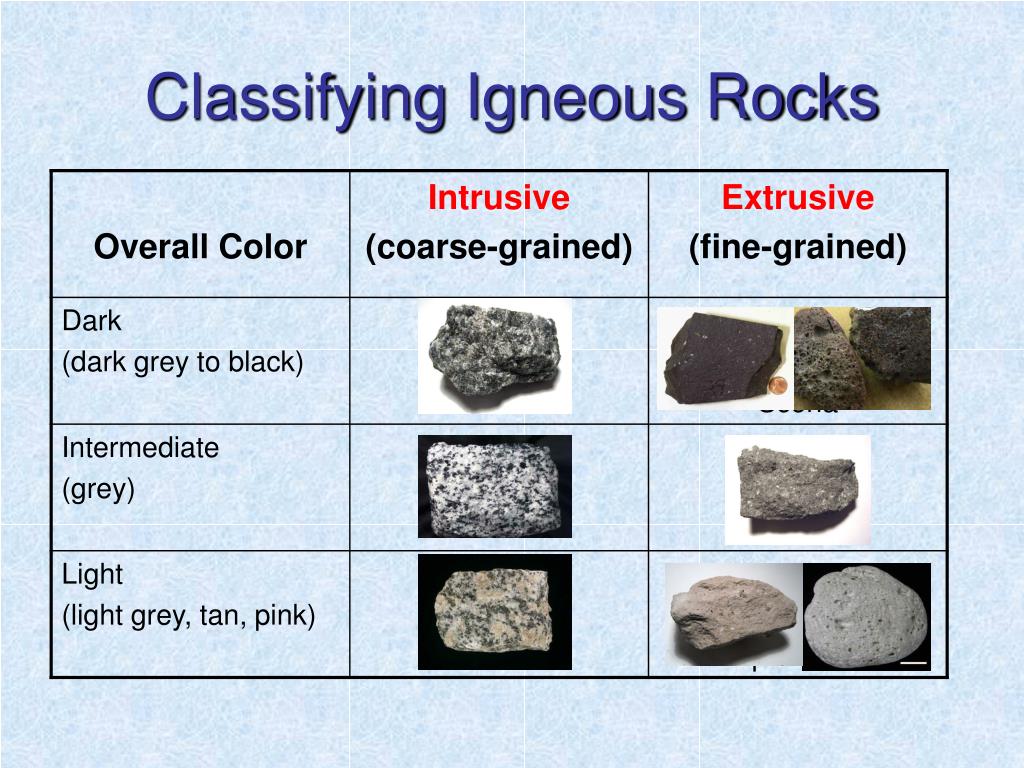
Classifying Igneous Rocks

Classifying Igneous Rocks Figure 4.1.1 4.1. 1: granite is a classic coarse grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock. the different colors are unique minerals. the black colors are likely two or three different minerals. if magma cools slowly, deep within the crust, the resulting rock is called intrusive or plutonic. The classification of igneous rocks based on composition revolves around the silica (sio 2) content and the proportion of various minerals present in the rock. this classification categorizes igneous rocks into four primary groups: felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic.
Classifying Igneous Rocks Classifying igneous rocks according to the proportion of dark minerals. if you’re unsure of which minerals are present in an intrusive igneous rock, there’s is a quick way to approximate the composition of that rock. in general, igneous rocks have an increasing proportion of dark minerals as they become more mafic (figure 7.16). Classifying igneous rocks according to the proportion of dark minerals. if you unsure of which minerals are present in an intrusive igneous rock, there is a quick way to approximate the composition of that rock. in general, igneous rocks have an increasing proportion of dark minerals as they become more mafic (figure 4.16). Classifying igneous rocks according to the proportion of dark minerals. if you unsure of which minerals are present in an intrusive igneous rock, there is a quick way to approximate the composition of that rock. in general, igneous rocks have an increasing proportion of dark minerals as they become more mafic (figure 7.16). As has already been described, igneous rocks are classified into four categories, based on either their chemistry or their mineral composition: felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic. the diagram in figure 3.16 can be used to help classify igneous rocks by their mineral composition. an important feature to note on this diagram is the red.

General Classification Of Igneous Rocks Classifying igneous rocks according to the proportion of dark minerals. if you unsure of which minerals are present in an intrusive igneous rock, there is a quick way to approximate the composition of that rock. in general, igneous rocks have an increasing proportion of dark minerals as they become more mafic (figure 7.16). As has already been described, igneous rocks are classified into four categories, based on either their chemistry or their mineral composition: felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic. the diagram in figure 3.16 can be used to help classify igneous rocks by their mineral composition. an important feature to note on this diagram is the red. Igneous rock, any of various crystalline or glassy rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of molten earth material. igneous rocks constitute one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary. igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to. Grain size in igneous rocks results from cooling time so porphyritic rocks are created when the magma has two distinct phases of cooling. [18] igneous rocks are classified on the basis of texture and composition. texture refers to the size, shape, and arrangement of the mineral grains or crystals of which the rock is composed. [citation needed].

Comments are closed.