Comparing Foil Vs Box Method For Multiplying Binomials Or Polynomials

Comparing Foil Vs Box Method For Multiplying Binomials Or Polynomials Multiplying binomials with the foil or box methods gives different opinions from students and teachers. i thought it might be interesting to see them side. To multiply binomials using foil, you must follow these steps: note that foil is an acronym that stands for first outer inner last. first: multiply the first terms of each binomial together. in this case: 8 x 8 = 64. outer: multiply the outer terms of each binomial together. in this case: 8 x 5x = 40x. inner: multiply the inner terms of each.
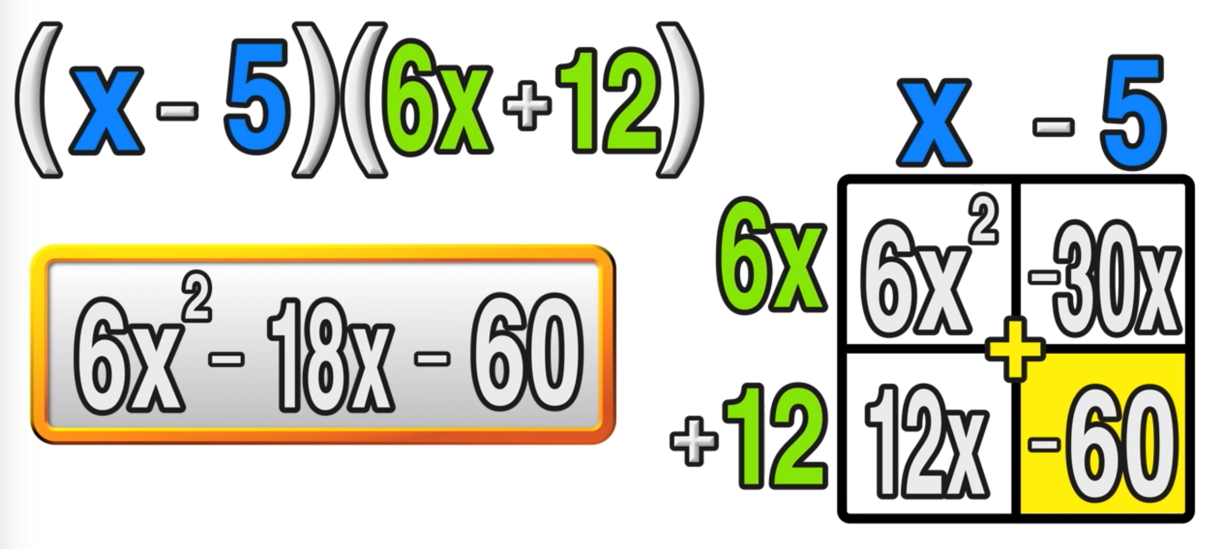
Complete Guide To Multiplying Binomials Foil Method And Box Methodо Foil. method to multiply the following binomials: (y 3)(y 7) (y 3)(y 7) f tells you to multiply the first terms of each binomial. y2. (y 3)(y 7) o tells you to multiply the outer terms of each binomial. y2 7y. (y 3)(y 7) i tells you to multiply the inner terms of each binomial. y2 7y 3y. Box method: draw a box with four squares. place the binomials on the outside of the boxes. 3x 5 2x 7 . multiply terms: 3x 5 2x . 2x·3x . 2x( 5). Multiplication of binomials and polynomials requires an understanding of the distributive property, rules for exponents, and a keen eye for collecting like terms. whether the polynomials are monomials, binomials, or trinomials, carefully multiply each term in one polynomial by each term in the other polynomial. Example 10.5.17 10.5. 17: multiply using the vertical method: (x 3) (2x 2 − 5x 8). solution. it is easier to put the polynomial with fewer terms on the bottom because we get fewer partial products this way. multiply (2x 2 − 5x 8) by 3. multiply (2x 2 − 5x 8) by x. add like terms.

Multiply Binomials Foil Method Polynomials Algebra 1 Eat Pi Multiplication of binomials and polynomials requires an understanding of the distributive property, rules for exponents, and a keen eye for collecting like terms. whether the polynomials are monomials, binomials, or trinomials, carefully multiply each term in one polynomial by each term in the other polynomial. Example 10.5.17 10.5. 17: multiply using the vertical method: (x 3) (2x 2 − 5x 8). solution. it is easier to put the polynomial with fewer terms on the bottom because we get fewer partial products this way. multiply (2x 2 − 5x 8) by 3. multiply (2x 2 − 5x 8) by x. add like terms. This video explains multiplying binomials focusing on using the box method (area model) but foil and distribution methods are also explained.the box method p. Foil (the acronym for first, outer, inner and last) method is an efficient way of remembering how to multiply two binomials in a very organized manner. the word foil is an acronym that stands for : to put this in perspective, suppose we want to multiply two arbitrary binomials, [latex]\left( {a b} \right)\left( {c d} \right)[ latex].

Complete Guide To Multiplying Binomials Foil Method And Box Methodо This video explains multiplying binomials focusing on using the box method (area model) but foil and distribution methods are also explained.the box method p. Foil (the acronym for first, outer, inner and last) method is an efficient way of remembering how to multiply two binomials in a very organized manner. the word foil is an acronym that stands for : to put this in perspective, suppose we want to multiply two arbitrary binomials, [latex]\left( {a b} \right)\left( {c d} \right)[ latex].

Comments are closed.