Copd Abstract Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Emphysema
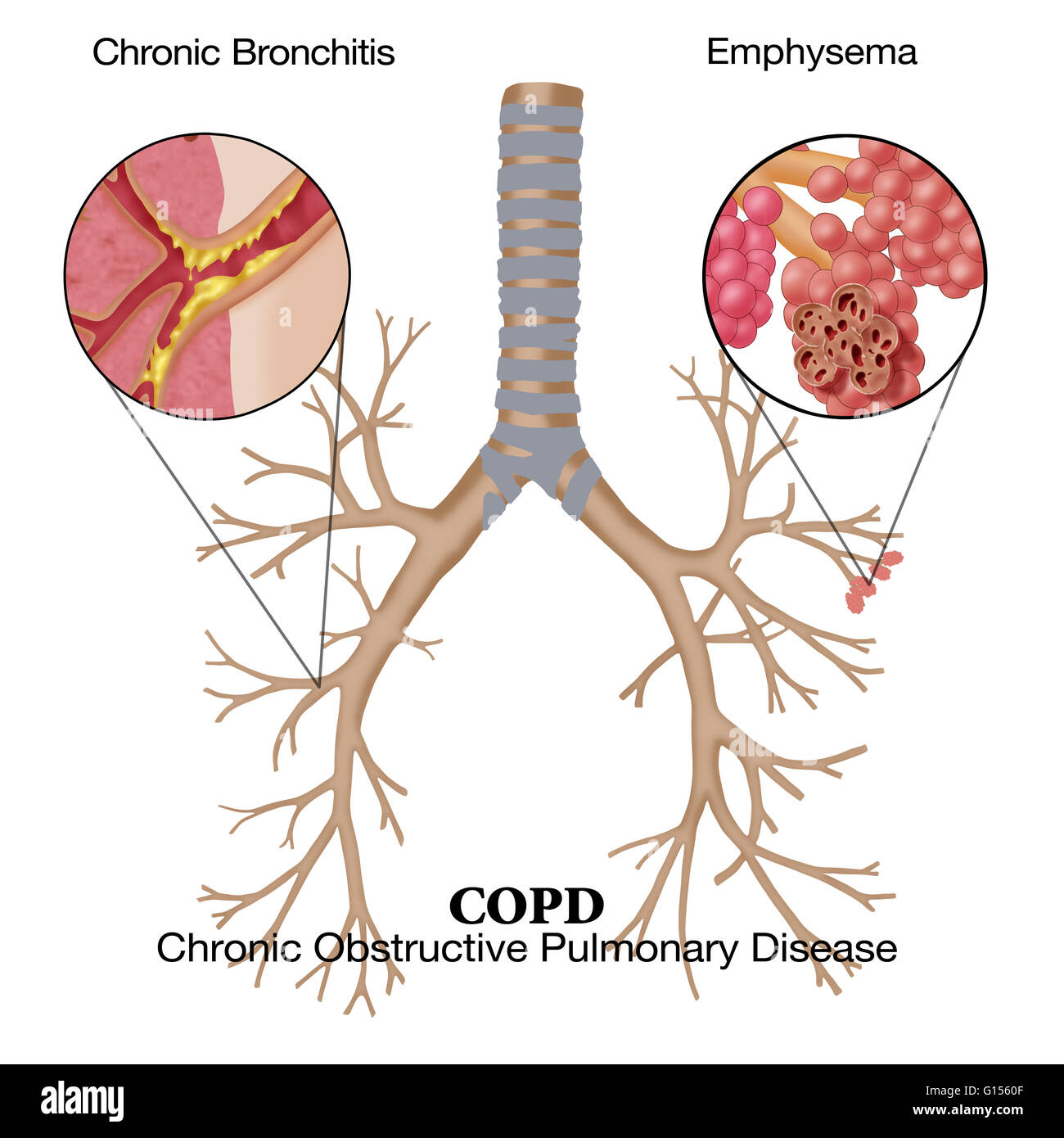
Illustration Of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Copd A Stock Abstract. chronic bronchitis (cb) is a common but variable phenomenon in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd). it has numerous clinical consequences, including an accelerated decline in lung function, greater risk of the development of airflow obstruction in smokers, a predisposition to lower respiratory tract infection, higher. Abstract. chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) is a common respiratory disorder with significant morbidity and mortality. despite its prevalence, copd is underdiagnosed, and many patients do not receive a diagnosis until the disease is clinically advanced. recent basic science and clinical research have focused on the early physiologic.
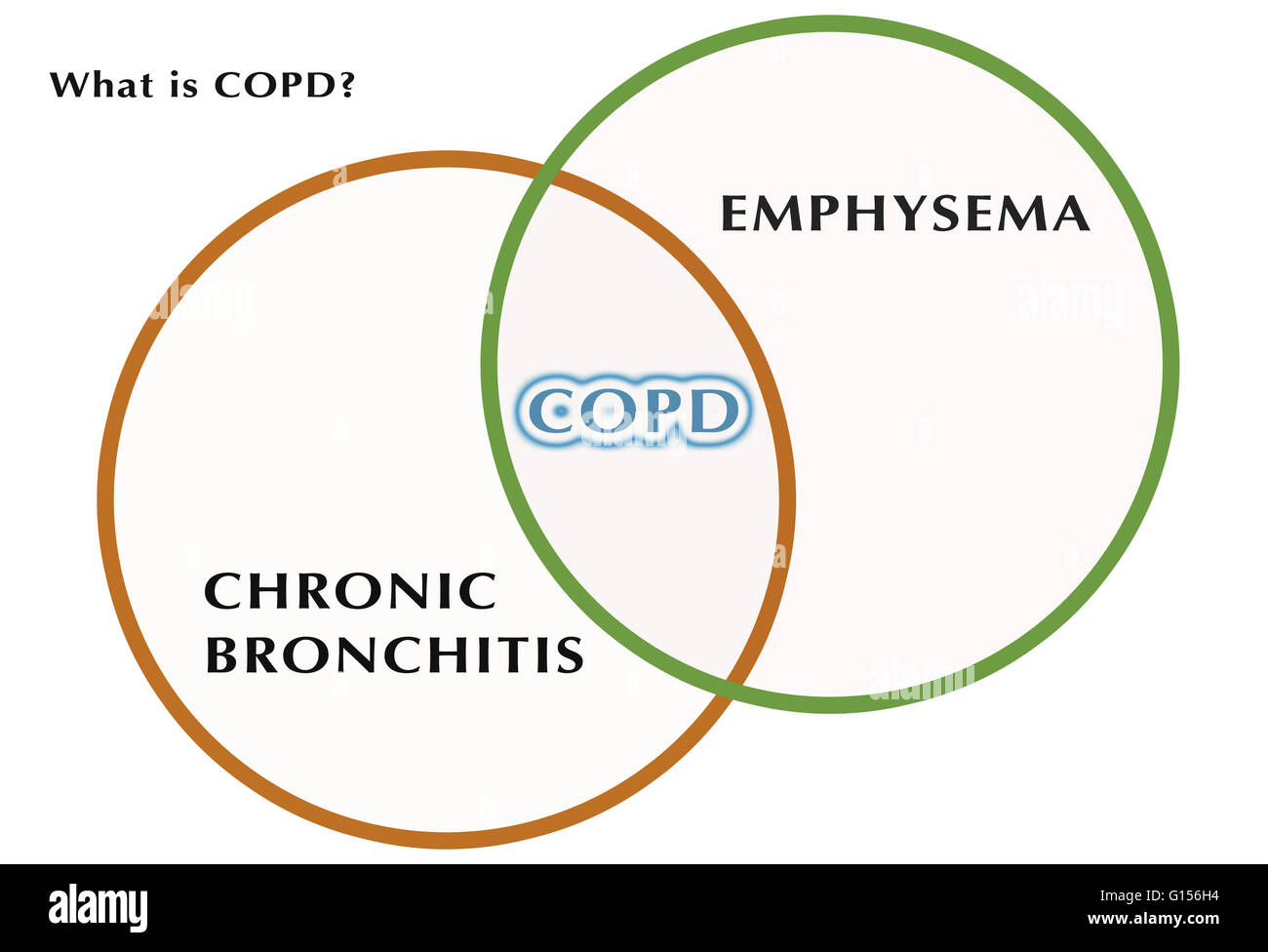
Diagram Showing The Relationship Between Chronic Bronchitis Copd Abstract. chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) is a common disease with high global morbidity and mortality. copd is characterized by poorly reversible airway obstruction, which is. A hallmark of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) is the chronic obstruction of the airways. copd is a progressive condition caused by inhalation of toxic particles or gases [ 1 , 2 ]. tobacco smoking and inhalation of other pollutants are the leading causes of copd [ 3 , 4 , 5 ]. The aim of this review is to update and synthesize the molecular mechanisms that lead to the heterogeneous effect on tissue remodeling observed in the two most important clinical phenotypes of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd), pulmonary emphysema (pe) and chronic bronchitis (cb). clinica …. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) has increasingly been identified as a major cause of death worldwide. 1 substantial variation in onset, progression, and lung function trajectories at different life stages across populations limits understanding of copd predisposing factors. 2 however, tobacco smoking and exposure to indoor air pollution (including from biomass combustion), ambient.

Copd Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease And Emphysema The aim of this review is to update and synthesize the molecular mechanisms that lead to the heterogeneous effect on tissue remodeling observed in the two most important clinical phenotypes of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd), pulmonary emphysema (pe) and chronic bronchitis (cb). clinica …. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) has increasingly been identified as a major cause of death worldwide. 1 substantial variation in onset, progression, and lung function trajectories at different life stages across populations limits understanding of copd predisposing factors. 2 however, tobacco smoking and exposure to indoor air pollution (including from biomass combustion), ambient. Abstract. chronic bronchitis and (pulmonary) emphysema are two respiratory disorders with similar patterns of symptoms: shortness of breath (dyspnea), sputum production, coughing and chest. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) is a common, preventable, and controllable respiratory disease characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation, typically resulting from long term damage and chronic inflammatory responses in the lungs and or airways. the complexity and variability of pathological changes with copd make it a focal point in basic research and.

Comments are closed.