Curing Taste Disorders

Curing Taste Disorders Youtube Dysgeusia is a taste disorder. people with this condition feel that all foods taste metallic, sweet, sour or bitter. many things can cause dysgeusia, like smoking, medical conditions, medication or poor oral hygiene. treatment addresses the underlying cause, like quitting smoking, changing medication or improving oral hygiene. 410 955 5000 maryland. 855 695 4872 outside of maryland. 1 410 502 7683 international. smell and taste disorders may include loss of smell or taste or reduced ability to smell or taste. it can be caused by certain underlying conditions or illness, medicines, and dental problems. some people are born with these disorders.
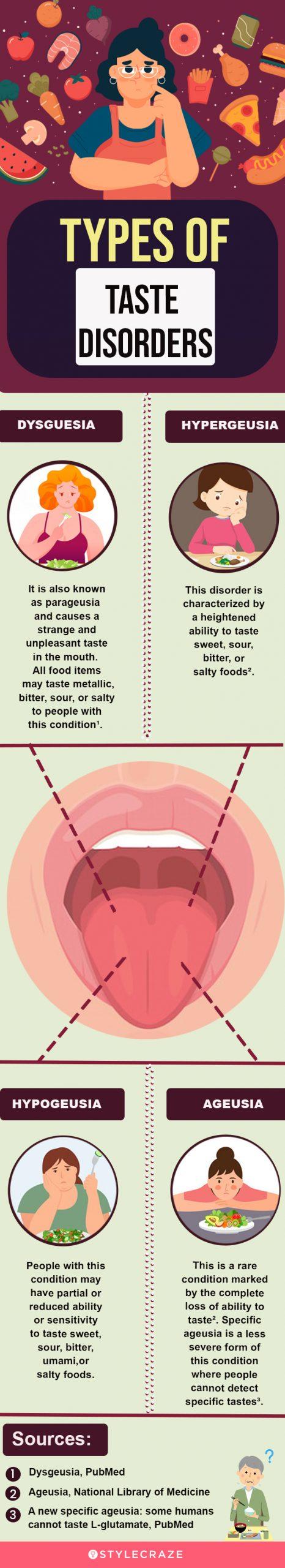
11 Home Remedies For Bad Taste In The Mouth Causes Symptoms Impaired taste can be caused by smell disorders, nutritional deficiencies, and some medications. smoking, gum inflammation, and certain types of infections or other health conditions can also. Most often, people are experiencing a loss of smell instead of a loss of taste. in other disorders of the chemical senses, an odor, a taste, or a flavor may be distorted. dysgeusia [dis gyoo zee a] is a condition in which a foul, salty, rancid, or metallic taste sensation persists in the mouth. dysgeusia is sometimes accompanied by burning. Dysgeusia is a condition where a person’s perception of taste is altered; everything seems sweet, sour, bitter, or metallic. taste disorders are common in adults. a study performed on adults in the united states indicated that up to 17 percent of those tested had some impairment in taste. impaired taste can take many forms, including:. Possible causes of taste disorders and a loss of taste can include: upper respiratory infections, such as the common cold. covid 19. sinus infections. middle ear infections. poor oral hygiene and.

Overview Of The Current Most Frequently Encountered Differential Dysgeusia is a condition where a person’s perception of taste is altered; everything seems sweet, sour, bitter, or metallic. taste disorders are common in adults. a study performed on adults in the united states indicated that up to 17 percent of those tested had some impairment in taste. impaired taste can take many forms, including:. Possible causes of taste disorders and a loss of taste can include: upper respiratory infections, such as the common cold. covid 19. sinus infections. middle ear infections. poor oral hygiene and. Taste disorders include: dysgeusia [dis gyoo zee a], a condition in which a foul, salty, rancid, or metallic taste persists in your mouth. dysgeusia is sometimes accompanied by burning mouth syndrome, which is characterized by a painful burning sensation in your mouth. hypogeusia [hy po gyoo zee a], in which your ability to taste is reduced. The senses of smell and taste. the processes of smelling and tasting are complex. they begin when molecules are released into the air we breathe or dissolve into our saliva or nasal mucus from fragrances or foods. these molecules then stimulate the sensory cells in the nose, mouth, or throat. olfactory nerve cells are stimulated by odors.

Figure 2 From From The Cover Drug Induced Taste Disorders In Clinical Taste disorders include: dysgeusia [dis gyoo zee a], a condition in which a foul, salty, rancid, or metallic taste persists in your mouth. dysgeusia is sometimes accompanied by burning mouth syndrome, which is characterized by a painful burning sensation in your mouth. hypogeusia [hy po gyoo zee a], in which your ability to taste is reduced. The senses of smell and taste. the processes of smelling and tasting are complex. they begin when molecules are released into the air we breathe or dissolve into our saliva or nasal mucus from fragrances or foods. these molecules then stimulate the sensory cells in the nose, mouth, or throat. olfactory nerve cells are stimulated by odors.

Overview Of The Current Most Frequently Encountered Differential

Comments are closed.