Chart Prostate Cancer Stages Zero Prostate Cancer

Chart Prostate Cancer Stages Zero Prostate Cancer Stage iii (localized advanced) the cancer has spread beyond the prostate to nearby lymph glands or seminal vesicals. stage iv (metastatic advanced) the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as to the bones, liver, or lungs. if prostate cancer has metastasized to the bone, you have prostate cancer cells in the bone — not bone cancer. The prostate cancer grade is described using the gleason score. this score is used to estimate how aggressive the cancer may be—if and how quickly the tumor may grow and spread. the pathologist assigns a number to the cells based on how abnormal they appear. the scale goes from 1 (non aggressive) to 5 (very aggressive).

Stages Grading Overview Zero Prostate Cancer For prostate cancer there are 4 stages. often the stages 1 to 4 are written as the roman numerals i, ii, iii and iv. generally, the higher the stage number, the more the cancer has spread. the stages can be further divided into a, b or c. an earlier letter means a lower stage. The grade of the cancer corresponds to the pattern number. gleason patterns 1 and 2 look a lot like normal cells. gleason pattern 5 looks very abnormal compared to normal cells. gleason patterns 3 and 4 are somewhere in between. most prostate cancers have a gleason pattern of 3, 4 or 5. The main stages of prostate cancer range from i (1) through iv (4). some stages are split further (iia, iib, iic, etc.). as a rule, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. a higher number, such as stage iv, means cancer has spread more. and within a stage, an earlier letter means a lower stage. Cancer recurrence is the return of cancer after a period when no cancer cells could be detected. a fear of recurrence is normal for all cancer survivors. learn about prostate cancer recurrence rates, common symptoms, and treatment options. find strategies for coping with the fear of recurrence and navigating survivorship.
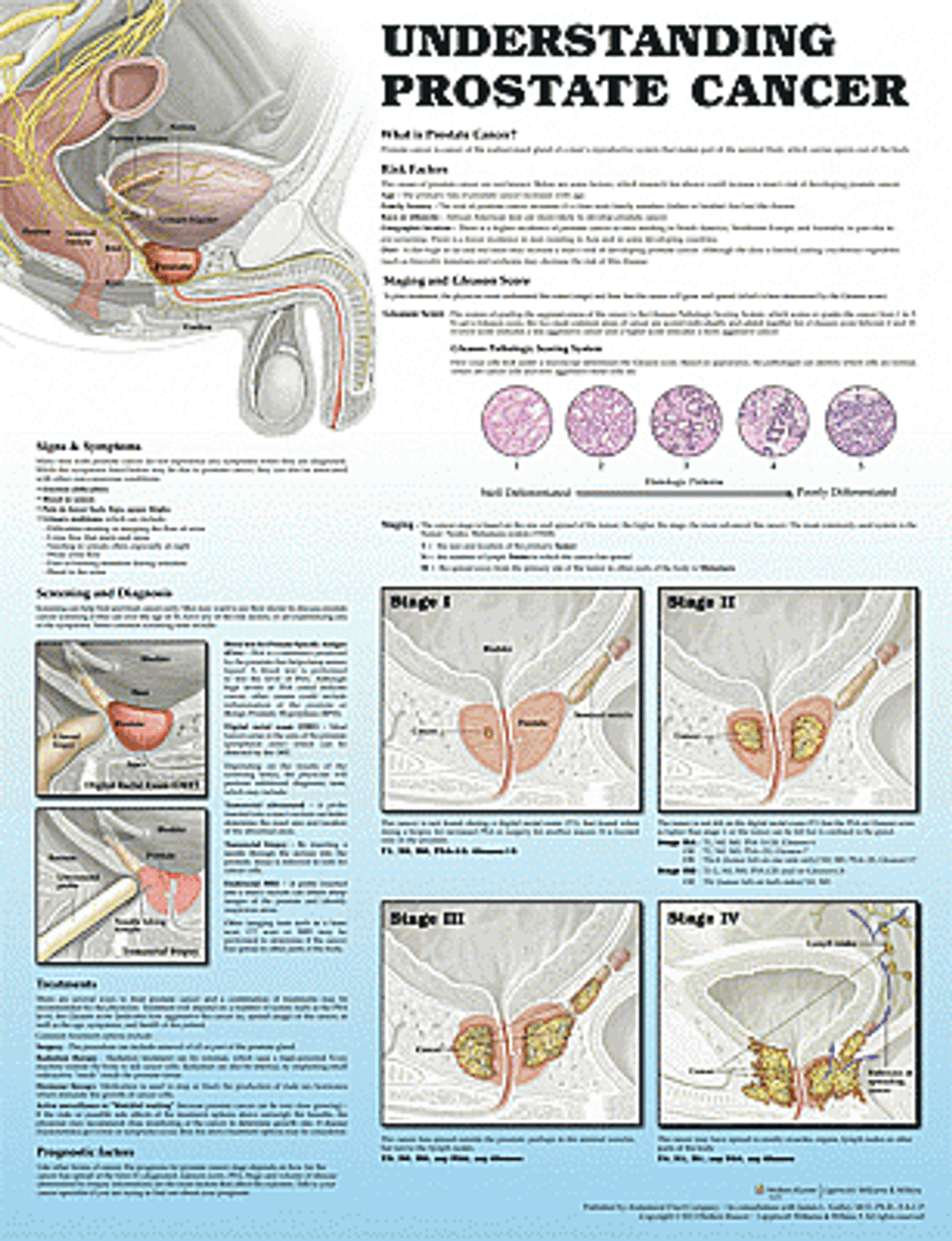
Understanding Prostate Cancer Poster Prostate Cancer Anatomical Chart The main stages of prostate cancer range from i (1) through iv (4). some stages are split further (iia, iib, iic, etc.). as a rule, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. a higher number, such as stage iv, means cancer has spread more. and within a stage, an earlier letter means a lower stage. Cancer recurrence is the return of cancer after a period when no cancer cells could be detected. a fear of recurrence is normal for all cancer survivors. learn about prostate cancer recurrence rates, common symptoms, and treatment options. find strategies for coping with the fear of recurrence and navigating survivorship. Unfavorable intermediate risk group. initial treatment options for men with cancers in this risk group might include: surgery (radical prostatectomy, along with the removal of nearby lymph nodes) external radiation therapy plus hormone therapy. external radiation plus brachytherapy (possibly along with hormone therapy) if surgery is done and it. The following clinical stages are used to describe prostate cancer: t1: the tumor cannot be felt during the dre or seen during imaging (e.g., a computed tomography (ct) scan or transrectal ultrasound). it may be found when surgery is done for another medical condition. t1a: the tumor is discovered accidentally during a surgical procedure used.
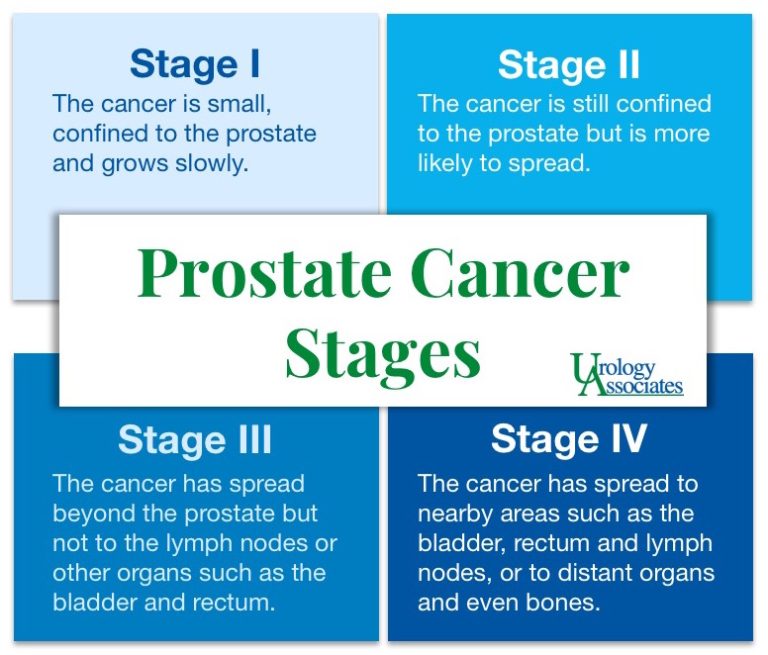
Prostate Cancer Stages Options Urology Associates Co Unfavorable intermediate risk group. initial treatment options for men with cancers in this risk group might include: surgery (radical prostatectomy, along with the removal of nearby lymph nodes) external radiation therapy plus hormone therapy. external radiation plus brachytherapy (possibly along with hormone therapy) if surgery is done and it. The following clinical stages are used to describe prostate cancer: t1: the tumor cannot be felt during the dre or seen during imaging (e.g., a computed tomography (ct) scan or transrectal ultrasound). it may be found when surgery is done for another medical condition. t1a: the tumor is discovered accidentally during a surgical procedure used.

Comments are closed.