Celestial Sphere Explained
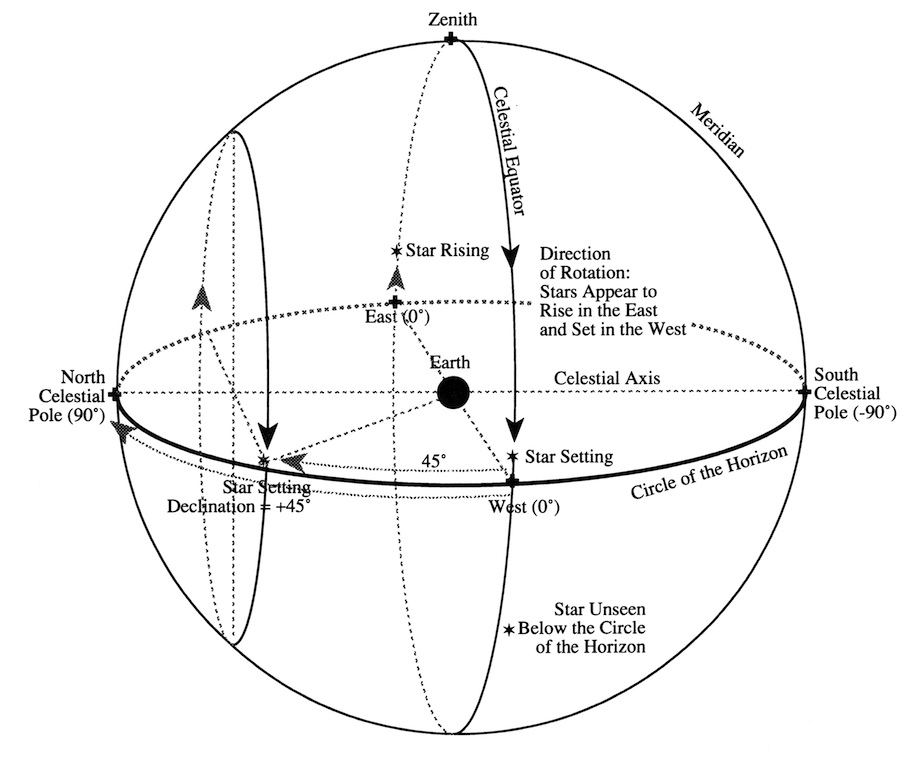
The Celestial Sphere Celestial sphere, the apparent surface of the heavens, on which the stars seem to be fixed. for the purpose of establishing coordinate systems to mark the positions of heavenly bodies, it can be considered a real sphere at an infinite distance from the earth. the earth’s axis, extended to infinity, touches this sphere at the north and south. The celestial sphere is a conceptual tool used in spherical astronomy to specify the position of an object in the sky without consideration of its linear distance from the observer. the celestial equator divides the celestial sphere into northern and southern hemispheres.

The Celestial Sphere вђ Science Learning Hub The celestial sphere is an imaginary projection of the sun, moon, planets, stars, and all astronomical bodies upon an imaginary sphere surrounding earth. although originally developed as part of the ancient greek concept of an earth centered (geocentric) universe, the hypothetical celestial sphere gives astronomers an important tool for fixing. Author: kyle denny. views: 2643. the celestial objects we see in the sky appear to be located on the surface of a great sphere of immense diameter, with us at the center. this is called “the celestial sphere”. understanding the celestial sphere is critical to understanding why, for example, an equatorial mount is needed for astrophotography. The celestial sphere was a way of explaining the visible universe in ancient times. although we now understand the universe differently, the idea of a celestial sphere is still used because it offers a simple way to think about the stars that is helpful for navigation. to an observer on earth, the stars appear to move together across the sky. The celestial sphere presupposes that earth is at the center of the view, which extends into infinity. three dimensional coordinates are used to mark the position of stars, planets, constellations, and other heavenly bodies. the earth rotates eastward daily on its axis, and that rotation produces an apparent westward rotation of the starry.

Celestial Sphere Model Explained The celestial sphere was a way of explaining the visible universe in ancient times. although we now understand the universe differently, the idea of a celestial sphere is still used because it offers a simple way to think about the stars that is helpful for navigation. to an observer on earth, the stars appear to move together across the sky. The celestial sphere presupposes that earth is at the center of the view, which extends into infinity. three dimensional coordinates are used to mark the position of stars, planets, constellations, and other heavenly bodies. the earth rotates eastward daily on its axis, and that rotation produces an apparent westward rotation of the starry. Celestial latitude and longitude. on page 10 there is a box that describes the celestial coordinates. there are angles like longitude and latitude on the celestial sphere that describe the location of a star, such as betelguese. these angles are called right ascension and declination. we will not use these coordinates in this course but you. The celestial sphere is tipped relative to the observer in the same way as is the earth. the extension of the earth's rotation axis to the sky defines the north and south celestial poles (the ncp and scp), while the extension of the earth's equatorial plane defines the celestial equator. the ncp is in the constellation ursa minor (the smaller.
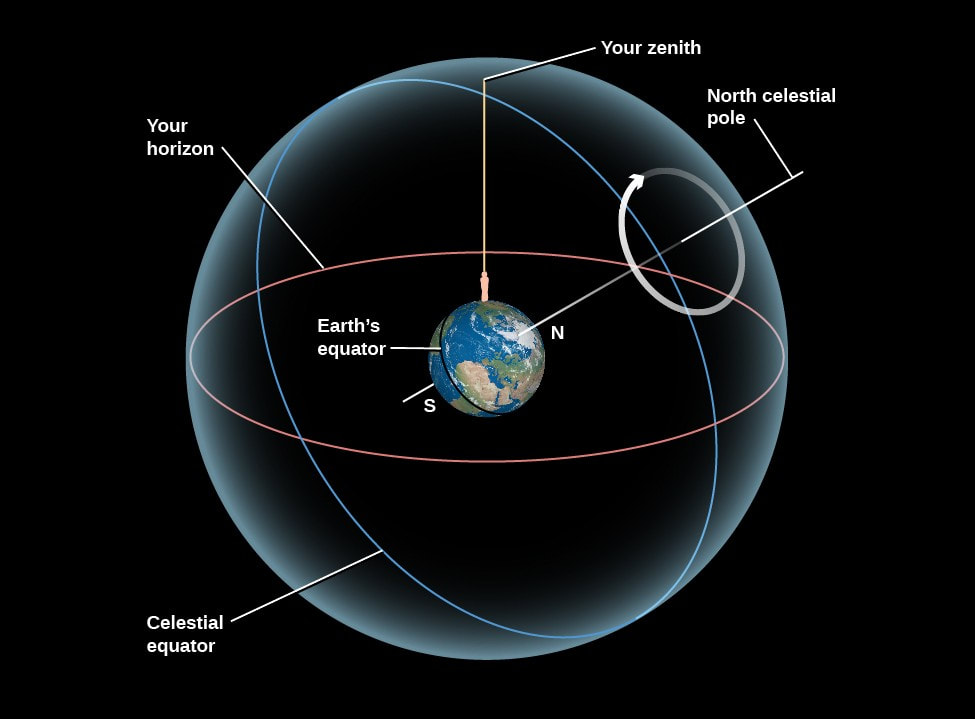
Celestial Sphere Island Physics Celestial latitude and longitude. on page 10 there is a box that describes the celestial coordinates. there are angles like longitude and latitude on the celestial sphere that describe the location of a star, such as betelguese. these angles are called right ascension and declination. we will not use these coordinates in this course but you. The celestial sphere is tipped relative to the observer in the same way as is the earth. the extension of the earth's rotation axis to the sky defines the north and south celestial poles (the ncp and scp), while the extension of the earth's equatorial plane defines the celestial equator. the ncp is in the constellation ursa minor (the smaller.

Comments are closed.