Ccskin Cu Under Microscope Ccmagnified Cu Cchuman Cu Ccskin Cu O Co Oo Uo Co Oo O Uo Io O Oo Co O U
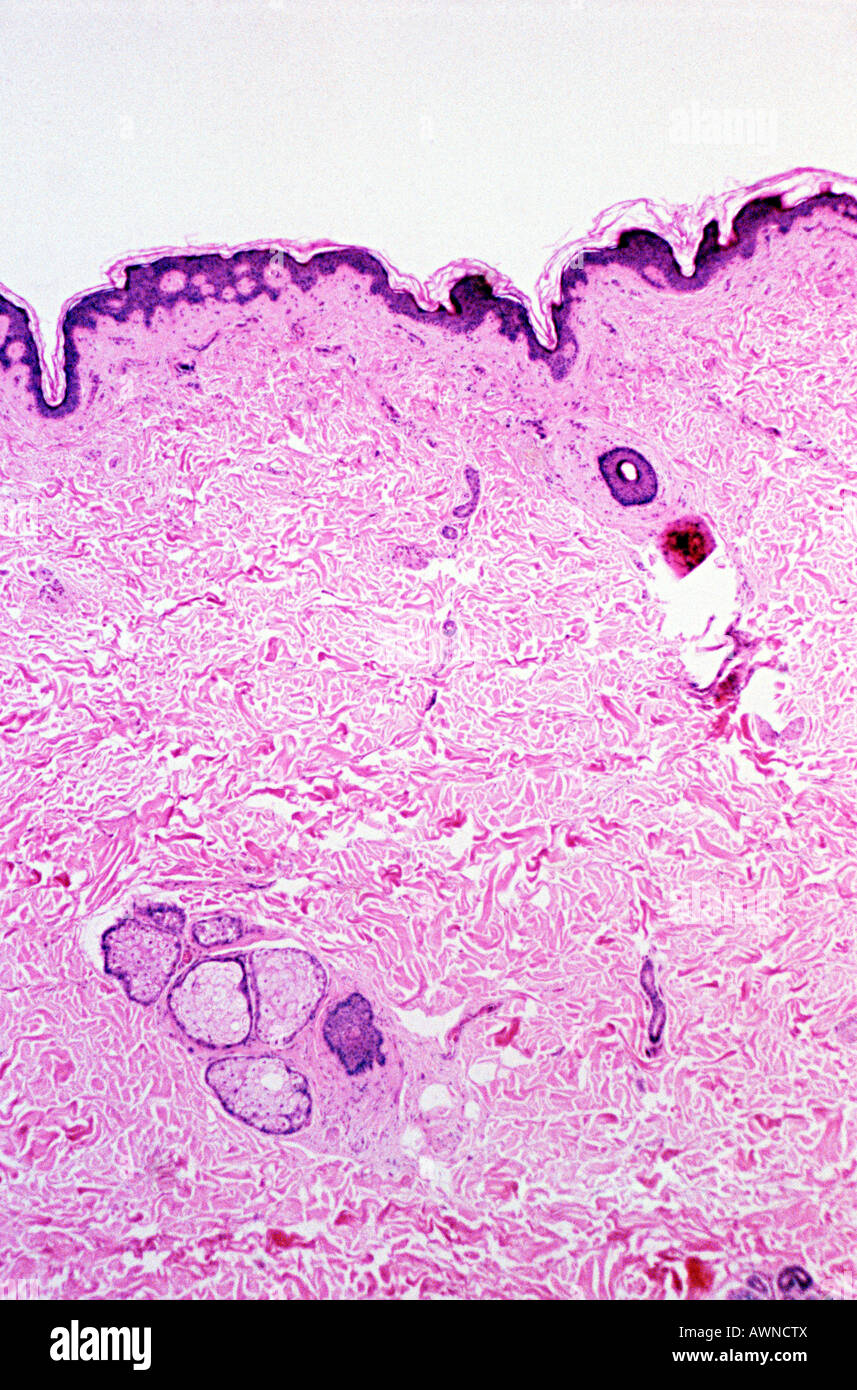
Human Skin Cell Labeled In situ stm studies of nanoscale surface restructuring. stm studies of cu(100) electrodes in co 2 saturated 0.1 m khco 3, prepared by a procedure that rigorously avoids cu oxidation (see methods. For cu 2 (oh) 2 co 3 and cu(oh) 2 with slow electroreduction kinetics, the temporary presence of mixed cu oxidation states (cu 2 from cu 2 (oh) 2 co 3 or cu(oh) 2, cu from cu 2 o, and metallic.
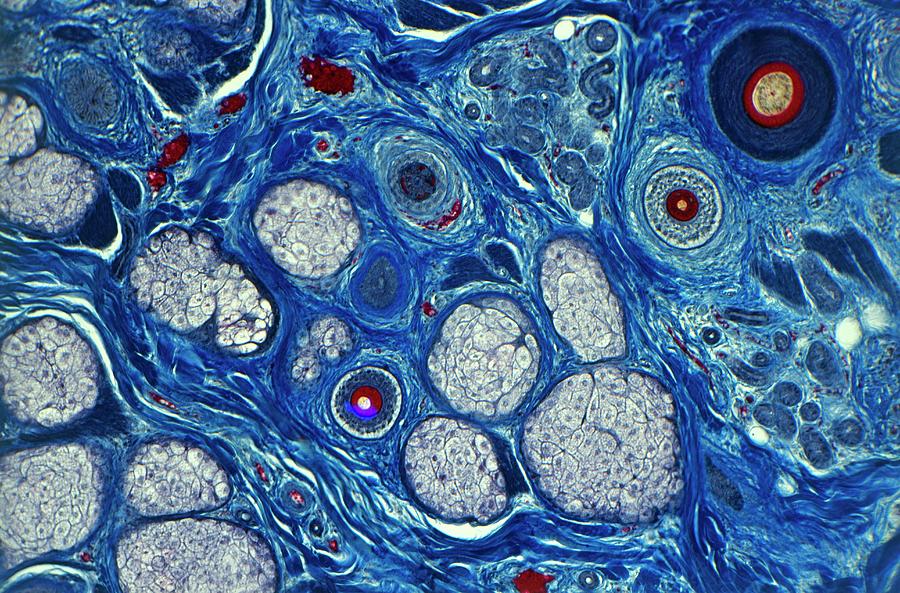
Skin Cells Under Microscope Labeled Micropedia Images And Photos Finder The bands in the range of 1900–2150 cm −1 arise from the c ≡ o stretching of the *co on the cu pb cu under 10% co is similar to the value on com cu under 100% co at the same potential. The c cu 2 o sample was much more active than the o cu 2 o sample. a co conversion of 98 % was achieved at 175 °c on c cu 2 o. at this temperature, the co conversion on o cu 2 o was only 4 %. full co conversion for this catalyst requires a temperature higher than 300 °c. the catalytic performance in the second cycle is similar to the first one. Copper oxide nanomaterials have been suggested to be efficient for highly selective multi carbon (c 2 ) production in co 2 reduction reaction (co 2 rr), due to the introduction of surface cu species from oxide catalysts. however, the cu species on the catalyst surface are prone to being reduced to cu 0 under reductive conditions during co 2 rr. In this work, various cu, ni, ag microalloyed sn–5sb cu joints, ordinary sn–5sb cu joints, and low melting point sn–3ag–0.5cu (sac305) cu (used for comparison) were prepared, focusing on the influence of cu, ni, and ag on the microstructure evolution, interfacial imc growth, and microhardness of sn–5sb cu joint under long time isothermal aging process. results showed that the.

Human Skin Microscope Copper oxide nanomaterials have been suggested to be efficient for highly selective multi carbon (c 2 ) production in co 2 reduction reaction (co 2 rr), due to the introduction of surface cu species from oxide catalysts. however, the cu species on the catalyst surface are prone to being reduced to cu 0 under reductive conditions during co 2 rr. In this work, various cu, ni, ag microalloyed sn–5sb cu joints, ordinary sn–5sb cu joints, and low melting point sn–3ag–0.5cu (sac305) cu (used for comparison) were prepared, focusing on the influence of cu, ni, and ag on the microstructure evolution, interfacial imc growth, and microhardness of sn–5sb cu joint under long time isothermal aging process. results showed that the. Copper oxides have attracted great attention in oxidation of co due to its high activity at low temperature. in this work, uniform cu 2 o nanospheres were synthesized through a high temperature polyol process, and they were further transformed into a series of cu 2 o–cuo nanosphere catalysts with a tunable cu 2 cu ratio by controlled calcination in air. Figure 1. structural and chemical characterization as well as co 2 rr performance of cu 2 o nanocubes. tem images of cu 2 o nanocubes in their as prepared state (a) and after 1 h co 2 rr at −1.0 v rhe (b). (c) quasi in situ cu lmm xaes spectra of cu 2 o nanocubes in the as prepared state and after 1 h of co 2 rr at −1.0 v rhe without air.
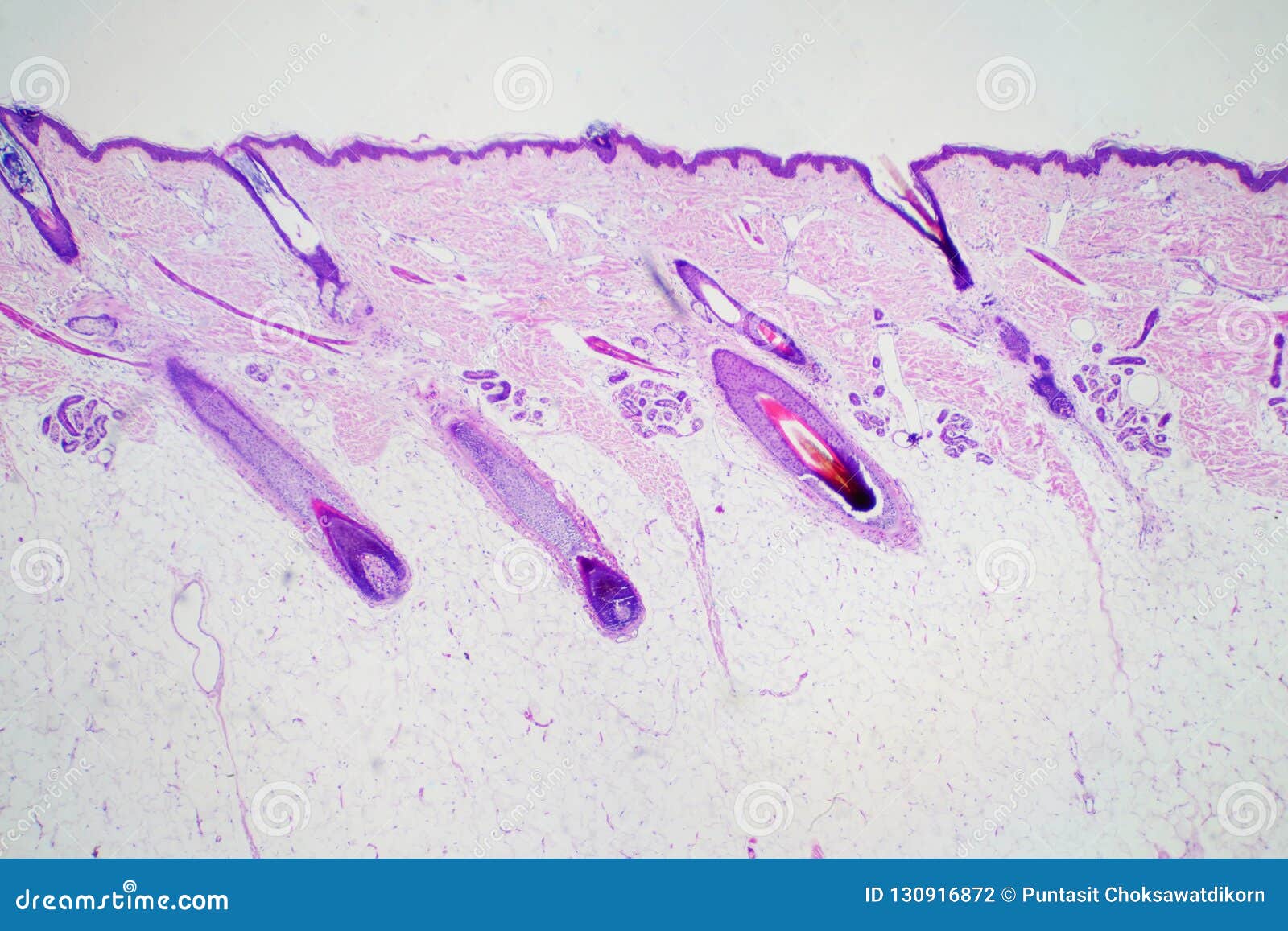
Human Skin Layers Histology Copper oxides have attracted great attention in oxidation of co due to its high activity at low temperature. in this work, uniform cu 2 o nanospheres were synthesized through a high temperature polyol process, and they were further transformed into a series of cu 2 o–cuo nanosphere catalysts with a tunable cu 2 cu ratio by controlled calcination in air. Figure 1. structural and chemical characterization as well as co 2 rr performance of cu 2 o nanocubes. tem images of cu 2 o nanocubes in their as prepared state (a) and after 1 h co 2 rr at −1.0 v rhe (b). (c) quasi in situ cu lmm xaes spectra of cu 2 o nanocubes in the as prepared state and after 1 h of co 2 rr at −1.0 v rhe without air.
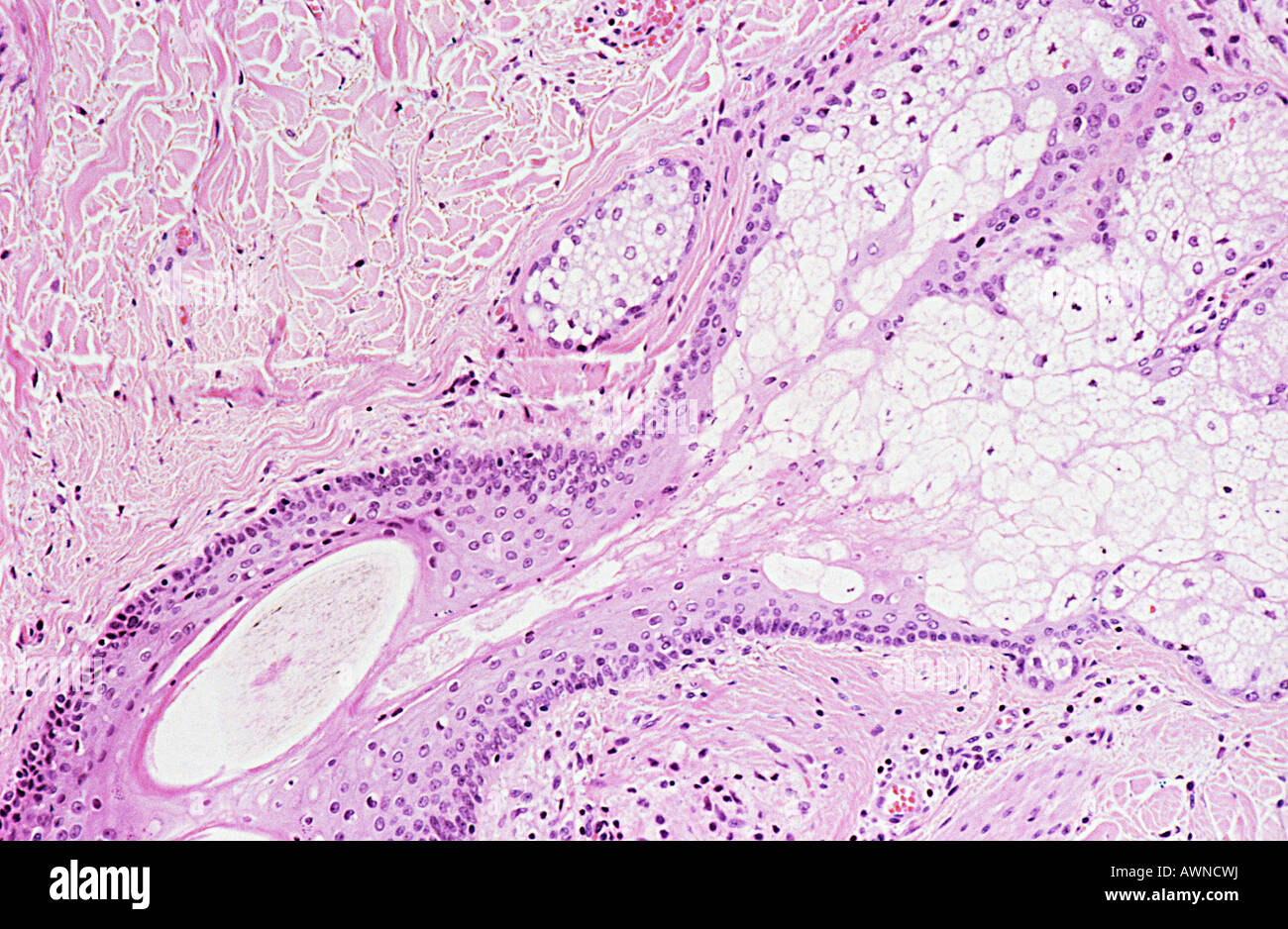
Human Skin Cell Under Microscope

Comments are closed.