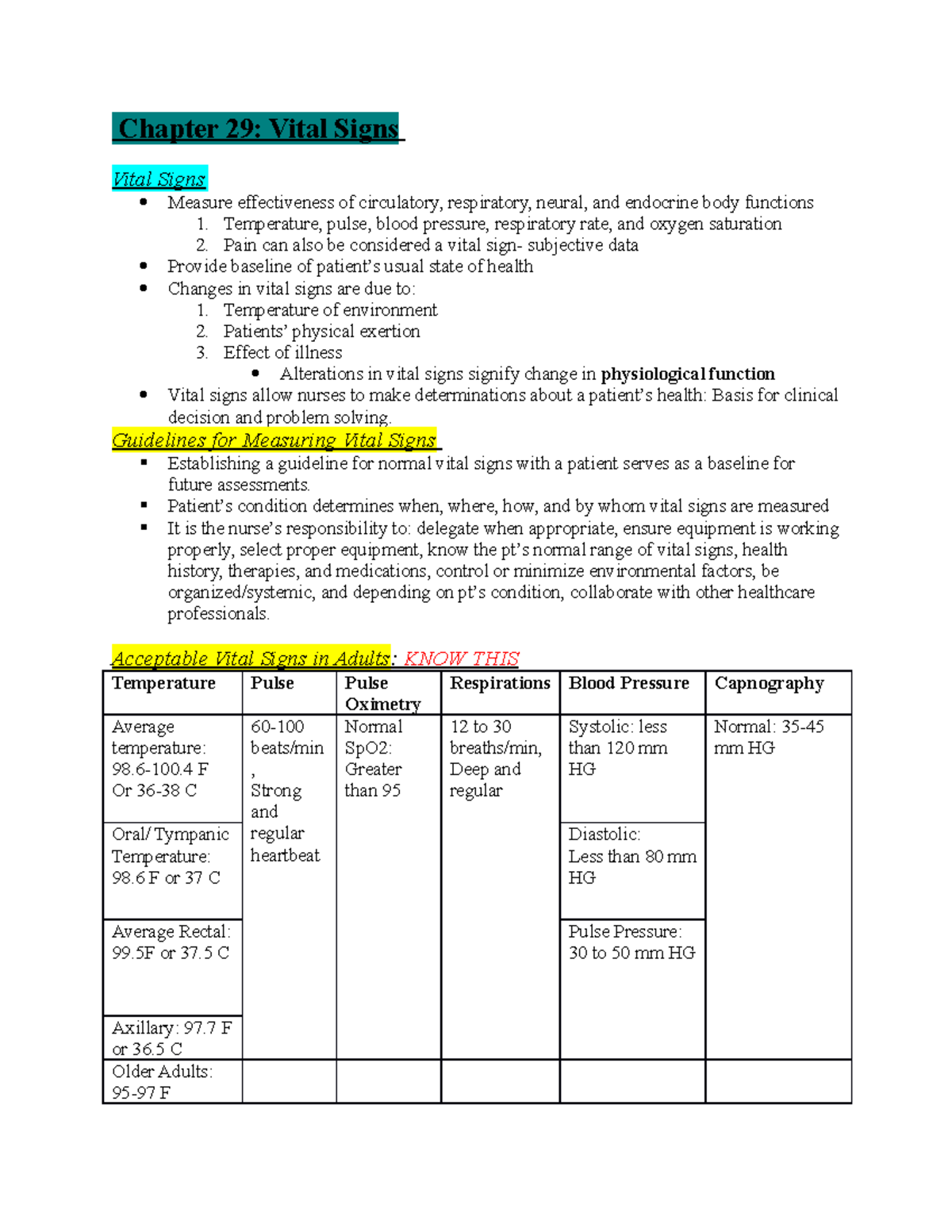
Chapter 29 Vital Signs Notes Chapter 29 Vital Signs Vital Signs
Chapter 29 Vital Signs Notes Chapter 29 Vital Signs Vital Signs 2)when a client has a change in health status or reports. symptoms such as chest pain or feeling hot or faint. 3)before and after surgery or an invasive procedure. 4)before and or after administration of a medicine that could affect the resp or cardio systems (ex:dig prep) 5)before and after any nursing intervention that could affect the vitals. Use vitals to determine indications for administering meds (ex: fever gets antipyretics) analyze the results of vital signs based on patient condition & past medical history verify & communicate significant changes in vital signs; if abnormal, have another nurse or provider repeat the measurement to verify reading.

Chapter 29 Notes Chapter 29 Vital Signs Test Bank Multiple Vital signs can be monitored every 5 to 10 minutes in patients with conditions worsening. can be used to determine indication for medication administration o example: certain cardiac drug only within a range of pulse or bp values analyze vital signs on basis of patient’s condition and past health history o communicate any changes in patients. B. tachypnea—regular, rapid respirations. c. kussmaul's—abnormally deep, regular, fast respirations. a nurse is assessing results of vital signs for a group of patients. match the condition to the assessment findings the nurse is reviewing. a. patient's temperature is 113° f (45° c) with hot, dry skin. b. Chapter 29: vital signs potter et al.: fundamentals of nursing, 10th edition multiple choice 1. a patient has a head injury and damages the hypothalamus. which vital sign will the nurse monitor most closely? a. pulse b. respirations c. temperature d. blood pressure ans: c. A. the nurse may delegate the measurement of vital signs but is responsible for analyzing and interpreting their significance and select appropriate interventions. b. equipment needs to be appropriate and functional. d. know the patient's usual range of vital signs. e. know the patient's medical history. f.

Ch 29 Vital Signs Skills Ch 29 Vital Signs Skills An Chapter 29: vital signs potter et al.: fundamentals of nursing, 10th edition multiple choice 1. a patient has a head injury and damages the hypothalamus. which vital sign will the nurse monitor most closely? a. pulse b. respirations c. temperature d. blood pressure ans: c. A. the nurse may delegate the measurement of vital signs but is responsible for analyzing and interpreting their significance and select appropriate interventions. b. equipment needs to be appropriate and functional. d. know the patient's usual range of vital signs. e. know the patient's medical history. f. A. attach a finger probe to the patient’s index finger. b. place a nonadhesive sensor on the patient’s earlobe. c. attach a disposable adhesive sensor to the bridge of the patient’s nose. d. place the sensor on the same arm that the electronic blood pressure cuff is on. Rationale: having the arm above heart level can cause an erroneous low bloodpressure result. having the cuff wrapped too loosely or unevenly, having thebladder cuff too narrow, and assessing immediately after a meal or while theclient smokes or has pain can cause an erroneous high blood pressure result. author.

Reviewer Chapter 29 Vital Signs Pdf Blood Pressure Fever A. attach a finger probe to the patient’s index finger. b. place a nonadhesive sensor on the patient’s earlobe. c. attach a disposable adhesive sensor to the bridge of the patient’s nose. d. place the sensor on the same arm that the electronic blood pressure cuff is on. Rationale: having the arm above heart level can cause an erroneous low bloodpressure result. having the cuff wrapped too loosely or unevenly, having thebladder cuff too narrow, and assessing immediately after a meal or while theclient smokes or has pain can cause an erroneous high blood pressure result. author.

Chapter 29 Vital Signs Flashcards Quizlet

Comments are closed.