Chemistry Unit Two Matter And Energy Temperature And Kinetics

Chemistry Unit 2 Matter And Energy Matter Introductory Chemistry unit 2: matter and energy. get a hint. physical property. click the card to flip 👆. a characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance. ex: density, solubility, conductivity, melting point, boiling point click the card to flip 👆. 1 36. 1. matter is a substance that occupies a space and has. 2. what are the three states in which matter is commonly found. solids, liquids, and gases. 3. is the term used for water when it is in the solid state. 4. in what direction does a solid exert force. upwards or downwards.
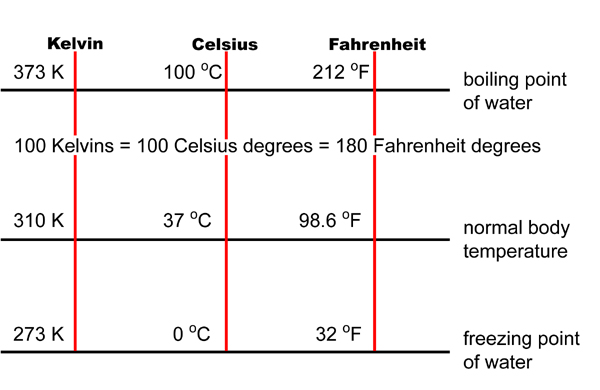
Temperature Conversion Table C F K Cabinets Matttroy Its newly acquired potential energy begins to re appear as kinetic energy as it accelerates downward at a velocity increasing by 9.8 m sec every second (9.8 m sec –2 or 32 ft sec –2). at the instant it strikes the surface, the potential energy you gave supplied to the book has now been entirely converted into kinetic energy. The kelvin temperature of a substance is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of the particles of the substance. for example, the particles in a sample of hydrogen gas at 200 k 200 k have twice the average kinetic energy as the particles in a hydrogen sample at 100 k 100 k. figure 13.5.3 13.5. 3: helium gas liquefies at 4k 4 k. T k = t c 273 or t k – 273 = t c. (remember that there is no degree symbol (°) for kelvin!) how do temperatures in fahrenheit, celsius, and kelvin relate? practice problems. answer the following questions: 1. the temperature of a room is set at 22°c. if that temperature is lowered by 1°c, it can save as much as 5% in energy costs. what. Energy. the capacity to do some kind of work. examples: moving an object, forming a new compound, or generating light. physical changes in energy. affects only the physical properties of matter. examples: ice melting, water boiling only the physical state of the substance changes to a solid, liquid, or gas. chemical changes in energy.

Comments are closed.