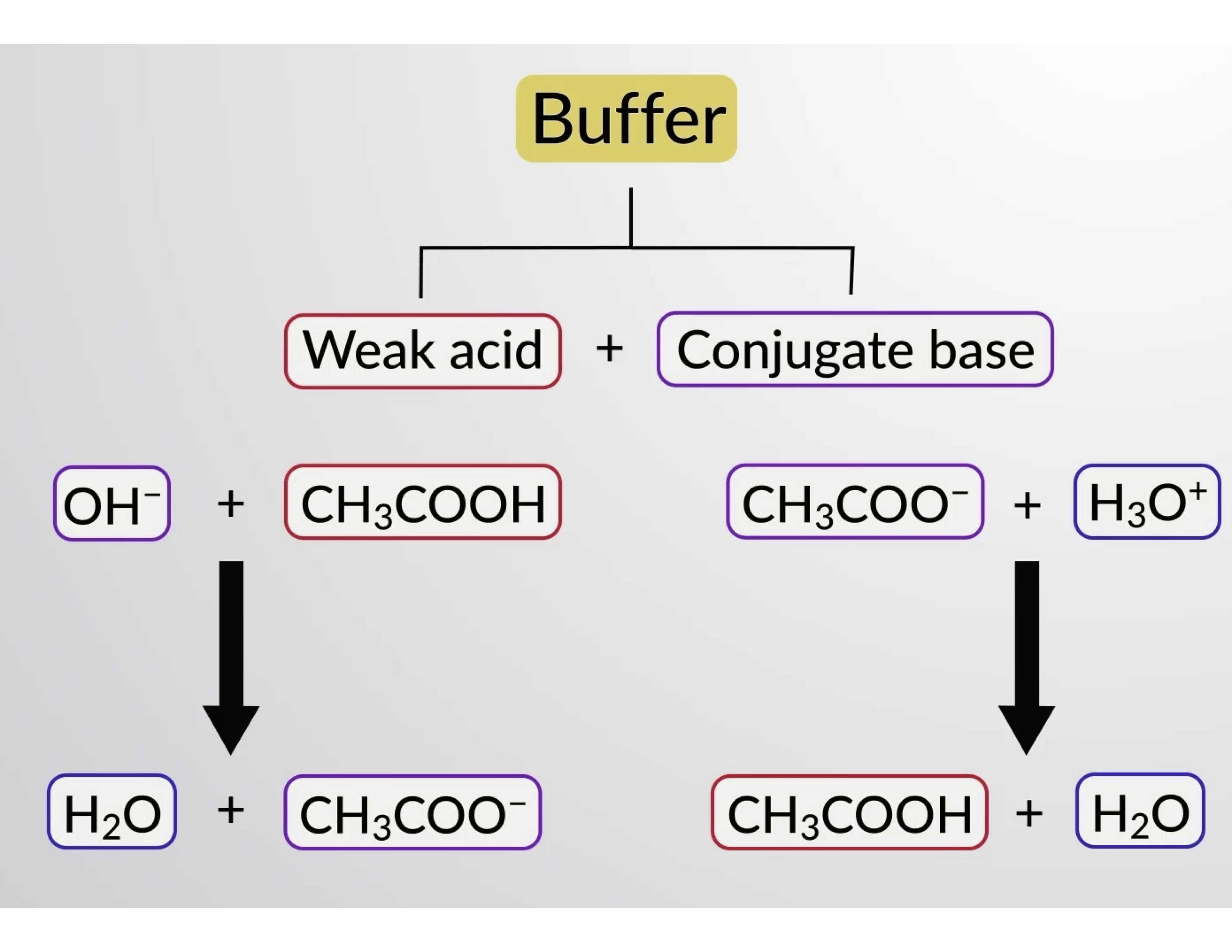
Buffers Buffer Components And Buffer Action Concept Chemistry Jove For example, a buffer can be composed of dissolved acetic acid (hc 2 h 3 o 2, a weak acid) and sodium acetate (nac 2 h 3 o 2, a salt derived from that acid). another example of a buffer is a solution containing ammonia (nh 3, a weak base) and ammonium chloride (nh 4 cl, a salt derived from that base). let us use an acetic acid–sodium acetate. The bicarbonate buffer system is an acid base homeostatic mechanism involving the balance of carbonic acid (h 2 co 3), bicarbonate ion (hco −. 3), and carbon dioxide (co 2) in order to maintain ph in the blood and duodenum, among other tissues, to support proper metabolic function. [1] catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase, carbon dioxide (co 2.

Comments are closed.