Definition Vector Concepts Normal Vector Media4math
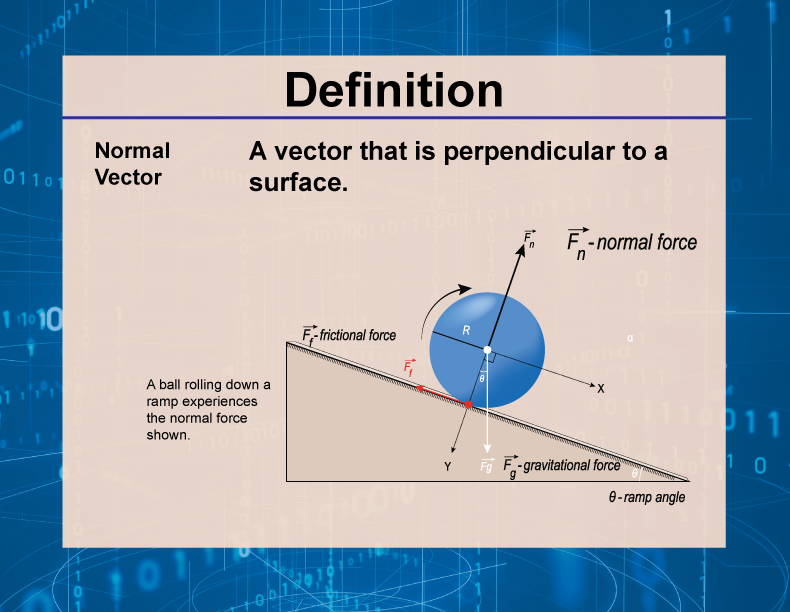
Definition Vector Concepts Normal Vector Media4math Definition vector concepts normal vector this is part of a collection of definitions on the topic of vectors. —click on preview to see the definition card.—. A unit normal vector of a curve, by its definition, is perpendicular to the curve at given point. this means a normal vector of a curve at a given point is perpendicular to the tangent vector at the same point. furthermore, a normal vector points towards the center of curvature, and the derivative of tangent vector also points towards the.
Normal Vector Explanation And Everything You Need To Know Normal vectors are inclined at an angle of 90° from a surface, plane, another vector, or even an axis. its representation is as shown in the following figure: the concept of normal vectors is usually applied to unit vectors. normal vectors are the vectors that are perpendicular or orthogonal to the other vectors. A normal vector is a perpendicular vector. given a vector v in the space, there are infinitely many perpendicular vectors. our goal is to select a special vector that is normal to the unit tangent vector. geometrically, for a non straight curve, this vector is the unique vector that point into the curve. algebraically we can compute the vector. The normal vector, often simply called the "normal," to a surface is a vector which is perpendicular to the surface at a given point. when normals are considered on closed surfaces, the inward pointing normal (pointing towards the interior of the surface) and outward pointing normal are usually distinguished. the unit vector obtained by normalizing the normal vector (i.e., dividing a nonzero. The normal vector, officially known as the principal normal vector, is the vector pointing directly towards the centre of curvature. thus, it unveils the direction in which the curve is heading. the binormal vector, a cross product of the tangent and the normal vector, identifies a unique direction orthogonal to both.
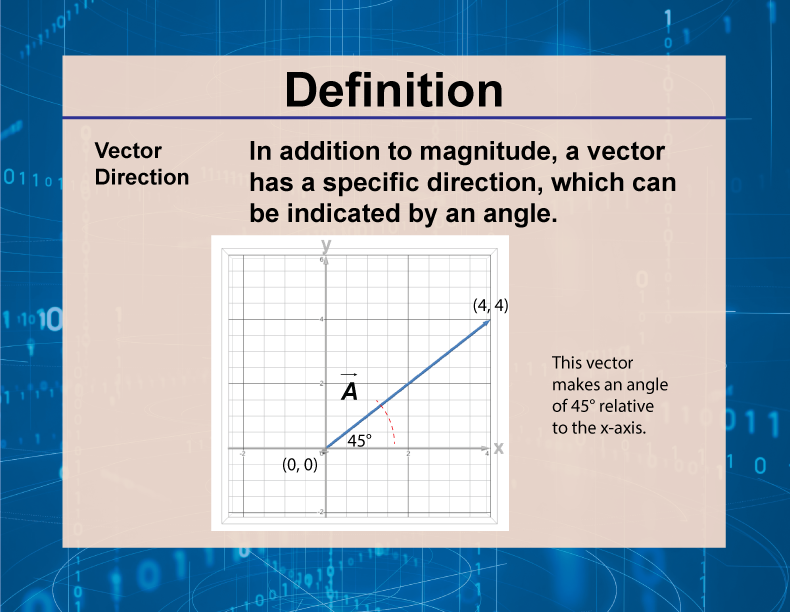
Definition Vector Concepts Vector Direction Media4math The normal vector, often simply called the "normal," to a surface is a vector which is perpendicular to the surface at a given point. when normals are considered on closed surfaces, the inward pointing normal (pointing towards the interior of the surface) and outward pointing normal are usually distinguished. the unit vector obtained by normalizing the normal vector (i.e., dividing a nonzero. The normal vector, officially known as the principal normal vector, is the vector pointing directly towards the centre of curvature. thus, it unveils the direction in which the curve is heading. the binormal vector, a cross product of the tangent and the normal vector, identifies a unique direction orthogonal to both. Because the binormal vector is defined to be the cross product of the unit tangent and unit normal vector we then know that the binormal vector is orthogonal to both the tangent vector and the normal vector. example 3 find the normal and binormal vectors for →r (t) = t,3sint,3cost r → (t) = t, 3 sin t, 3 cos t . A line with an arrowhead is called a directed line. fig. 1 (i) and (ii) are both directed lines. a point to note here: a directed line can go up to the end of the plane or the three dimensional space. we can also restrict a directed line to a line segment. in fig. 1 (iii), you can see that we have restricted the line ‘l’ to the line segment ab.

Comments are closed.