Cellular Level Of Organization Part 3 Tissues Part 1 Youtube

Cellular Level Of Organization Part 3 Tissues Part 1 Youtube About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. In this episode of crash course anatomy & physiology, hank gives you a brief history of histology and introduces you to the different types and functions of.

Chapter 3 The Cellular Level Of Organization Youtube About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Chapter 20. the cardiovascular system: blood vessels and circulation. 20.0 introduction. 20.1 structure and function of blood vessels. Tissues are groups of similar cells that have a common function. the four basic tissue types are epithelial, muscle, connective, and nervous tissue. each tissue type has a characteristic role in the body: epithelium covers the body surface and lines body cavities. muscle provides movement. Cellular and developmental biologists study how the continued division of a single cell leads to such complexity and differentiation. consider the difference between a structural cell in the skin and a nerve cell. a structural skin cell may be shaped like a flat plate (squamous) and live only for a short time before it is shed and replaced.
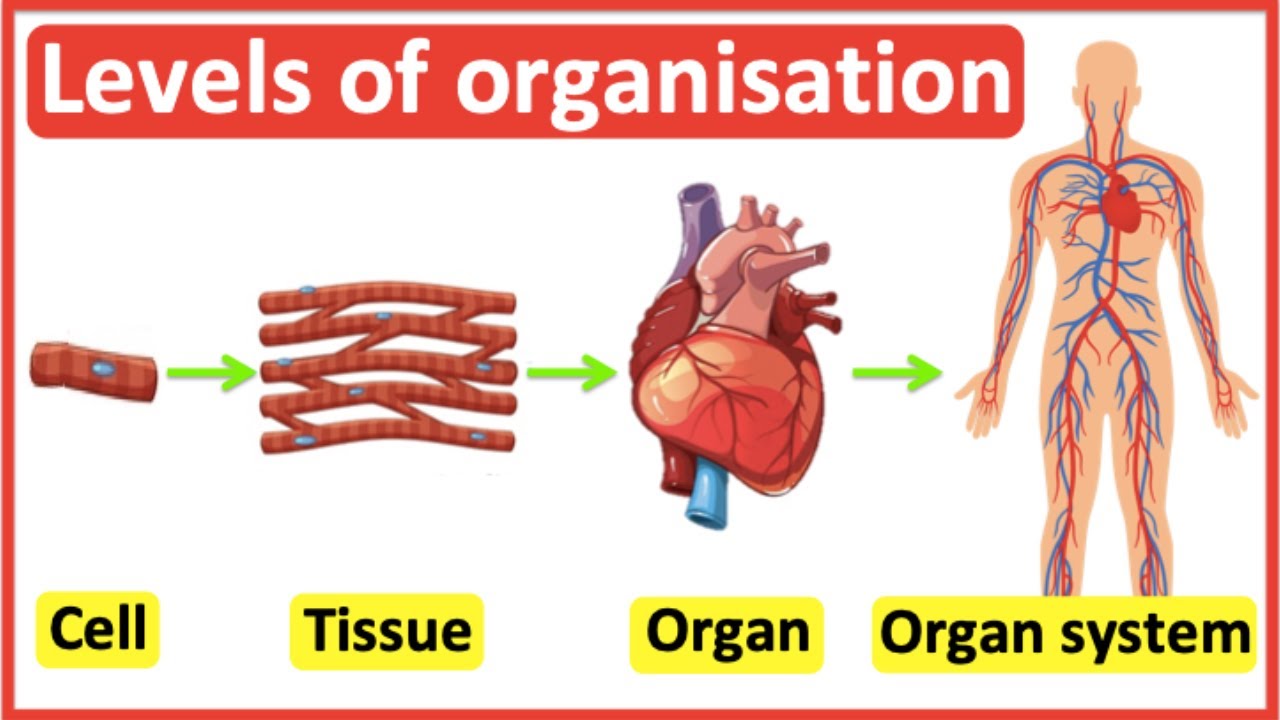
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Level Of Organisation In Tissues are groups of similar cells that have a common function. the four basic tissue types are epithelial, muscle, connective, and nervous tissue. each tissue type has a characteristic role in the body: epithelium covers the body surface and lines body cavities. muscle provides movement. Cellular and developmental biologists study how the continued division of a single cell leads to such complexity and differentiation. consider the difference between a structural cell in the skin and a nerve cell. a structural skin cell may be shaped like a flat plate (squamous) and live only for a short time before it is shed and replaced. Anatomy & physiology 1. chapter 1 an introduction to the human body ; chapter 2 the chemical level of organization ; chapter 3 the cellular level of organization ; chapter 4 the tissue level of organization ; chapter 5 the integumentary system ; chapter 6 bone tissue and the skeletal system ; chapter 7 axial skeleton. 3.1: the cell membrane. despite differences in structure and function, all living cells in multicellular organisms have a surrounding cell membrane. as the outer layer of your skin separates your body from its environment, the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) separates the inner contents of a cell from its exterior environment.

Chapter 3 The Cellular Level Of Organization Youtube Anatomy & physiology 1. chapter 1 an introduction to the human body ; chapter 2 the chemical level of organization ; chapter 3 the cellular level of organization ; chapter 4 the tissue level of organization ; chapter 5 the integumentary system ; chapter 6 bone tissue and the skeletal system ; chapter 7 axial skeleton. 3.1: the cell membrane. despite differences in structure and function, all living cells in multicellular organisms have a surrounding cell membrane. as the outer layer of your skin separates your body from its environment, the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) separates the inner contents of a cell from its exterior environment.

Comments are closed.