Conic Sections Hyperbola Find Equation Given Foci And Vertices Y

Conic Sections Hyperbola Find Equation Given Foci And V This calculator will find either the equation of the hyperbola from the given parameters or the center, foci, vertices, co vertices, (semi)major axis length, (semi)minor axis length, latera recta, length of the latera recta (focal width), focal parameter, eccentricity, linear eccentricity (focal distance), directrices, asymptotes, x intercepts, y intercepts, domain, and range of the entered. Thanks to all of you who support me on patreon. you da real mvps! $1 per month helps!! 🙂 patreon patrickjmt !! conic sections, hyperbola:.

Equations And Formula Of Conic Sections Directrix. a directrix (plural: directrices) is a line used to construct and define a conic section; a parabola has one directrix; ellipses and hyperbolas have two. discriminant. the value \ (4ac−b^2\), which is used to identify a conic when the equation contains a term involving \ (xy\), is called a discriminant. In analytic geometry, a hyperbola is a conic section formed by intersecting a right circular cone with a plane at an angle such that both halves of the cone are intersected. this intersection produces two separate unbounded curves that are mirror images of each other (figure 10.2.2). figure 10.2.2: a hyperbola. Identifying the conic sections. in this section, the challenge is to identify a conic section given its equation in general form. to distinguish between the conic sections, use the exponents and coefficients. if the equation is quadratic in only one variable and linear in the other, then its graph will be a parabola. The equations of the asymptotes are y = ±b ax y = ± b a x. the standard form of the equation of a hyperbola with center (0,0) (0, 0) and transverse axis on the y axis is. y2 a2 − x2 b2 =1 y 2 a 2 − x 2 b 2 = 1. where. the length of the transverse axis is 2a 2 a. the coordinates of the vertices are (0,±a) (0, ± a).

The Hyperbola в Precalculus Identifying the conic sections. in this section, the challenge is to identify a conic section given its equation in general form. to distinguish between the conic sections, use the exponents and coefficients. if the equation is quadratic in only one variable and linear in the other, then its graph will be a parabola. The equations of the asymptotes are y = ±b ax y = ± b a x. the standard form of the equation of a hyperbola with center (0,0) (0, 0) and transverse axis on the y axis is. y2 a2 − x2 b2 =1 y 2 a 2 − x 2 b 2 = 1. where. the length of the transverse axis is 2a 2 a. the coordinates of the vertices are (0,±a) (0, ± a). It may be shown that the equation of the hyperbola is given by $\frac{y^2}{a^2} \frac{x^2}{b^2} = 1, where \space c^2 = a^2 b^2$ hyperbolas have many useful applications, one of which is their use in navigation systems to determine the location of a ship. Example: the equation of the hyperbola is given as (x 5) 2 4 2 (y 2) 2 2 2 = 1. use the hyperbola formulas to find the length of the major axis and minor axis. solution: using the hyperbola formula for the length of the major and minor axis. length of major axis = 2a, and length of minor axis = 2b.
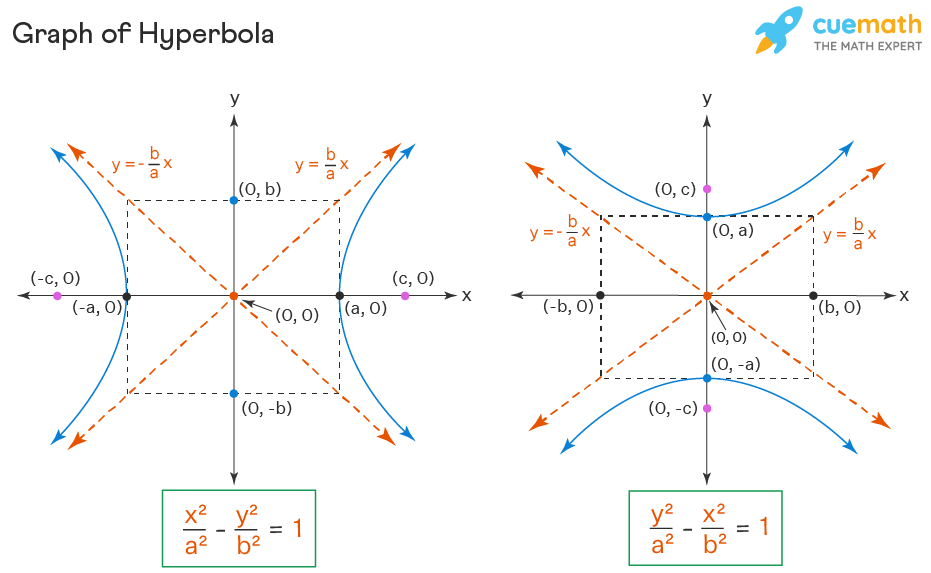
Hyperbola Equation Properties Examples Hyperbola Formula It may be shown that the equation of the hyperbola is given by $\frac{y^2}{a^2} \frac{x^2}{b^2} = 1, where \space c^2 = a^2 b^2$ hyperbolas have many useful applications, one of which is their use in navigation systems to determine the location of a ship. Example: the equation of the hyperbola is given as (x 5) 2 4 2 (y 2) 2 2 2 = 1. use the hyperbola formulas to find the length of the major axis and minor axis. solution: using the hyperbola formula for the length of the major and minor axis. length of major axis = 2a, and length of minor axis = 2b.

Comments are closed.