Ceen 545 Lecture 3 Basic Seismology Structure Of The Earth And Plate Tectonics

Ceen 545 Lecture 3 Basic Seismology Structure Of The Ea This lecture reviews some of the basic principles associated with seismology including the structure of the earth, the theory of plate tectonics, and differe. Jun 22, 2014 •. 42 likes • 73,933 views. ai enhanced description. the earth's crust is divided into tectonic plates that move due to convection currents in the mantle. there are three types of plate boundaries divergent where new crust is formed, convergent where plates collide and one subducts under the other, and transform boundaries.

Plate Tectonics This lesson reviews lateral earth pressures in soil and discusses how earthquakes can affect them. mononabe okabe equation is discussed, as well as seed & wh. More information than is available from seismic velocities is needed to estimate the earth’s density distribution. seismology gives us p and s wave velocities: v p = s k 4 3 ¶ ” v s = r ¶ ” these equations contain three unknowns, the elastic moduli k and ¶ and the density ”, which cannot be found from just two measurements. 3 seismology and earth structure, 119 3.1 introduction, 119 3.2 refraction seismology, 120 3.2.1 flat layer method, 120 3.2.2 dipping layer method, 123 3.2.3 advanced analysis methods, 126 3.2.4 crustal structure, 128 3.2.5 rocks and minerals, 132 3.3 reflection seismology, 134 3.3.1 travel time curves for reflections, 134. Tectonics is the study of the origin and arrangement of the broad structural features of earth’s surface including: folds and faults. mountain ranges. continents. earthquake belts. the basic premise of plate tectonics is that the earth’s surface is divided into a few large, thick plates that move slowly and change in size. 2.

Diagram Of Earth S Plates 3 seismology and earth structure, 119 3.1 introduction, 119 3.2 refraction seismology, 120 3.2.1 flat layer method, 120 3.2.2 dipping layer method, 123 3.2.3 advanced analysis methods, 126 3.2.4 crustal structure, 128 3.2.5 rocks and minerals, 132 3.3 reflection seismology, 134 3.3.1 travel time curves for reflections, 134. Tectonics is the study of the origin and arrangement of the broad structural features of earth’s surface including: folds and faults. mountain ranges. continents. earthquake belts. the basic premise of plate tectonics is that the earth’s surface is divided into a few large, thick plates that move slowly and change in size. 2. A metal alloy containing mainly iron (fe) and nickel (ni) also rich in heavy metals such as platinum (pt) and gold (au) inner core is solid. density is 13 g cm3 1220 km thick. outer core is liquid. density is 10‒12 g cm3 2255 km thick. initially mostly liquid, but has cooled over time and partially solidified. Aimed at presenting the structure and dynamics of the solid earth in a fairly elementary way, the book starts with a description of tectonics on a sphere and the geometry of plate tectonic motions.
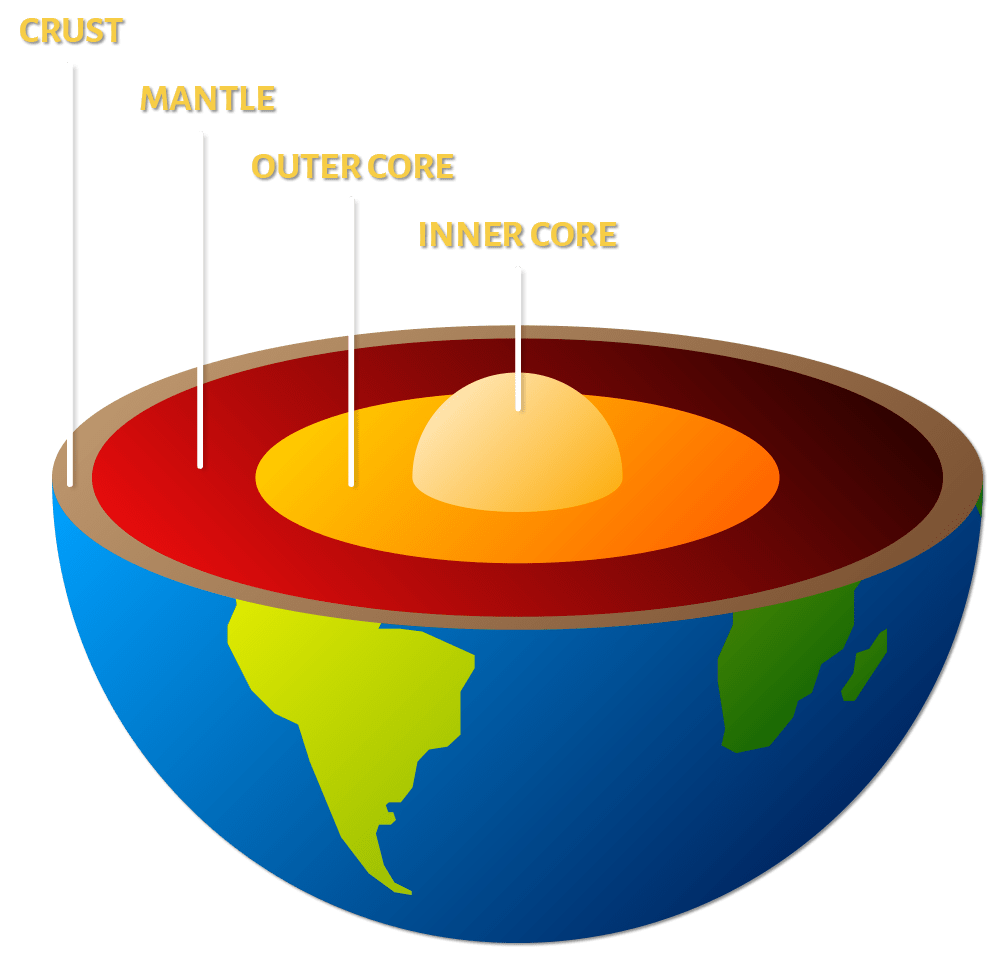
Power Of Plate Tectonics Structure Of Earth Amnh A metal alloy containing mainly iron (fe) and nickel (ni) also rich in heavy metals such as platinum (pt) and gold (au) inner core is solid. density is 13 g cm3 1220 km thick. outer core is liquid. density is 10‒12 g cm3 2255 km thick. initially mostly liquid, but has cooled over time and partially solidified. Aimed at presenting the structure and dynamics of the solid earth in a fairly elementary way, the book starts with a description of tectonics on a sphere and the geometry of plate tectonic motions.

Comments are closed.