Common Routs Of Entry For Listeria In Food Processing Facilities

Common Routs Of Entry For Listeria In Food Processing Facilities Figure 3 summarizes the most common routs of entry of environmental listeria into food processing facilities. in detail, the importance of food handling practices within the food facility, the compliance to good manufacturing practices in terms of worker hygiene and pest control, and the role l. monocytogenes transmission by wild and domestic. Download scientific diagram | | common routs of entry for listeria in food processing facilities. from publication: the saprophytic lifestyle of listeria monocytogenes and entry into the food.
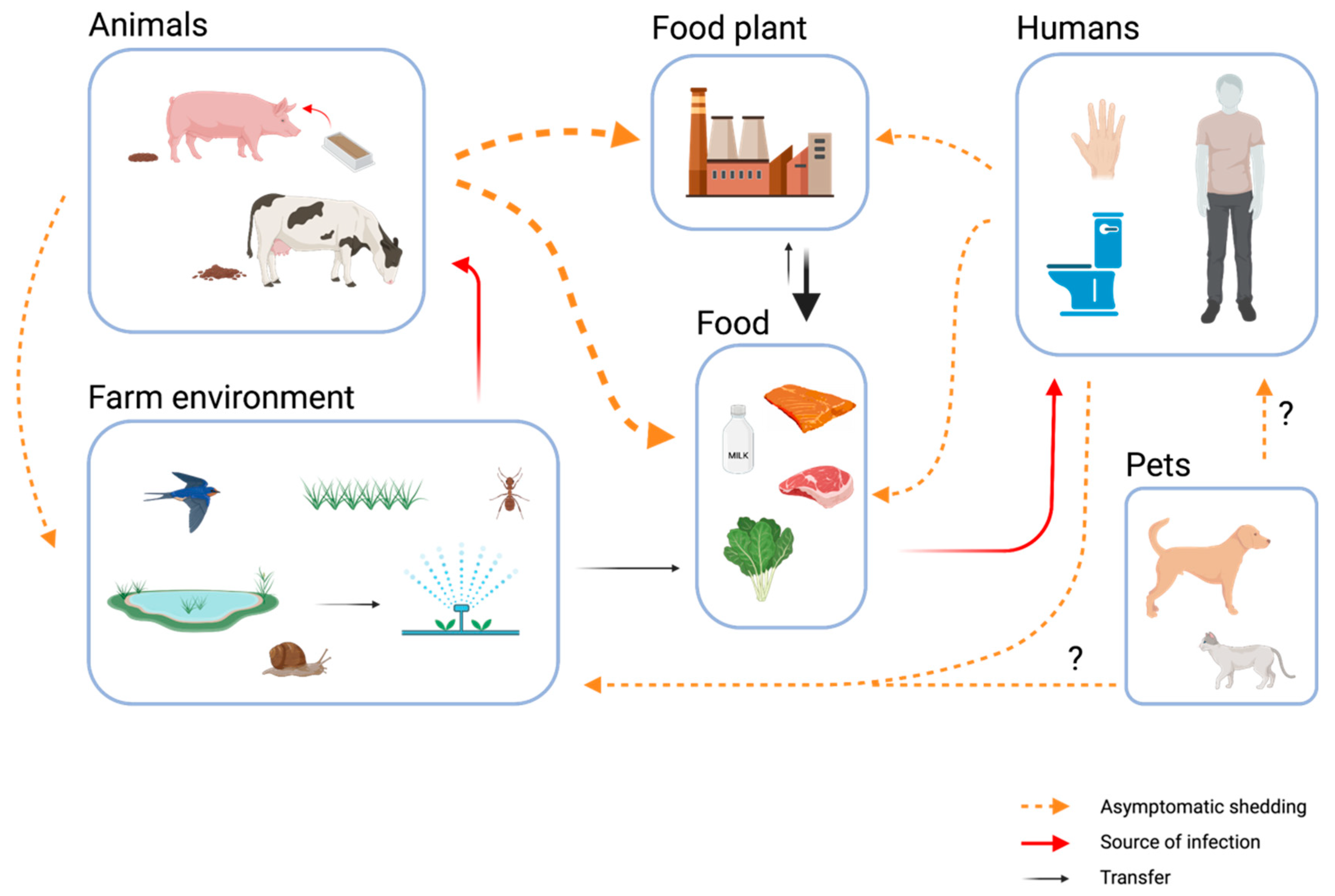
Foods Free Full Text Asymptomatic Carriage Of Listeria Common routs of entry for listeria in food processing facilities. figure 3 common routs of entry for listeria in food processing facilities. The foodborne pathogen listeria monocytogenes is the causative agent of human listeriosis, a severe disease, especially dangerous for the elderly, pregnant women, and newborns. although this infection is comparatively rare, it is often associated with a significant mortality rate of 20–30% worldwide. therefore, this microorganism has an. 2. establish a swabbing site map of all the locations on the equipment that, if not effectively cleaned, can result in product contamination or harborage. 3. operate the equipment with product for a full and normal production run: 8–16–20 hours if that is the usual run time. 4. Purpose of review listeria monocytogenes is a foodborne pathogen that causes listeriosis, a relatively rare but potentially fatal disease with a 19% mortality rate and a 99% hospitalisation rate. it affects mainly elderly and immunocompromised individuals. ready to eat (rte) foods are particularly dangerous with regard to l. monocytogenes as there is no further anti microbial step between.
Frontiers The Saprophytic Lifestyle Of Listeria Monocytogenes And 2. establish a swabbing site map of all the locations on the equipment that, if not effectively cleaned, can result in product contamination or harborage. 3. operate the equipment with product for a full and normal production run: 8–16–20 hours if that is the usual run time. 4. Purpose of review listeria monocytogenes is a foodborne pathogen that causes listeriosis, a relatively rare but potentially fatal disease with a 19% mortality rate and a 99% hospitalisation rate. it affects mainly elderly and immunocompromised individuals. ready to eat (rte) foods are particularly dangerous with regard to l. monocytogenes as there is no further anti microbial step between. In addition to summarizing the existing knowledge on listeria persistence in food processing facilities, this review also delineates additional research needs, such as studies on listeria persistence in produce operations and studies that identify risk factors for persistence as well as successful intervention strategies (i.e., corrective. The preventive controls for human foods under the u.s. food safety modernization act (fsma) mandate related food facilities to establish and implement preventive controls, including sanitation controls, to ensure the food processing environment is kept in a sanitary condition and to minimize or prevent contamination by environmental pathogens.

Comments are closed.