Definition Prime And Composite Properties Divisor Media4math

Definition Prime And Composite Properties Divisor Media4math Definition prime and composite properties divisor this is a collection of definitions related to prime and composite numbers. this includes general definitions for primes and composites, as well as related terms around factors, divisibility rules, area models for primes and composites, and the fundamental theorem of arithmetic. Here are the first ten prime numbers: 2, 3, 5 7, 11, 13, 17 19, 23, 29. notice that all of them, except for 2, are odd numbers. 2 is the only even prime number. also, notice that 1 isn't prime. it does seem to follow the rule that it's only divisible by 1 and itself. the difference is that 1 only has one factor.
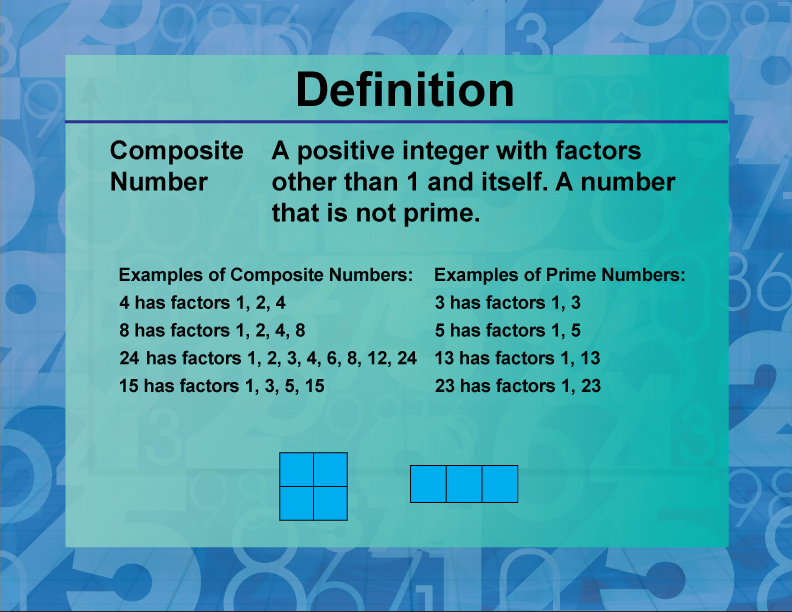
Definition Prime And Composite Properties Composite Number Media4ma Prime factors are the prime numbers that when multiplied together give a particular result. description. prime factors play a crucial role in the study of prime and composite numbers. a prime factor is a factor that is a prime number, one of the building blocks of all numbers. for example, the prime factors of 12 are 2 and 3, because 2 • 2. Definition of prime numbers: a prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has exactly two factors: 1 and itself. odd composite numbers: many odd numbers have factors other than 1 and themselves, making them composite. for example: 9 = 3 × 3. 15 = 3 × 5. 21 = 3 × 7. 25 = 5 × 5. 27 = 3 × 3 × 3. pattern of odd composites: in fact. A useful tool for helping with prime factorization is a factor tree. to create a factor tree for the natural number n n (where n n is not 1), perform the following steps: step 1: if n n is prime, you're done. if n n is composite, continue to the next step. step 2: identify two divisors of n n, call them a a and b b. At least three elements are present in numbers bigger than one. the least but only even prime number is 2. the smallest composite number is 4. prime numbers include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, and so on are examples of composite numbers. there is no even prime numbers except 2.

Definition Prime And Composite Properties Divisibility Rule For 2 A useful tool for helping with prime factorization is a factor tree. to create a factor tree for the natural number n n (where n n is not 1), perform the following steps: step 1: if n n is prime, you're done. if n n is composite, continue to the next step. step 2: identify two divisors of n n, call them a a and b b. At least three elements are present in numbers bigger than one. the least but only even prime number is 2. the smallest composite number is 4. prime numbers include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, and so on are examples of composite numbers. there is no even prime numbers except 2. And the composite numbers are made up of prime numbers multiplied together. here we see it in action: 2 is prime, 3 is prime, 4 is composite (=2×2), 5 is prime, and so on example: 12 is made by multiplying the prime numbers 2, 2 and 3 together. 12 = 2 × 2 × 3. the number 2 was repeated, which is ok. 13 is a prime number, so, it is the one and only prime factor of itself. hence, answer is 13. practice questions on prime and composite numbers. here are some practice questions problems based on prime and composite numbers: q1. is 1 a composite number? q2. check whether 23 is a prime number. q3. check whether 56 is a prime number. q4.

Comments are closed.