Business Revenues Tutor2u Economics

Business Revenues Tutor2u Economics Price inelastic demand: when coefficient of ped < 1. price maker: a firm with pricing power because ar curve is downward sloping. price taker: associated with perfect competition, where ar=mr. total revenue: tr = average revenue x output. unitary elasticity: when the coefficient of ped = 1. share : economics. reference. Revenue is the income a firm generates from selling goods and services. in some cases shown below, businesses have been able to scale quickly and achieve rapid growth in their sales revenue. netflix. netflix is a superb example or sales revenue growth that has a classic ‘ice hockey stick’ appearance. founded on august 29, 1997 in scotts.

Business Revenues Tutor2u Economics Activity 1: video introduction to revenue. in this video, we introduce some of the essential key terms and important formulae. revenue: video 1. activity 2: video revenue in imperfect markets. in this video, we consider the differences between competitive and imperfectly competitive markets, and think about the meaning of "price taker" and. In this short revision video we show how to draw average and marginal revenue in your theory diagrams.#businesseconomics #microeconomics #tutor2ueconomics. 6. 2. 2. all, the prices within the market are the same, in this example that price is 2. the total revenue is equal to the price multiplied by the quantity and therefore the total revenue will consist of 2, 4 and 6. for each extra good service produced, total revenue increases by 2. therefore, the marginal revenue is 2. Shown in revenue? average monthly retail revenue per (post paid) subscriber in the united kingdom – source statista 2020 outline the features of: a perfect market an imperfect market complete the calculations price per unit (= average revenue) demand (units) total revenue (ar x quantity) marginal revenue (change in total revenue ÷ change in.

Business Revenues Tutor2u Economics 6. 2. 2. all, the prices within the market are the same, in this example that price is 2. the total revenue is equal to the price multiplied by the quantity and therefore the total revenue will consist of 2, 4 and 6. for each extra good service produced, total revenue increases by 2. therefore, the marginal revenue is 2. Shown in revenue? average monthly retail revenue per (post paid) subscriber in the united kingdom – source statista 2020 outline the features of: a perfect market an imperfect market complete the calculations price per unit (= average revenue) demand (units) total revenue (ar x quantity) marginal revenue (change in total revenue ÷ change in. Total revenue is calculated by price x quantity sold. it is the revenue received from the sale of a given level of output. when price is constant, tr is as shown in the diagram. prices are lowered to achieve higher sales. marginal revenue: this is the extra revenue a firm earns from the sale of one extra unit. This 30 minute study livestream for all gcse business students focuses the key topic of revenue, costs and profit.#gcsebusiness #gcses #tutor2ubusiness.
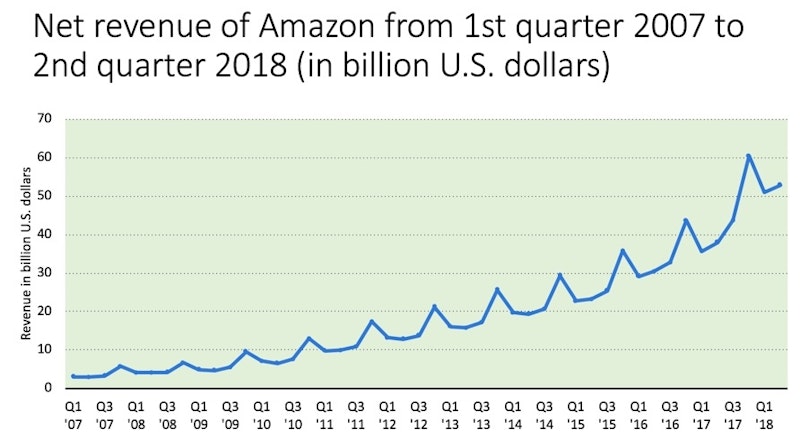
Focus On Business Revenues Reference Library Economics Tutor2u Total revenue is calculated by price x quantity sold. it is the revenue received from the sale of a given level of output. when price is constant, tr is as shown in the diagram. prices are lowered to achieve higher sales. marginal revenue: this is the extra revenue a firm earns from the sale of one extra unit. This 30 minute study livestream for all gcse business students focuses the key topic of revenue, costs and profit.#gcsebusiness #gcses #tutor2ubusiness.

Comments are closed.