Consumer Protection In Marketing
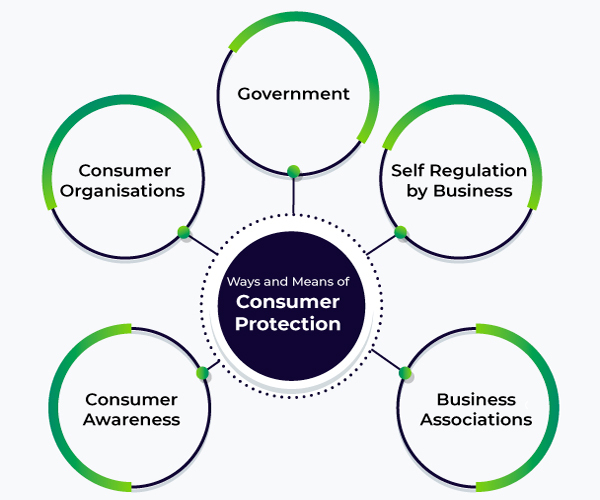
Consumer Protection Meaning Importance And Means Geeksforgeeks The ftc’s bureau of consumer protection stops unfair, deceptive and fraudulent business practices by collecting reports from consumers and conducting investigations, suing companies and people that break the law, developing rules to maintain a fair marketplace, and educating consumers and businesses about their rights and responsibilities. Consumer protection is the practice of safeguarding buyers of goods and services, and the public, against unfair practices in the marketplace. consumer protection measures are often established by law. such laws are intended to prevent businesses from engaging in fraud or specified unfair practices to gain an advantage over competitors or to.

Product Safety Consumer Protection Deceptive Marketing Ppt Download Certain consumer protection laws can help in particular situations. the controlling the assault of non solicited pornography and marketing act of 2003 is a law that governs email communication. Truth in advertising. when the federal trade commission finds a case of fraud perpetrated on consumers, the agency files actions in federal district court for immediate and permanent orders to stop scams; prevent fraudsters from perpetrating scams in the future; freeze their assets; and get compensation for victims.when consumers see or hear an. Online advertising and marketing. the internet connects marketers to customers across the country and around the world. if you advertise online, remember the rules and guidelines that protect consumers also help businesses by maintaining the credibility of the internet as a marketing medium. in addition, truth in advertising standards apply if. Summary. consumer protection policy seeks to mitigate information asymmetries between providers and consumers and other factors, such as limited bargaining power and digital literacy, that impede consumer choice, and to provide protections for vulnerable consumers. many of these factors are exacerbated in digital commerce where consumers may.

Comments are closed.